


THE TRAVELS OF
MARCO POLO
YULE-CORDIER EDITION
Henry Yule’s annotated translation, as revised
by Henri Cordier; together with Cordier’s later
volume of notes and addenda (1920)
DEDICATION.
TO THE MEMORY OFSIR RODERICK I. MURCHISON, BART., K.C.B., G.C.ST.A., G.C.ST.S.,
ETC.
THE PERFECT FRIEND
WHO FIRST BROUGHT HENRY YULE AND JOHN MURRAY TOGETHER
(HE ENTERED INTO REST, OCTOBER 22ND, 1871,)
AND TO THAT OF HIS MUCH LOVED NIECE,
HARRIET ISABELLA MURCHISON,
WIFE OF KENNETH ROBERT MURCHISON, D.L., J.P.,
(SHE ENTERED INTO REST, AUGUST 9TH, 1902,)
UNDER WHOSE EVER HOSPITABLE ROOF MANY OF THE PROOF
SHEETS OF THIS EDITION WERE READ BY ME,
I DEDICATE THESE VOLUMES FROM
THE OLD MURCHISON HOME,
IN THANKFUL REMEMBRANCE OF ALL I OWE TO
THE ABIDING AFFECTION, SYMPATHY, AND EXAMPLE OF BOTH.
September 11th, 1902.
ROSS-SHIRE,
SCOTLAND.
(Florence, 1824, pp. 83 seqq.)

CONTENTS OF VOL. I.
page
NOTE BY MISS YULE.
I desire to take this opportunity of recording my grateful sense of the unsparing labour, learning, and devotion, with which my father’s valued friend, Professor Henri Cordier, has performed the difficult and delicate task which I entrusted to his loyal friendship.
Apart from Professor Cordier’s very special qualifications for the work, I feel sure that no other Editor could have been more entirely acceptable to my father. I can give him no higher praise than to say that he has laboured in Yule’s own spirit.
The slight Memoir which I have contributed (for which I accept all responsibility), attempts no more than a rough sketch of my father’s character and career, but it will, I hope, serve to recall pleasantly his remarkable individuality to the few remaining who knew him in his prime, whilst it may also afford some idea of the man, and his work and environment, to those who had not that advantage.
vi
No one can be more conscious than myself of its many shortcomings, which I will not attempt to excuse. I can, however, honestly say that these have not been due to negligence, but are rather the blemishes almost inseparable from the fulfilment under the gloom of bereavement and amidst the pressure of other duties, of a task undertaken in more favourable circumstances.
Nevertheless, in spite of all defects, I believe this sketch to be such a record as my father would himself have approved, and I know also that he would have chosen my hand to write it.
In conclusion, I may note that the first edition of this work was dedicated to that very noble lady, the Queen (then Crown Princess) Margherita of Italy. In the second edition the Dedication was reproduced within brackets (as also the original preface), but not renewed. That precedent is again followed.
I have, therefore, felt at liberty to associate the present edition of my father’s work with the Name Murchison, which for more than a generation was the name most generally representative of British Science in Foreign Lands, as of Foreign Science in Britain.
PREFACE TO THIRD EDITION.

Little did I think, some thirty years ago, when I received a copy of the first edition of this grand work, that I should be one day entrusted with the difficult but glorious task of supervising the third edition. When the first edition of the Book of Ser Marco Polo reached “Far Cathay,” it created quite a stir in the small circle of the learned foreigners, who then resided there, and became a starting-point for many researches, of which the results have been made use of partly in the second edition, and partly in the present. The Archimandrite Palladius and Dr. E. Bretschneider, at Peking, Alex. Wylie, at Shang-hai—friends of mine who have, alas! passed away, with the exception of the Right Rev. Bishop G. E. Moule, of Hang-chau, the only survivor of this little group of hard-working scholars,—were the first to explore the Chinese sources of information which were to yield a rich harvest into their hands.
When I returned home from China in 1876, I was introduced to Colonel Henry Yule, at the India Office, by our common friend, Dr. Reinhold Rost, and from that time we met frequently and kept up a correspondence which terminated only with the life of the great geographer, whose friend I had become. A new edition of the travels of Friar Odoric of Pordenone, viiiour “mutual friend,” in which Yule had taken the greatest interest, was dedicated by me to his memory. I knew that Yule contemplated a third edition of his Marco Polo, and all will regret that time was not allowed to him to complete this labour of love, to see it published. If the duty of bringing out the new edition of Marco Polo has fallen on one who considers himself but an unworthy successor of the first illustrious commentator, it is fair to add that the work could not have been entrusted to a more respectful disciple. Many of our tastes were similar; we had the same desire to seek the truth, the same earnest wish to be exact, perhaps the same sense of humour, and, what is necessary when writing on Marco Polo, certainly the same love for Venice and its history. Not only am I, with the late Charles Schefer, the founder and the editor of the Recueil de Voyages et de Documents pour servir à l’Histoire de la Géographie depuis le XIIIe jusqu’à la fin du XVIe siècle, but I am also the successor, at the École des langues Orientales Vivantes, of G. Pauthier, whose book on the Venetian Traveller is still valuable, so the mantle of the last two editors fell upon my shoulders.
I therefore, gladly and thankfully, accepted Miss Amy Francis Yule’s kind proposal to undertake the editorship of the third edition of the Book of Ser Marco Polo, and I wish to express here my gratitude to her for the great honour she has thus done me.[1]
Unfortunately for his successor, Sir Henry Yule, evidently trusting to his own good memory, left but few notes. These are contained in an interleaved copy obligingly placed at my disposal by Miss Yule, but I luckily found assistance from various other ixquarters. The following works have proved of the greatest assistance to me:—The articles of General Houtum-Schindler in the Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, and the excellent books of Lord Curzon and of Major P. Molesworth Sykes on Persia, M. Grenard’s account of Dutreuil de Rhins’ Mission to Central Asia, Bretschneider’s and Palladius’ remarkable papers on Mediæval Travellers and Geography, and above all, the valuable books of the Hon. W. W. Rockhill on Tibet and Rubruck, to which the distinguished diplomatist, traveller, and scholar kindly added a list of notes of the greatest importance to me, for which I offer him my hearty thanks.
My thanks are also due to H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte, who kindly gave me permission to reproduce some of the plates of his Recueil de Documents de l’Époque Mongole, to M. Léopold Delisle, the learned Principal Librarian of the Bibliothèque Nationale, who gave me the opportunity to study the inventory made after the death of the Doge Marino Faliero, to the Count de Semallé, formerly French Chargé d’Affaires at Peking, who gave me for reproduction a number of photographs from his valuable personal collection, and last, not least, my old friend Comm. Nicolò Barozzi, who continued to lend me the assistance which he had formerly rendered to Sir Henry Yule at Venice.
Since the last edition was published, more than twenty-five years ago, Persia has been more thoroughly studied; new routes have been explored in Central Asia, Karakorum has been fully described, and Western and South-Western China have been opened up to our knowledge in many directions. The results of these investigations form the main features of this new edition of Marco Polo. I have suppressed hardly any of Sir xHenry Yule’s notes and altered but few, doing so only when the light of recent information has proved him to be in error, but I have supplemented them by what, I hope, will be found useful, new information.[2]
Before I take leave of the kind reader, I wish to thank sincerely Mr. John Murray for the courtesy and the care he has displayed while this edition was going through the press.
PREFACE TO SECOND EDITION.

The unexpected amount of favour bestowed on the former edition of this Work has been a great encouragement to the Editor in preparing this second one.
Not a few of the kind friends and correspondents who lent their aid before have continued it to the present revision. The contributions of Mr. A. Wylie of Shang-hai, whether as regards the amount of labour which they must have cost him, or the value of the result, demand above all others a grateful record here. Nor can I omit to name again with hearty acknowledgment Signor Comm. G. Berchet of Venice, the Rev. Dr. Caldwell, Colonel (now Major-General) R. Maclagan, R.E., Mr. D. Hanbury, F.R.S., Mr. Edward Thomas, F.R.S. (Corresponding Member of the Institute), and Mr. R. H. Major.
But besides these old names, not a few new ones claim my thanks.
The Baron F. von Richthofen, now President of the Geographical Society of Berlin, a traveller who not only has trodden many hundreds of miles in the footsteps of our Marco, but has perhaps travelled over more of the Interior of China than Marco ever did, and who carried to that survey high scientific accomplishments xiiof which the Venetian had not even a rudimentary conception, has spontaneously opened his bountiful stores of new knowledge in my behalf. Mr. Ney Elias, who in 1872 traversed and mapped a line of upwards of 2000 miles through the almost unknown tracts of Western Mongolia, from the Gate in the Great Wall at Kalghan to the Russian frontier in the Altai, has done likewise.[1] To the Rev. G. Moule, of the Church Mission at Hang-chau, I owe a mass of interesting matter regarding that once great and splendid city, the Kinsay of our Traveller, which has enabled me, I trust, to effect great improvement both in the Notes and in the Map, which illustrate that subject. And to the Rev. Carstairs Douglas, LL.D., of the English Presbyterian Mission at Amoy, I am scarcely less indebted. The learned Professor Bruun, of Odessa, whom I never have seen, and have little likelihood of ever seeing in this world, has aided me with zeal and cordiality like that of old friendship. To Mr. Arthur Burnell, Ph.D., of the Madras Civil Service, I am grateful for many valuable notes bearing on these and other geographical studies, and particularly for his generous communication of the drawing and photograph of the ancient Cross at St. Thomas’s Mount, long before any publication of that subject was made xiiion his own account. My brother officer, Major Oliver St. John, R.E., has favoured me with a variety of interesting remarks regarding the Persian chapters, and has assisted me with new data, very materially correcting the Itinerary Map in Kerman.
Mr. Blochmann of the Calcutta Madrasa, Sir Douglas Forsyth, C.B., lately Envoy to Kashgar, M. de Mas Latrie, the Historian of Cyprus, Mr. Arthur Grote, Mr. Eugene Schuyler of the U.S. Legation at St. Petersburg, Dr. Bushell and Mr. W. F. Mayers, of H.M.’s Legation at Peking, Mr. G. Phillips of Fuchau, Madame Olga Fedtchenko, the widow of a great traveller too early lost to the world, Colonel Keatinge, V.C., C.S.I., Major-General Keyes, C.B., Dr. George Birdwood, Mr. Burgess, of Bombay, my old and valued friend Colonel W. H. Greathed, C.B., and the Master of Mediæval Geography, M. D’Avezac himself, with others besides, have kindly lent assistance of one kind or another, several of them spontaneously, and the rest in prompt answer to my requests.
Having always attached much importance to the matter of illustrations,[2] I feel greatly indebted to the liberal action of Mr. Murray in enabling me largely to increase their number in this edition. Though many are original, we have also borrowed a good many;[3] a proceeding which seems to me entirely unobjectionable when the engravings are truly illustrative of the text, and not hackneyed.
I regret the augmented bulk of the volumes. There xivhas been some excision, but the additions visibly and palpably preponderate. The truth is that since the completion of the first edition, just four years ago, large additions have been made to the stock of our knowledge bearing on the subjects of this Book; and how these additions have continued to come in up to the last moment, may be seen in Appendix L,[4] which has had to undergo repeated interpolation after being put in type. Karakorum, for a brief space the seat of the widest empire the world has known, has been visited; the ruins of Shang-tu, the “Xanadu of Cublay Khan,” have been explored; Pamir and Tangut have been penetrated from side to side; the famous mountain Road of Shen-si has been traversed and described; the mysterious Caindu has been unveiled; the publication of my lamented friend Lieutenant Garnier’s great work on the French Exploration of Indo-China has provided a mass of illustration of that Yun-nan for which but the other day Marco Polo was well-nigh the most recent authority. Nay, the last two years have thrown a promise of light even on what seemed the wildest of Marco’s stories, and the bones of a veritable Ruc from New Zealand lie on the table of Professor Owen’s Cabinet!
M. Vivien de St. Martin, during the interval of which we have been speaking, has published a History of Geography. In treating of Marco Polo, he alludes to the first edition of this work, most evidently with no intention of disparagement, but speaks of it as merely a revision of Marsden’s Book. The last thing I should allow myself to do would be to apply to a xvGeographer, whose works I hold in so much esteem, the disrespectful definition which the adage quoted in my former Preface[5] gives of the vir qui docet quod non sapit; but I feel bound to say that on this occasion M. Vivien de St. Martin has permitted himself to pronounce on a matter with which he had not made himself acquainted; for the perusal of the very first lines of the Preface (I will say nothing of the Book) would have shown him that such a notion was utterly unfounded.
In concluding these “forewords” I am probably taking leave of Marco Polo,[6] the companion of many pleasant and some laborious hours, whilst I have been contemplating with him (“vôlti a levante”) that Orient in which I also had spent years not a few.
And as the writer lingered over this conclusion, his thoughts wandered back in reverie to those many venerable libraries in which he had formerly made search for mediæval copies of the Traveller’s story; and it seemed to him as if he sate in a recess of one of these with a manuscript before him which had never till then been examined with any care, and which he found with delight to contain passages that appear in no version of the Book hitherto known. It was written in clear Gothic text, and in the Old French tongue of the early 14th century. Was it possible that he had lighted on the xvilong-lost original of Ramusio’s Version? No; it proved to be different. Instead of the tedious story of the northern wars, which occupies much of our Fourth Book, there were passages occurring in the later history of Ser Marco, some years after his release from the Genoese captivity. They appeared to contain strange anachronisms certainly; but we have often had occasion to remark on puzzles in the chronology of Marco’s story![7] And in some respects they tended to justify our intimated suspicion that he was a man of deeper feelings and wider sympathies than the book of Rusticiano had allowed to appear.[8] Perhaps this time the Traveller had found an amanuensis whose faculties had not been stiffened by fifteen years of Malapaga?[9] One of the most important passages ran thus:—
“Bien est voirs que, après ce que Messires Marc Pol avoit pris fame et si estoit demouré plusours ans de sa vie a Venysse, il avint que mourut Messires Mafés qui oncles Monseignour Marc estoit: (et mourut ausi ses granz chiens mastins qu’avoit amenei dou Catai,[10] et qui avoit non Bayan pour l’amour au bon chievetain Bayan Cent-iex); adonc n’avoit oncques puis Messires Marc nullui, fors son esclave Piere le Tartar, avecques lequel pouvoit penre soulas à s’entretenir de ses voiages et des choses dou Levant. Car la gent de Venysse si avoit de grant piesce moult anuy pris des loncs contes Monseignour Marc; et quand ledit Messires Marc issoit de l’uys sa meson ou Sain Grisostome, souloient li petit marmot es voies dariere-li courir en cryant Messer Marco Miliòn! cont’a nu un busiòn! que veult dire en François ‘Messires Marcs des millions di-nous un de vos gros mensonges.’ En oultre, la Dame Donate fame anuyouse estoit, et de trop estroit esprit, et plainne de convoitise.[11] Ansi avint que Messires Marc desiroit es voiages rantrer durement.
“Si se partist de Venisse et chevaucha aux parties d’occident. Et demoura mainz jours es contrées de Provence et de France et puys fist passaige aux Ysles de la tremontaingne et s’en retourna par la Magne, si comme vous orrez cy-après. Et fist-il escripre son voiage atout les devisements les contrées; mes de la France n’y parloit mie grantment pour ce que maintes genz la scevent apertement. Et pour ce en lairons atant, et commencerons d’autres choses, assavoir, de Bretaingne la Grant.
xviiCy devyse dou roiaume de Bretaingne la grant.“Et sachiés que quand l’en se part de Calés, et l’en nage xx ou xxx milles à trop grant mesaise, si treuve l’en une grandisme Ysle qui s’appelle Bretaingne la Grant. Elle est à une grant royne et n’en fait treuage à nulluy. Et ensevelissent lor mors, et ont monnoye de chartres et d’or et d’argent, et ardent pierres noyres, et vivent de marchandises et d’ars, et ont toutes choses de vivre en grant habondance mais non pas à bon marchié. Et c’est une Ysle de trop grant richesce, et li marinier de celle partie dient que c’est li plus riches royaumes qui soit ou monde, et qu’il y a li mieudre marinier dou monde et li mieudre coursier et li mieudre chevalier (ains ne chevauchent mais lonc com François). Ausi ont-il trop bons homes d’armes et vaillans durement (bien que maint n’y ait), et les dames et damoseles bonnes et loialles, et belles com lys souef florant. Et quoi vous en diroie-je? Il y a citez et chasteau assez, et tant de marchéanz et si riches qui font venir tant d’avoir-de-poiz et de toute espece de marchandise qu’il n’est hons qui la verité en sceust dire. Font venir d’Ynde et d’autres parties coton a grant planté, et font venir soye de Manzi et de Bangala, et font venir laine des ysles de la Mer Occeane et de toutes parties. Et si labourent maintz bouquerans et touailles et autres draps de coton et de laine et de soye. Encores sachiés que ont vaines d’acier assez, et si en labourent trop soubtivement de tous hernois de chevalier, et de toutes choses besoignables à ost; ce sont espées et glaive et esperon et heaume et haches, et toute espèce d’arteillerie et de coutelerie, et en font grant gaaigne et grant marchandise. Et en font si grant habondance que tout li mondes en y puet avoir et à bon marchié.
Encores cy devise dou dyt roiaume, et de ce qu’en dist Messires Marcs.“Et sachiés que tient icelle Royne la seigneurie de l’Ynde majeure et de Mutfili et de Bangala, et d’une moitié de Mien. Et moult est saige et noble dame et pourvéans, si que est elle amée de chascun. Et avoit jadis mari; et depuys qu’il mourut bien XIV ans avoit; adonc la royne sa fame l’ama tant que oncques puis ne se voult marier a nullui, pour l’amour le prince son baron, ançois moult maine quoye vie. Et tient son royaume ausi bien ou miex que oncques le tindrent li roy si aioul. Mes ores en ce royaume li roy n’ont guieres pooir, ains la poissance commence a trespasser à la menue gent. Et distrent aucun marinier de celes parties à Monseignour Marc que hui-et-le jour li royaumes soit auques abastardi come je vous diroy. Car bien est voirs que ci-arrières estoit ciz pueple de Bretaingne la Grant bonne et granz et loialle gent qui servoit Diex moult volontiers selonc lor usaige; et tuit li labour qu’il labouroient et portoient a vendre estoient honnestement labouré, et dou greigneur vaillance, et chose pardurable; et se vendoient à jouste pris sanz barguignier. En tant que se aucuns labours portoit l’estanpille Bretaingne la Grant c’estoit regardei com pleges de bonne estoffe. Mes orendroit li labours n’est mie tousjourz si bons; et quand l’en achate pour un quintal pesant de toiles de coton, adonc, par trop souvent, si treuve l’en de chascun C pois de coton, bien xxx ou xl pois de plastre de gifs, ou de blanc xviiid’Espaigne, ou de choses semblables. Et se l’en achate de cammeloz ou de tireteinne ou d’autre dras de laine, cist ne durent mie, ains sont plain d’empoise, ou de glu et de balieures.
“Et bien qu’il est voirs que chascuns hons egalement doit de son cors servir son seigneur ou sa commune, pour aler en ost en tens de besoingne; et bien que trestuit li autre royaume d’occident tieingnent ce pour ordenance, ciz pueple de Bretaingne la Grant n’en veult nullement, ains si dient: ‘Veez-là: n’avons nous pas la Manche pour fossé de nostre pourpris, et pourquoy nous penerons-nous pour nous faire homes d’armes, en lessiant nos gaaignes et nos soulaz? Cela lairons aus soudaiers.’ Or li preudhome entre eulx moult scevent bien com tiex paroles sont nyaises; mes si ont paour de lour en dire la verité pour ce que cuident desplaire as bourjois et à la menue gent.
“Or je vous di sanz faille que, quand Messires Marcs Pols sceust ces choses, moult en ot pitié de cestui pueple, et il li vint à remembrance ce que avenu estoit, ou tens Monseignour Nicolas et Monseignour Mafé, à l’ore quand Alau, frère charnel dou Grant Sire Cublay, ala en ost seur Baudas, et print le Calife et sa maistre cité, atout son vaste tresor d’or et d’argent, et l’amère parolle que dist ledit Alau au Calife, com l’a escripte li Maistres Rusticiens ou chief de cestui livre.[12]
“Car sachiés tout voirement que Messires Marc moult se deleitoit à faire appert combien sont pareilles au font les condicions des diverses regions dou monde, et soloit-il clorre son discours si disant en son language de Venisse: ‘Sto mondo xe fato tondo, com uzoit dire mes oncles Mafés.’
“Ore vous lairons à conter de ceste matière et retournerons à parler de la Loy des genz de Bretaingne la Grant.
Cy devise des diverses créances de la gent Bretaingne la Grant et de ce qu’en cuidoit Messires Marcs.“Il est voirs que li pueples est Crestiens, mes non pour le plus selonc la foy de l’Apostoille Rommain, ains tiennent le en mautalent assez. Seulement il y en a aucun qui sont féoil du dit Apostoille et encore plus forment que li nostre prudhome de Venisse. Car quand dit li Papes: ‘Telle ou telle chose est noyre,’ toute ladite gent si en jure: ‘Noyre est com poivre.’ Et puis se dira li Papes de la dite chose: ‘Elle est blanche,’ si en jurera toute ladite gent: ‘Il est voirs qu’elle est blanche; blanche est com noifs.’ Et dist Messires Marc Pol: ‘Nous n’avons nullement tant de foy à Venyse, ne li prudhome de Florence non plus, com l’en puet savoir bien apertement dou livre Monseignour Dantès Aldiguiere, que j’ay congneu a Padoe le meisme an que Messires Thibault de Cepoy à Venisse estoit.[13] Mes c’est joustement ce que j’ay veu autre foiz près le Grant Bacsi qui est com li Papes des Ydres.’
“Encore y a une autre manière de gent; ce sont de celz qui s’appellent filsoufes;[14] et si il disent: ‘S’il y a Diex n’en scavons nul, mes il est voirs xixqu’il est une certeinne courance des choses laquex court devers le bien.’ Et fist Messires Marcs: ‘Encore la créance des Bacsi qui dysent que n’y a ne Diex Eternel ne Juge des homes, ains il est une certeinne chose laquex s’appelle Kerma.’[15]
“Une autre foiz avint que disoit un des filsoufes à Monseignour Marc: ‘Diex n’existe mie jeusqu’ores, ainçois il se fait desorendroit.’ Et fist encore Messires Marcs: ‘Veez-là, une autre foiz la créance des ydres, car dient que li seuz Diex est icil hons qui par force de ses vertuz et de son savoir tant pourchace que d’home il se face Diex presentement. Et li Tartar l’appelent Borcan. Tiex Diex Sagamoni Borcan estoit, dou quel parle li livres Maistre Rusticien.’[16]
“Encore ont une autre manière de filsoufes, et dient-il: ‘Il n’est mie ne Diex ne Kerma ne courance vers le bien, ne Providence, ne Créerres, ne Sauvours, ne sainteté ne pechiés ne conscience de pechié, ne proyère ne response à proyère, il n’est nulle riens fors que trop minime grain ou paillettes qui ont à nom atosmes, et de tiex grains devient chose qui vive, et chose qui vive devient une certeinne creature qui demoure au rivaige de la Mer: et ceste creature devient poissons, et poissons devient lezars, et lezars devient blayriaus, et blayriaus devient gat-maimons, et gat-maimons devient hons sauvaiges qui menjue char d’homes, et hons sauvaiges devient hons crestien.’
“Et dist Messires Marc: ‘Encore une foiz, biaus sires, li Bacsi de Tebet et de Kescemir et li prestre de Seilan, qui si dient que l’arme vivant doie trespasser par tous cez changes de vestemens; si com se treuve escript ou livre Maistre Rusticien que Sagamoni Borcan mourut iiij vint et iiij foiz et tousjourz resuscita, et à chascune foiz d’une diverse manière de beste, et à la derreniere foyz mourut hons et devint diex, selonc ce qu’il dient.’[17] Et fist encore Messires Marc: ‘A moy pert-il trop estrange chose se juesques à toutes les créances des ydolastres deust dechéoir ceste grantz et saige nation. Ainsi peuent jouer Misire li filsoufe atout lour propre perte, mes à l’ore quand tiex fantaisies se respanderont es joenes bacheliers et parmy la menue gent, celz averont pour toute Loy manducemus et bibamus, cras enim moriemur; et trop isnellement l’en raccomencera la descente de l’eschiele, et d’home crestien deviendra hons sauvaiges, et d’home sauvaige gat-maimons, et de gat-maimon blayriaus.’ Et fist encores Messires Marc: ‘Maintes contrées et provinces et ysles et citéz je Marc Pol ay veues et de maintes genz de maintes manières ay les condicionz congneues, et je croy bien que il est plus assez dedens l’univers que ce que li nostre prestre n’y songent. Et puet bien estre, biaus sires, que li mondes n’a estés creés à tous poinz com nous creiens, ains d’une sorte encore plus merveillouse. Mes cil n’amenuise nullement nostre pensée de Diex et de sa majesté, ains la fait greingnour. Et contrée n’ay veue ou Dame Diex ne manifeste apertement les granz euvres de sa tout-poissante saigesse; gent n’ay congneue esquiex ne se fait sentir li fardels de pechié, et la besoingne de Phisicien des maladies de l’arme tiex com est nostre Seignours Ihesus Crist, Beni soyt son Non. Pensez doncques à cel qu’a dit uns de ses xxApostres: Nolite esse prudentes apud vosmet ipsos; et uns autres: Quoniam multi pseudo-prophetae exierint; et uns autres: Quod venient in novissimis diebus illusores ... dicentes, Ubi est promissio? et encores aus parolles que dist li Signours meismes: Vide ergo ne lumen quod in te est tenebrae sint.
Commant Messires Marcs se partist de l’ysle de Bretaingne et de la proyère que fist.“Et pourquoy vous en feroie-je lonc conte? Si print nef Messires Marcs et se partist en nageant vers la terre ferme. Or Messires Marc Pol moult ama cel roiaume de Bretaingne la grant pour son viex renon et s’ancienne franchise, et pour sa saige et bonne Royne (que Diex gart), et pour les mainz homes de vaillance et bons chaceours et les maintes bonnes et honnestes dames qui y estoient. Et sachiés tout voirement que en estant delez le bort la nef, et en esgardant aus roches blanches que l’en par dariere-li lessoit, Messires Marc prieoit Diex, et disoit-il: ‘Ha Sires Diex ay merci de cestuy vieix et noble royaume; fay-en pardurable forteresse de liberté et de joustice, et garde-le de tout meschief de dedens et de dehors; donne à sa gent droit esprit pour ne pas Diex guerroyer de ses dons, ne de richesce ne de savoir; et conforte-les fermement en ta foy’ ...”
A loud Amen seemed to peal from without, and the awakened reader started to his feet. And lo! it was the thunder of the winter-storm crashing among the many-tinted crags of Monte Pellegrino,—with the wind raging as it knows how to rage here in sight of the Isles of Æolus, and the rain dashing on the glass as ruthlessly as it well could have done, if, instead of Æolic Isles and many-tinted crags, the window had fronted a dearer shore beneath a northern sky, and looked across the grey Firth to the rain-blurred outline of the Lomond Hills.
But I end, saying to Messer Marco’s prayer, Amen.
Palermo, 31st December, 1874.
ORIGINAL PREFACE.

The amount of appropriate material, and of acquaintance with the mediæval geography of some parts of Asia, which was acquired during the compilation of a work of kindred character for the Hakluyt Society,[1] could hardly fail to suggest as a fresh labour in the same field the preparation of a new English edition of Marco Polo. Indeed one kindly critic (in the Examiner) laid it upon the writer as a duty to undertake that task.
Though at least one respectable English edition has appeared since Marsden’s,[2] the latter has continued to be the standard edition, and maintains not only its reputation but its market value. It is indeed the work of a sagacious, learned, and right-minded man, which can never be spoken of otherwise than with respect. But since Marsden published his quarto (1818) vast stores of new knowledge have become available in elucidation both of the contents of Marco Polo’s book and of its literary history. The works of writers such as Klaproth, Abel Rémusat, D’Avezac, Reinaud, Quatremère, Julien, I. J. Schmidt, Gildemeister, Ritter, Hammer-Purgstall, Erdmann, D’Ohsson, Defrémery, Elliot, Erskine, and many more, which throw light directly or incidentally on Marco Polo, have, for the most part, appeared since then. Nor, as regards the literary history of the book, were any just views possible at a time when what may be called the Fontal MSS. (in French) were unpublished and unexamined.
Besides the works which have thus occasionally or incidentally xxiithrown light upon the Traveller’s book, various editions of the book itself have since Marsden’s time been published in foreign countries, accompanied by comments of more or less value. All have contributed something to the illustration of the book or its history; the last and most learned of the editors, M. Pauthier, has so contributed in large measure. I had occasion some years ago[3] to speak freely my opinion of the merits and demerits of M. Pauthier’s work; and to the latter at least I have no desire to recur here.
Another of his critics, a much more accomplished as well as more favourable one,[4] seems to intimate the opinion that there would scarcely be room in future for new commentaries. Something of the kind was said of Marsden’s at the time of its publication. I imagine, however, that whilst our libraries endure the Iliad will continue to find new translators, and Marco Polo—though one hopes not so plentifully—new editors.
The justification of the book’s existence must however be looked for, and it is hoped may be found, in the book itself, and not in the Preface. The work claims to be judged as a whole, but it may be allowable, in these days of scanty leisure, to indicate below a few instances of what is believed to be new matter in an edition of Marco Polo; by which however it is by no means intended that all such matter is claimed by the editor as his own.[5]
xxiii
From the commencement of the work it was felt that the task was one which no man, though he were far better equipped and much more conveniently situated than the present writer, could satisfactorily accomplish from his own resources, and help was sought on special points wherever it seemed likely to be found. In scarcely any quarter was the application made in vain. Some who have aided most materially are indeed very old and valued friends; but to many others who have done the same the applicant was unknown; and some of these again, with whom the editor began correspondence on this subject as a stranger, he is happy to think that he may now call friends.
To none am I more indebted than to the Comm. Guglielmo Berchet, of Venice, for his ample, accurate, and generous assistance in furnishing me with Venetian documents, and in many other ways. Especial thanks are also due to Dr. William Lockhart, who has supplied the materials for some of the most valuable illustrations; to Lieutenant Francis Garnier, of the French Navy, the gallant and accomplished leader (after the death of Captain Doudart de la Grée) of the memorable expedition xxivup the Mekong to Yun-nan; to the Rev. Dr. Caldwell, of the S. P. G. Mission in Tinnevelly, for copious and valuable notes on Southern India; to my friends Colonel Robert Maclagan, R.E., Sir Arthur Phayre, and Colonel Henry Man, for very valuable notes and other aid; to Professor A. Schiefner, of St. Petersburg, for his courteous communication of very interesting illustrations not otherwise accessible; to Major-General Alexander Cunningham, of my own corps, for several valuable letters; to my friends Dr. Thomas Oldham, Director of the Geological Survey of India, Mr. Daniel Hanbury, F.R.S., Mr. Edward Thomas, Mr. James Fergusson, F.R.S., Sir Bartle Frere, and Dr. Hugh Cleghorn, for constant interest in the work and readiness to assist its progress; to Mr. A. Wylie, the learned Agent of the B. and F. Bible Society at Shang-hai, for valuable help; to the Hon. G. P. Marsh, U.S. Minister at the Court of Italy, for untiring kindness in the communication of his ample stores of knowledge, and of books. I have also to express my obligations to Comm. Nicolò Barozzi, Director of the City Museum at Venice, and to Professor A. S. Minotto, of the same city; to Professor Arminius Vámbéry, the eminent traveller; to Professor Flückiger of Bern; to the Rev. H. A. Jaeschke, of the Moravian Mission in British Tibet; to Colonel Lewis Pelly, British Resident in the Persian Gulf; to Pandit Manphul, C.S.I. (for a most interesting communication on Badakhshan); to my brother officer, Major T. G. Montgomerie, R.E., of the Indian Trigonometrical Survey; to Commendatore Negri the indefatigable President of the Italian Geographical Society; to Dr. Zotenberg, of the Great Paris Library, and to M. Ch. Maunoir, Secretary-General of the Société de Géographie; to Professor Henry xxvGiglioli, at Florence; to my old friend Major-General Albert Fytche, Chief Commissioner of British Burma; to Dr. Rost and Dr. Forbes-Watson, of the India Office Library and Museum; to Mr. R. H. Major, and Mr. R. K. Douglas, of the British Museum; to Mr. N. B. Dennys, of Hong-kong; and to Mr. C. Gardner, of the Consular Establishment in China. There are not a few others to whom my thanks are equally due; but it is feared that the number of names already mentioned may seem ridiculous, compared with the result, to those who do not appreciate from how many quarters the facts needful for a work which in its course intersects so many fields required to be collected, one by one. I must not, however, omit acknowledgments to the present Earl of Derby for his courteous permission, when at the head of the Foreign Office, to inspect Mr. Abbott’s valuable unpublished Report upon some of the Interior Provinces of Persia; and to Mr. T. T. Cooper, one of the most adventurous travellers of modern times, for leave to quote some passages from his unpublished diary.
Palermo, 31st December, 1870.
TO
HER ROYAL HIGHNESS,
MARGHERITA,
Princess of Piedmont,
THIS ENDEAVOUR TO ILLUSTRATE THE LIFE AND WORK
OF A RENOWNED ITALIAN
IS
BY HER ROYAL HIGHNESS’S GRACIOUS PERMISSION
Dedicated
WITH THE DEEPEST RESPECT
BY
As regards geographical elucidations, I may point to the explanation of the name Gheluchelan (i. p. 58), to the discussion of the route from Kerman to Hormuz, and the identification of the sites of Old Hormuz, of Cobinan and Dogana, the establishment of the position and continued existence of Keshm, the note on Pein and Charchan, on Gog and Magog, on the geography of the route from Sindafu to Carajan, on Anin and Coloman, on Mutafili, Cail, and Ely.
As regards historical illustrations, I would cite the notes regarding the Queens Bolgana and Cocachin, on the Karaunahs, etc., on the title of King of Bengal applied to the K. of Burma, and those bearing upon the Malay and Abyssinian chronologies.
In the interpretation of outlandish phrases, I may refer to the notes on Ondanique, Nono, Barguerlac, Argon, Sensin, Keshican, Toscaol, Bularguchi, Gat-paul, etc.
Among miscellaneous elucidations, to the disquisition on the Arbre Sol or Sec in vol. i., and to that on Mediæval Military Engines in vol. ii.
In a variety of cases it has been necessary to refer to Eastern languages for pertinent elucidations or etymologies. The editor would, however, be sorry to fall under the ban of the mediæval adage:
and may as well reprint here what was written in the Preface to Cathay:
“I am painfully sensible that in regard to many subjects dealt with in the following pages, nothing can make up for the want of genuine Oriental learning. A fair familiarity with Hindustani for many years, and some reminiscences of elementary Persian, have been useful in their degree; but it is probable that they may sometimes also have led me astray, as such slender lights are apt to do.”
PREFACE TO SECOND EDITION.

The unexpected amount of favour bestowed on the former edition of this Work has been a great encouragement to the Editor in preparing this second one.
Not a few of the kind friends and correspondents who lent their aid before have continued it to the present revision. The contributions of Mr. A. Wylie of Shang-hai, whether as regards the amount of labour which they must have cost him, or the value of the result, demand above all others a grateful record here. Nor can I omit to name again with hearty acknowledgment Signor Comm. G. Berchet of Venice, the Rev. Dr. Caldwell, Colonel (now Major-General) R. Maclagan, R.E., Mr. D. Hanbury, F.R.S., Mr. Edward Thomas, F.R.S. (Corresponding Member of the Institute), and Mr. R. H. Major.
But besides these old names, not a few new ones claim my thanks.
The Baron F. von Richthofen, now President of the Geographical Society of Berlin, a traveller who not only has trodden many hundreds of miles in the footsteps of our Marco, but has perhaps travelled over more of the Interior of China than Marco ever did, and who carried to that survey high scientific accomplishments xiiof which the Venetian had not even a rudimentary conception, has spontaneously opened his bountiful stores of new knowledge in my behalf. Mr. Ney Elias, who in 1872 traversed and mapped a line of upwards of 2000 miles through the almost unknown tracts of Western Mongolia, from the Gate in the Great Wall at Kalghan to the Russian frontier in the Altai, has done likewise.[1] To the Rev. G. Moule, of the Church Mission at Hang-chau, I owe a mass of interesting matter regarding that once great and splendid city, the Kinsay of our Traveller, which has enabled me, I trust, to effect great improvement both in the Notes and in the Map, which illustrate that subject. And to the Rev. Carstairs Douglas, LL.D., of the English Presbyterian Mission at Amoy, I am scarcely less indebted. The learned Professor Bruun, of Odessa, whom I never have seen, and have little likelihood of ever seeing in this world, has aided me with zeal and cordiality like that of old friendship. To Mr. Arthur Burnell, Ph.D., of the Madras Civil Service, I am grateful for many valuable notes bearing on these and other geographical studies, and particularly for his generous communication of the drawing and photograph of the ancient Cross at St. Thomas’s Mount, long before any publication of that subject was made xiiion his own account. My brother officer, Major Oliver St. John, R.E., has favoured me with a variety of interesting remarks regarding the Persian chapters, and has assisted me with new data, very materially correcting the Itinerary Map in Kerman.
Mr. Blochmann of the Calcutta Madrasa, Sir Douglas Forsyth, C.B., lately Envoy to Kashgar, M. de Mas Latrie, the Historian of Cyprus, Mr. Arthur Grote, Mr. Eugene Schuyler of the U.S. Legation at St. Petersburg, Dr. Bushell and Mr. W. F. Mayers, of H.M.’s Legation at Peking, Mr. G. Phillips of Fuchau, Madame Olga Fedtchenko, the widow of a great traveller too early lost to the world, Colonel Keatinge, V.C., C.S.I., Major-General Keyes, C.B., Dr. George Birdwood, Mr. Burgess, of Bombay, my old and valued friend Colonel W. H. Greathed, C.B., and the Master of Mediæval Geography, M. D’Avezac himself, with others besides, have kindly lent assistance of one kind or another, several of them spontaneously, and the rest in prompt answer to my requests.
Having always attached much importance to the matter of illustrations,[2] I feel greatly indebted to the liberal action of Mr. Murray in enabling me largely to increase their number in this edition. Though many are original, we have also borrowed a good many;[3] a proceeding which seems to me entirely unobjectionable when the engravings are truly illustrative of the text, and not hackneyed.
I regret the augmented bulk of the volumes. There xivhas been some excision, but the additions visibly and palpably preponderate. The truth is that since the completion of the first edition, just four years ago, large additions have been made to the stock of our knowledge bearing on the subjects of this Book; and how these additions have continued to come in up to the last moment, may be seen in Appendix L,[4] which has had to undergo repeated interpolation after being put in type. Karakorum, for a brief space the seat of the widest empire the world has known, has been visited; the ruins of Shang-tu, the “Xanadu of Cublay Khan,” have been explored; Pamir and Tangut have been penetrated from side to side; the famous mountain Road of Shen-si has been traversed and described; the mysterious Caindu has been unveiled; the publication of my lamented friend Lieutenant Garnier’s great work on the French Exploration of Indo-China has provided a mass of illustration of that Yun-nan for which but the other day Marco Polo was well-nigh the most recent authority. Nay, the last two years have thrown a promise of light even on what seemed the wildest of Marco’s stories, and the bones of a veritable Ruc from New Zealand lie on the table of Professor Owen’s Cabinet!
M. Vivien de St. Martin, during the interval of which we have been speaking, has published a History of Geography. In treating of Marco Polo, he alludes to the first edition of this work, most evidently with no intention of disparagement, but speaks of it as merely a revision of Marsden’s Book. The last thing I should allow myself to do would be to apply to a xvGeographer, whose works I hold in so much esteem, the disrespectful definition which the adage quoted in my former Preface[5] gives of the vir qui docet quod non sapit; but I feel bound to say that on this occasion M. Vivien de St. Martin has permitted himself to pronounce on a matter with which he had not made himself acquainted; for the perusal of the very first lines of the Preface (I will say nothing of the Book) would have shown him that such a notion was utterly unfounded.
In concluding these “forewords” I am probably taking leave of Marco Polo,[6] the companion of many pleasant and some laborious hours, whilst I have been contemplating with him (“vôlti a levante”) that Orient in which I also had spent years not a few.
And as the writer lingered over this conclusion, his thoughts wandered back in reverie to those many venerable libraries in which he had formerly made search for mediæval copies of the Traveller’s story; and it seemed to him as if he sate in a recess of one of these with a manuscript before him which had never till then been examined with any care, and which he found with delight to contain passages that appear in no version of the Book hitherto known. It was written in clear Gothic text, and in the Old French tongue of the early 14th century. Was it possible that he had lighted on the xvilong-lost original of Ramusio’s Version? No; it proved to be different. Instead of the tedious story of the northern wars, which occupies much of our Fourth Book, there were passages occurring in the later history of Ser Marco, some years after his release from the Genoese captivity. They appeared to contain strange anachronisms certainly; but we have often had occasion to remark on puzzles in the chronology of Marco’s story![7] And in some respects they tended to justify our intimated suspicion that he was a man of deeper feelings and wider sympathies than the book of Rusticiano had allowed to appear.[8] Perhaps this time the Traveller had found an amanuensis whose faculties had not been stiffened by fifteen years of Malapaga?[9] One of the most important passages ran thus:—
“Bien est voirs que, après ce que Messires Marc Pol avoit pris fame et si estoit demouré plusours ans de sa vie a Venysse, il avint que mourut Messires Mafés qui oncles Monseignour Marc estoit: (et mourut ausi ses granz chiens mastins qu’avoit amenei dou Catai,[10] et qui avoit non Bayan pour l’amour au bon chievetain Bayan Cent-iex); adonc n’avoit oncques puis Messires Marc nullui, fors son esclave Piere le Tartar, avecques lequel pouvoit penre soulas à s’entretenir de ses voiages et des choses dou Levant. Car la gent de Venysse si avoit de grant piesce moult anuy pris des loncs contes Monseignour Marc; et quand ledit Messires Marc issoit de l’uys sa meson ou Sain Grisostome, souloient li petit marmot es voies dariere-li courir en cryant Messer Marco Miliòn! cont’a nu un busiòn! que veult dire en François ‘Messires Marcs des millions di-nous un de vos gros mensonges.’ En oultre, la Dame Donate fame anuyouse estoit, et de trop estroit esprit, et plainne de convoitise.[11] Ansi avint que Messires Marc desiroit es voiages rantrer durement.
“Si se partist de Venisse et chevaucha aux parties d’occident. Et demoura mainz jours es contrées de Provence et de France et puys fist passaige aux Ysles de la tremontaingne et s’en retourna par la Magne, si comme vous orrez cy-après. Et fist-il escripre son voiage atout les devisements les contrées; mes de la France n’y parloit mie grantment pour ce que maintes genz la scevent apertement. Et pour ce en lairons atant, et commencerons d’autres choses, assavoir, de Bretaingne la Grant.
xviiCy devyse dou roiaume de Bretaingne la grant.“Et sachiés que quand l’en se part de Calés, et l’en nage xx ou xxx milles à trop grant mesaise, si treuve l’en une grandisme Ysle qui s’appelle Bretaingne la Grant. Elle est à une grant royne et n’en fait treuage à nulluy. Et ensevelissent lor mors, et ont monnoye de chartres et d’or et d’argent, et ardent pierres noyres, et vivent de marchandises et d’ars, et ont toutes choses de vivre en grant habondance mais non pas à bon marchié. Et c’est une Ysle de trop grant richesce, et li marinier de celle partie dient que c’est li plus riches royaumes qui soit ou monde, et qu’il y a li mieudre marinier dou monde et li mieudre coursier et li mieudre chevalier (ains ne chevauchent mais lonc com François). Ausi ont-il trop bons homes d’armes et vaillans durement (bien que maint n’y ait), et les dames et damoseles bonnes et loialles, et belles com lys souef florant. Et quoi vous en diroie-je? Il y a citez et chasteau assez, et tant de marchéanz et si riches qui font venir tant d’avoir-de-poiz et de toute espece de marchandise qu’il n’est hons qui la verité en sceust dire. Font venir d’Ynde et d’autres parties coton a grant planté, et font venir soye de Manzi et de Bangala, et font venir laine des ysles de la Mer Occeane et de toutes parties. Et si labourent maintz bouquerans et touailles et autres draps de coton et de laine et de soye. Encores sachiés que ont vaines d’acier assez, et si en labourent trop soubtivement de tous hernois de chevalier, et de toutes choses besoignables à ost; ce sont espées et glaive et esperon et heaume et haches, et toute espèce d’arteillerie et de coutelerie, et en font grant gaaigne et grant marchandise. Et en font si grant habondance que tout li mondes en y puet avoir et à bon marchié.
Encores cy devise dou dyt roiaume, et de ce qu’en dist Messires Marcs.“Et sachiés que tient icelle Royne la seigneurie de l’Ynde majeure et de Mutfili et de Bangala, et d’une moitié de Mien. Et moult est saige et noble dame et pourvéans, si que est elle amée de chascun. Et avoit jadis mari; et depuys qu’il mourut bien XIV ans avoit; adonc la royne sa fame l’ama tant que oncques puis ne se voult marier a nullui, pour l’amour le prince son baron, ançois moult maine quoye vie. Et tient son royaume ausi bien ou miex que oncques le tindrent li roy si aioul. Mes ores en ce royaume li roy n’ont guieres pooir, ains la poissance commence a trespasser à la menue gent. Et distrent aucun marinier de celes parties à Monseignour Marc que hui-et-le jour li royaumes soit auques abastardi come je vous diroy. Car bien est voirs que ci-arrières estoit ciz pueple de Bretaingne la Grant bonne et granz et loialle gent qui servoit Diex moult volontiers selonc lor usaige; et tuit li labour qu’il labouroient et portoient a vendre estoient honnestement labouré, et dou greigneur vaillance, et chose pardurable; et se vendoient à jouste pris sanz barguignier. En tant que se aucuns labours portoit l’estanpille Bretaingne la Grant c’estoit regardei com pleges de bonne estoffe. Mes orendroit li labours n’est mie tousjourz si bons; et quand l’en achate pour un quintal pesant de toiles de coton, adonc, par trop souvent, si treuve l’en de chascun C pois de coton, bien xxx ou xl pois de plastre de gifs, ou de blanc xviiid’Espaigne, ou de choses semblables. Et se l’en achate de cammeloz ou de tireteinne ou d’autre dras de laine, cist ne durent mie, ains sont plain d’empoise, ou de glu et de balieures.
“Et bien qu’il est voirs que chascuns hons egalement doit de son cors servir son seigneur ou sa commune, pour aler en ost en tens de besoingne; et bien que trestuit li autre royaume d’occident tieingnent ce pour ordenance, ciz pueple de Bretaingne la Grant n’en veult nullement, ains si dient: ‘Veez-là: n’avons nous pas la Manche pour fossé de nostre pourpris, et pourquoy nous penerons-nous pour nous faire homes d’armes, en lessiant nos gaaignes et nos soulaz? Cela lairons aus soudaiers.’ Or li preudhome entre eulx moult scevent bien com tiex paroles sont nyaises; mes si ont paour de lour en dire la verité pour ce que cuident desplaire as bourjois et à la menue gent.
“Or je vous di sanz faille que, quand Messires Marcs Pols sceust ces choses, moult en ot pitié de cestui pueple, et il li vint à remembrance ce que avenu estoit, ou tens Monseignour Nicolas et Monseignour Mafé, à l’ore quand Alau, frère charnel dou Grant Sire Cublay, ala en ost seur Baudas, et print le Calife et sa maistre cité, atout son vaste tresor d’or et d’argent, et l’amère parolle que dist ledit Alau au Calife, com l’a escripte li Maistres Rusticiens ou chief de cestui livre.[12]
“Car sachiés tout voirement que Messires Marc moult se deleitoit à faire appert combien sont pareilles au font les condicions des diverses regions dou monde, et soloit-il clorre son discours si disant en son language de Venisse: ‘Sto mondo xe fato tondo, com uzoit dire mes oncles Mafés.’
“Ore vous lairons à conter de ceste matière et retournerons à parler de la Loy des genz de Bretaingne la Grant.
Cy devise des diverses créances de la gent Bretaingne la Grant et de ce qu’en cuidoit Messires Marcs.“Il est voirs que li pueples est Crestiens, mes non pour le plus selonc la foy de l’Apostoille Rommain, ains tiennent le en mautalent assez. Seulement il y en a aucun qui sont féoil du dit Apostoille et encore plus forment que li nostre prudhome de Venisse. Car quand dit li Papes: ‘Telle ou telle chose est noyre,’ toute ladite gent si en jure: ‘Noyre est com poivre.’ Et puis se dira li Papes de la dite chose: ‘Elle est blanche,’ si en jurera toute ladite gent: ‘Il est voirs qu’elle est blanche; blanche est com noifs.’ Et dist Messires Marc Pol: ‘Nous n’avons nullement tant de foy à Venyse, ne li prudhome de Florence non plus, com l’en puet savoir bien apertement dou livre Monseignour Dantès Aldiguiere, que j’ay congneu a Padoe le meisme an que Messires Thibault de Cepoy à Venisse estoit.[13] Mes c’est joustement ce que j’ay veu autre foiz près le Grant Bacsi qui est com li Papes des Ydres.’
“Encore y a une autre manière de gent; ce sont de celz qui s’appellent filsoufes;[14] et si il disent: ‘S’il y a Diex n’en scavons nul, mes il est voirs xixqu’il est une certeinne courance des choses laquex court devers le bien.’ Et fist Messires Marcs: ‘Encore la créance des Bacsi qui dysent que n’y a ne Diex Eternel ne Juge des homes, ains il est une certeinne chose laquex s’appelle Kerma.’[15]
“Une autre foiz avint que disoit un des filsoufes à Monseignour Marc: ‘Diex n’existe mie jeusqu’ores, ainçois il se fait desorendroit.’ Et fist encore Messires Marcs: ‘Veez-là, une autre foiz la créance des ydres, car dient que li seuz Diex est icil hons qui par force de ses vertuz et de son savoir tant pourchace que d’home il se face Diex presentement. Et li Tartar l’appelent Borcan. Tiex Diex Sagamoni Borcan estoit, dou quel parle li livres Maistre Rusticien.’[16]
“Encore ont une autre manière de filsoufes, et dient-il: ‘Il n’est mie ne Diex ne Kerma ne courance vers le bien, ne Providence, ne Créerres, ne Sauvours, ne sainteté ne pechiés ne conscience de pechié, ne proyère ne response à proyère, il n’est nulle riens fors que trop minime grain ou paillettes qui ont à nom atosmes, et de tiex grains devient chose qui vive, et chose qui vive devient une certeinne creature qui demoure au rivaige de la Mer: et ceste creature devient poissons, et poissons devient lezars, et lezars devient blayriaus, et blayriaus devient gat-maimons, et gat-maimons devient hons sauvaiges qui menjue char d’homes, et hons sauvaiges devient hons crestien.’
“Et dist Messires Marc: ‘Encore une foiz, biaus sires, li Bacsi de Tebet et de Kescemir et li prestre de Seilan, qui si dient que l’arme vivant doie trespasser par tous cez changes de vestemens; si com se treuve escript ou livre Maistre Rusticien que Sagamoni Borcan mourut iiij vint et iiij foiz et tousjourz resuscita, et à chascune foiz d’une diverse manière de beste, et à la derreniere foyz mourut hons et devint diex, selonc ce qu’il dient.’[17] Et fist encore Messires Marc: ‘A moy pert-il trop estrange chose se juesques à toutes les créances des ydolastres deust dechéoir ceste grantz et saige nation. Ainsi peuent jouer Misire li filsoufe atout lour propre perte, mes à l’ore quand tiex fantaisies se respanderont es joenes bacheliers et parmy la menue gent, celz averont pour toute Loy manducemus et bibamus, cras enim moriemur; et trop isnellement l’en raccomencera la descente de l’eschiele, et d’home crestien deviendra hons sauvaiges, et d’home sauvaige gat-maimons, et de gat-maimon blayriaus.’ Et fist encores Messires Marc: ‘Maintes contrées et provinces et ysles et citéz je Marc Pol ay veues et de maintes genz de maintes manières ay les condicionz congneues, et je croy bien que il est plus assez dedens l’univers que ce que li nostre prestre n’y songent. Et puet bien estre, biaus sires, que li mondes n’a estés creés à tous poinz com nous creiens, ains d’une sorte encore plus merveillouse. Mes cil n’amenuise nullement nostre pensée de Diex et de sa majesté, ains la fait greingnour. Et contrée n’ay veue ou Dame Diex ne manifeste apertement les granz euvres de sa tout-poissante saigesse; gent n’ay congneue esquiex ne se fait sentir li fardels de pechié, et la besoingne de Phisicien des maladies de l’arme tiex com est nostre Seignours Ihesus Crist, Beni soyt son Non. Pensez doncques à cel qu’a dit uns de ses xxApostres: Nolite esse prudentes apud vosmet ipsos; et uns autres: Quoniam multi pseudo-prophetae exierint; et uns autres: Quod venient in novissimis diebus illusores ... dicentes, Ubi est promissio? et encores aus parolles que dist li Signours meismes: Vide ergo ne lumen quod in te est tenebrae sint.
Commant Messires Marcs se partist de l’ysle de Bretaingne et de la proyère que fist.“Et pourquoy vous en feroie-je lonc conte? Si print nef Messires Marcs et se partist en nageant vers la terre ferme. Or Messires Marc Pol moult ama cel roiaume de Bretaingne la grant pour son viex renon et s’ancienne franchise, et pour sa saige et bonne Royne (que Diex gart), et pour les mainz homes de vaillance et bons chaceours et les maintes bonnes et honnestes dames qui y estoient. Et sachiés tout voirement que en estant delez le bort la nef, et en esgardant aus roches blanches que l’en par dariere-li lessoit, Messires Marc prieoit Diex, et disoit-il: ‘Ha Sires Diex ay merci de cestuy vieix et noble royaume; fay-en pardurable forteresse de liberté et de joustice, et garde-le de tout meschief de dedens et de dehors; donne à sa gent droit esprit pour ne pas Diex guerroyer de ses dons, ne de richesce ne de savoir; et conforte-les fermement en ta foy’ ...”
A loud Amen seemed to peal from without, and the awakened reader started to his feet. And lo! it was the thunder of the winter-storm crashing among the many-tinted crags of Monte Pellegrino,—with the wind raging as it knows how to rage here in sight of the Isles of Æolus, and the rain dashing on the glass as ruthlessly as it well could have done, if, instead of Æolic Isles and many-tinted crags, the window had fronted a dearer shore beneath a northern sky, and looked across the grey Firth to the rain-blurred outline of the Lomond Hills.
But I end, saying to Messer Marco’s prayer, Amen.
Palermo, 31st December, 1874.
ORIGINAL PREFACE.

The amount of appropriate material, and of acquaintance with the mediæval geography of some parts of Asia, which was acquired during the compilation of a work of kindred character for the Hakluyt Society,[1] could hardly fail to suggest as a fresh labour in the same field the preparation of a new English edition of Marco Polo. Indeed one kindly critic (in the Examiner) laid it upon the writer as a duty to undertake that task.
Though at least one respectable English edition has appeared since Marsden’s,[2] the latter has continued to be the standard edition, and maintains not only its reputation but its market value. It is indeed the work of a sagacious, learned, and right-minded man, which can never be spoken of otherwise than with respect. But since Marsden published his quarto (1818) vast stores of new knowledge have become available in elucidation both of the contents of Marco Polo’s book and of its literary history. The works of writers such as Klaproth, Abel Rémusat, D’Avezac, Reinaud, Quatremère, Julien, I. J. Schmidt, Gildemeister, Ritter, Hammer-Purgstall, Erdmann, D’Ohsson, Defrémery, Elliot, Erskine, and many more, which throw light directly or incidentally on Marco Polo, have, for the most part, appeared since then. Nor, as regards the literary history of the book, were any just views possible at a time when what may be called the Fontal MSS. (in French) were unpublished and unexamined.
Besides the works which have thus occasionally or incidentally xxiithrown light upon the Traveller’s book, various editions of the book itself have since Marsden’s time been published in foreign countries, accompanied by comments of more or less value. All have contributed something to the illustration of the book or its history; the last and most learned of the editors, M. Pauthier, has so contributed in large measure. I had occasion some years ago[3] to speak freely my opinion of the merits and demerits of M. Pauthier’s work; and to the latter at least I have no desire to recur here.
Another of his critics, a much more accomplished as well as more favourable one,[4] seems to intimate the opinion that there would scarcely be room in future for new commentaries. Something of the kind was said of Marsden’s at the time of its publication. I imagine, however, that whilst our libraries endure the Iliad will continue to find new translators, and Marco Polo—though one hopes not so plentifully—new editors.
The justification of the book’s existence must however be looked for, and it is hoped may be found, in the book itself, and not in the Preface. The work claims to be judged as a whole, but it may be allowable, in these days of scanty leisure, to indicate below a few instances of what is believed to be new matter in an edition of Marco Polo; by which however it is by no means intended that all such matter is claimed by the editor as his own.[5]
xxiii
From the commencement of the work it was felt that the task was one which no man, though he were far better equipped and much more conveniently situated than the present writer, could satisfactorily accomplish from his own resources, and help was sought on special points wherever it seemed likely to be found. In scarcely any quarter was the application made in vain. Some who have aided most materially are indeed very old and valued friends; but to many others who have done the same the applicant was unknown; and some of these again, with whom the editor began correspondence on this subject as a stranger, he is happy to think that he may now call friends.
To none am I more indebted than to the Comm. Guglielmo Berchet, of Venice, for his ample, accurate, and generous assistance in furnishing me with Venetian documents, and in many other ways. Especial thanks are also due to Dr. William Lockhart, who has supplied the materials for some of the most valuable illustrations; to Lieutenant Francis Garnier, of the French Navy, the gallant and accomplished leader (after the death of Captain Doudart de la Grée) of the memorable expedition xxivup the Mekong to Yun-nan; to the Rev. Dr. Caldwell, of the S. P. G. Mission in Tinnevelly, for copious and valuable notes on Southern India; to my friends Colonel Robert Maclagan, R.E., Sir Arthur Phayre, and Colonel Henry Man, for very valuable notes and other aid; to Professor A. Schiefner, of St. Petersburg, for his courteous communication of very interesting illustrations not otherwise accessible; to Major-General Alexander Cunningham, of my own corps, for several valuable letters; to my friends Dr. Thomas Oldham, Director of the Geological Survey of India, Mr. Daniel Hanbury, F.R.S., Mr. Edward Thomas, Mr. James Fergusson, F.R.S., Sir Bartle Frere, and Dr. Hugh Cleghorn, for constant interest in the work and readiness to assist its progress; to Mr. A. Wylie, the learned Agent of the B. and F. Bible Society at Shang-hai, for valuable help; to the Hon. G. P. Marsh, U.S. Minister at the Court of Italy, for untiring kindness in the communication of his ample stores of knowledge, and of books. I have also to express my obligations to Comm. Nicolò Barozzi, Director of the City Museum at Venice, and to Professor A. S. Minotto, of the same city; to Professor Arminius Vámbéry, the eminent traveller; to Professor Flückiger of Bern; to the Rev. H. A. Jaeschke, of the Moravian Mission in British Tibet; to Colonel Lewis Pelly, British Resident in the Persian Gulf; to Pandit Manphul, C.S.I. (for a most interesting communication on Badakhshan); to my brother officer, Major T. G. Montgomerie, R.E., of the Indian Trigonometrical Survey; to Commendatore Negri the indefatigable President of the Italian Geographical Society; to Dr. Zotenberg, of the Great Paris Library, and to M. Ch. Maunoir, Secretary-General of the Société de Géographie; to Professor Henry xxvGiglioli, at Florence; to my old friend Major-General Albert Fytche, Chief Commissioner of British Burma; to Dr. Rost and Dr. Forbes-Watson, of the India Office Library and Museum; to Mr. R. H. Major, and Mr. R. K. Douglas, of the British Museum; to Mr. N. B. Dennys, of Hong-kong; and to Mr. C. Gardner, of the Consular Establishment in China. There are not a few others to whom my thanks are equally due; but it is feared that the number of names already mentioned may seem ridiculous, compared with the result, to those who do not appreciate from how many quarters the facts needful for a work which in its course intersects so many fields required to be collected, one by one. I must not, however, omit acknowledgments to the present Earl of Derby for his courteous permission, when at the head of the Foreign Office, to inspect Mr. Abbott’s valuable unpublished Report upon some of the Interior Provinces of Persia; and to Mr. T. T. Cooper, one of the most adventurous travellers of modern times, for leave to quote some passages from his unpublished diary.
Palermo, 31st December, 1870.
TO
HER ROYAL HIGHNESS,
MARGHERITA,
Princess of Piedmont,
THIS ENDEAVOUR TO ILLUSTRATE THE LIFE AND WORK
OF A RENOWNED ITALIAN
IS
BY HER ROYAL HIGHNESS’S GRACIOUS PERMISSION
Dedicated
WITH THE DEEPEST RESPECT
BY
As regards geographical elucidations, I may point to the explanation of the name Gheluchelan (i. p. 58), to the discussion of the route from Kerman to Hormuz, and the identification of the sites of Old Hormuz, of Cobinan and Dogana, the establishment of the position and continued existence of Keshm, the note on Pein and Charchan, on Gog and Magog, on the geography of the route from Sindafu to Carajan, on Anin and Coloman, on Mutafili, Cail, and Ely.
As regards historical illustrations, I would cite the notes regarding the Queens Bolgana and Cocachin, on the Karaunahs, etc., on the title of King of Bengal applied to the K. of Burma, and those bearing upon the Malay and Abyssinian chronologies.
In the interpretation of outlandish phrases, I may refer to the notes on Ondanique, Nono, Barguerlac, Argon, Sensin, Keshican, Toscaol, Bularguchi, Gat-paul, etc.
Among miscellaneous elucidations, to the disquisition on the Arbre Sol or Sec in vol. i., and to that on Mediæval Military Engines in vol. ii.
In a variety of cases it has been necessary to refer to Eastern languages for pertinent elucidations or etymologies. The editor would, however, be sorry to fall under the ban of the mediæval adage:
and may as well reprint here what was written in the Preface to Cathay:
“I am painfully sensible that in regard to many subjects dealt with in the following pages, nothing can make up for the want of genuine Oriental learning. A fair familiarity with Hindustani for many years, and some reminiscences of elementary Persian, have been useful in their degree; but it is probable that they may sometimes also have led me astray, as such slender lights are apt to do.”

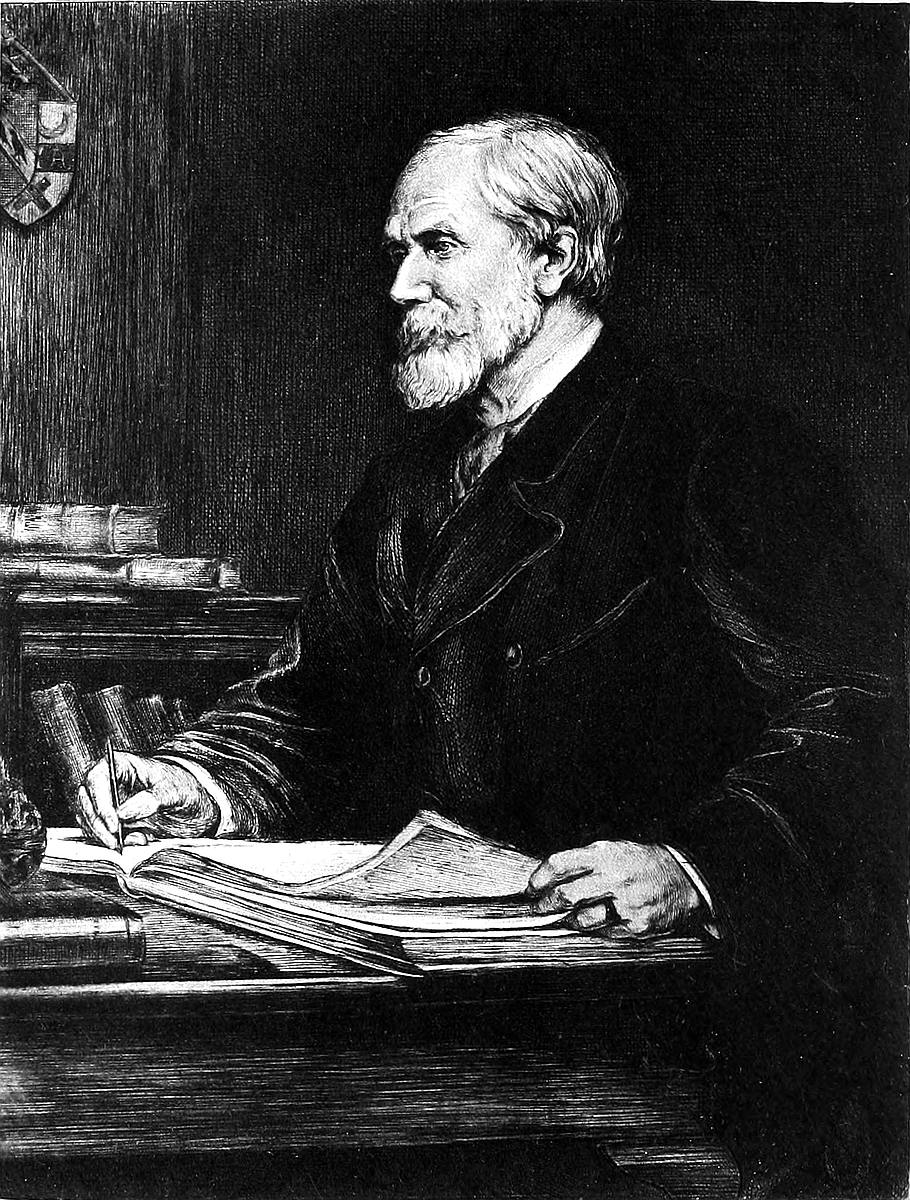
TO
HENRY YULE.
MEMOIR OF SIR HENRY YULE.
Henry Yule was the youngest son of Major William Yule, by his first wife, Elizabeth Paterson, and was born at Inveresk, in Midlothian, on 1st May, 1820. He was named after an aunt who, like Miss Ferrier’s immortal heroine, owned a man’s name.
On his father’s side he came of a hardy agricultural stock,[1] improved by a graft from that highly-cultured tree, Rose of Kilravock.[2] Through his mother, a somewhat prosaic person herself, he inherited strains from Huguenot and Highland ancestry. There were recognisable traces of all these elements xxviiiin Henry Yule, and as was well said by one of his oldest friends: “He was one of those curious racial compounds one finds on the east side of Scotland, in whom the hard Teutonic grit is sweetened by the artistic spirit of the more genial Celt.”[3] His father, an officer of the Bengal army (born 1764, died 1839), was a man of cultivated tastes and enlightened mind, a good Persian and Arabic scholar, and possessed of much miscellaneous Oriental learning. During the latter years of his career in India, he served successively as Assistant Resident at the (then independent) courts of Lucknow[4] and Delhi. In the latter office his chief was the noble Ouchterlony. William Yule, together with his younger brother Udny,[5] returned home in 1806. “A recollection of their voyage was that they hailed an outward bound ship, somewhere off the Cape, through the trumpet: ‘What news?’ Answer: ‘The King’s mad, and Humfrey’s beat Mendoza’ (two celebrated prize-fighters and often matched). ‘Nothing more?’ ‘Yes, Bonaparty’s made his Mother King of Holland!’
“Before his retirement, William Yule was offered the Lieut.-Governorship of St. Helena. Two of the detailed privileges of the office were residence at Longwood (afterwards the house of Napoleon), and the use of a certain number of the Company’s slaves. Major Yule, who was a strong supporter of the anti-slavery cause till its triumph in 1834, often recalled both of these offers with amusement.”[6]
xxix
William Yule was a man of generous chivalrous nature, who took large views of life, apt to be unfairly stigmatised as Radical in the narrow Tory reaction that prevailed in Scotland during the early years of the 19th century.[7] Devoid of literary ambition, he wrote much for his private pleasure, and his knowledge and library (rich in Persian and Arabic MSS.) were always placed freely at the service of his friends and correspondents, some of whom, such as Major C. Stewart and Mr. William Erskine, were more given to publication than himself. He never travelled without a little 8vo MS. of Hafiz, which often lay under his pillow. Major Yule’s only printed work was a lithographed edition of the Apothegms of ’Ali, the son of Abu Talib, in the Arabic, with an old Persian version and an English translation interpolated by himself. “This was privately issued in 1832, when the Duchesse d’Angoulême was living at Edinburgh, and the little work was inscribed to her, with whom an accident of neighbourhood and her kindness to the Major’s youngest child had brought him into relations of goodwill.”[8]
Henry Yule’s childhood was mainly spent at Inveresk. He used to say that his earliest recollection was sitting with the little cousin, who long after became his wife, on the doorstep of her father’s house in George Street, Edinburgh (now the Northern Club), listening to the performance of a passing piper. There was another episode which he recalled with humorous satisfaction. Fired by his father’s tales of the jungle, Yule (then about six years old) proceeded to improvise an elephant pit in the back garden, only too successfully, for soon, with mingled terror and delight, he saw his uncle John[9] fall headlong into the snare. He lost his mother before he was eight, and almost his only remembrance of her was the circumstance of her having given him a little lantern to light him home on winter nights from his first school. On Sundays it was the Major’s custom xxxto lend his children, as a picture-book, a folio Arabic translation of the Four Gospels, printed at Rome in 1591, which contained excellent illustrations from Italian originals.[10] Of the pictures in this volume Yule seems never to have tired. The last page bore a MS. note in Latin to the effect that the volume had been read in the Chaldæan Desert by Georgius Strachanus, Milnensis, Scotus, who long remained unidentified, not to say mythical, in Yule’s mind. But George Strachan never passed from his memory, and having ultimately run him to earth, Yule, sixty years later, published the results in an interesting article.[11]
Two or three years after his wife’s death, Major Yule removed to Edinburgh, and established himself in Regent’s Terrace, on the face of the Calton Hill.[12] This continued to be Yule’s home until his father’s death, shortly before he went to India. “Here he learned to love the wide scenes of sea and land spread out around that hill—a love he never lost, at home or far away. And long years after, with beautiful Sicilian hills before him and a lovely sea, he writes words of fond recollection of the bleak Fife hills, and the grey Firth of Forth.”[13]
Yule now followed his elder brother, Robert, to the famous High School, and in the summer holidays the two made expeditions xxxito the West Highlands, the Lakes of Cumberland, and elsewhere. Major Yule chose his boys to have every reasonable indulgence and advantage, and when the British Association, in 1834, held its first Edinburgh meeting, Henry received a member’s ticket. So, too, when the passing of the Reform Bill was celebrated in the same year by a great banquet, at which Lord Grey and other prominent politicians were present, Henry was sent to the dinner, probably the youngest guest there.[14]
At this time the intention was that Henry should go to Cambridge (where his name was, indeed, entered), and after taking his degree study for the Bar. With this view he was, in 1833, sent to Waith, near Ripon, to be coached by the Rev. H. P. Hamilton, author of a well-known treatise, On Conic Sections, and afterwards Dean of Salisbury. At his tutor’s hospitable rectory Yule met many notabilities of the day. One of them was Professor Sedgwick.
There was rumoured at this time the discovery of the first known (?) fossil monkey, but its tail was missing. “Depend upon it, Daniel O’Conell’s got hold of it!” said ‘Adam’ briskly.[15] Yule was very happy with Mr. Hamilton and his kind wife, but on his tutor’s removal to Cambridge other arrangements became necessary, and in 1835 he was transferred to the care of the Rev. James Challis, rector of Papworth St. Everard, a place which “had little to recommend it except a dulness which made reading almost a necessity.”[16] Mr. Challis had at this time two other resident pupils, who both, in most diverse ways, attained distinction in the Church. These were John Mason Neale, the future eminent ecclesiologist and founder of the devoted Anglican Sisterhood of St. Margaret, and Harvey Goodwin, long afterwards the studious and large-minded Bishop of Carlisle. With the latter, Yule remained on terms of cordial friendship to the end of his life. Looking back through more than fifty years to these boyish days, Bishop Goodwin wrote that Yule then “showed much more liking for Greek plays and for German than for mathematics, though he had considerable geometrical xxxiiingenuity.”[17] On one occasion, having solved a problem that puzzled Goodwin, Yule thus discriminated the attainments of the three pupils: “The difference between you and me is this: You like it and can’t do it; I don’t like it and can do it. Neale neither likes it nor can do it.” Not bad criticism for a boy of fifteen.[18]
On Mr. Challis being appointed Plumerian Professor at Cambridge, in the spring of 1836, Yule had to leave him, owing to want of room at the Observatory, and he became for a time, a most dreary time, he said, a student at University College, London.
By this time Yule had made up his mind that not London and the Law, but India and the Army should be his choice, and accordingly in Feb. 1837 he joined the East India Company’s Military College at Addiscombe. From Addiscombe he passed out, in December 1838, at the head of the cadets of his term (taking the prize sword[19]), and having been duly appointed to the Bengal Engineers, proceeded early in 1839 to the Headquarters of the Royal Engineers at Chatham, where, according to custom, he was enrolled as a “local and temporary Ensign.” For such was then the invidious designation at Chatham of the young Engineer officers of the Indian army, who ranked as full lieutenants in their own Service, from the time of leaving Addiscombe.[20] Yule once audaciously tackled the formidable Pasley on this very grievance. The venerable Director, after a minute’s pondering, replied: “Well, I don’t remember what the reason was, but I have no doubt (staccato) it ... was ... a very ... good reason.”[21]
“When Yule appeared among us at Chatham in 1839,” said his friend Collinson, “he at once took a prominent place in our little Society by his slightly advanced age [he was then 18½], but more by his strong character.... His earlier education ... gave him a better classical knowledge than most of us possessed; xxxiiithen he had the reserve and self-possession characteristic of his race; but though he took small part in the games and other recreations of our time, his knowledge, his native humour, and his good comradeship, and especially his strong sense of right and wrong, made him both admired and respected.... Yule was not a scientific engineer, though he had a good general knowledge of the different branches of his profession; his natural capacity lay rather in varied knowledge, combined with a strong understanding and an excellent memory, and also a peculiar power as a draughtsman, which proved of great value in after life.... Those were nearly the last days of the old régime, of the orthodox double sap and cylindrical pontoons, when Pasley’s genius had been leading to new ideas, and when Lintorn Simmons’ power, G. Leach’s energy, W. Jervois’ skill, and R. Tylden’s talent were developing under the wise example of Henry Harness.”[22]
In the Royal Engineer mess of those days (the present anteroom), the portrait of Henry Yule now faces that of his first chief, Sir Henry Harness. General Collinson said that the pictures appeared to eye each other as if the subjects were continuing one of those friendly disputes in which they so often engaged.[23]
It was in this room that Yule, Becher, Collinson, and other young R.E.’s, profiting by the temporary absence of the austere Colonel Pasley, acted some plays, including Pizarro. Yule bore the humble part of one of the Peruvian Mob in this performance, of which he has left a droll account.[24]
On the completion of his year at Chatham, Yule prepared to sail for India, but first went to take leave of his relative, General White. An accident prolonged his stay, and before he left he had proposed to and been refused by his cousin Annie. This occurrence, his first check, seems to have cast rather a gloom over his start for India. He went by the then newly-opened Overland Route, visiting Portugal, stopping at Gibraltar to see xxxivhis cousin, Major (afterwards General) Patrick Yule, R.E.[25] He was under orders “to stop at Aden (then recently acquired), to report on the water supply, and to deliver a set of meteorological and magnetic instruments for starting an observatory there. The overland journey then really meant so; tramping across the desert to Suez with camels and Arabs, a proceeding not conducive to the preservation of delicate instruments; and on arriving at Aden he found that the intended observer was dead, the observatory not commenced, and the instruments all broken. There was thus nothing left for him but to go on at once” to Calcutta,[26] where he arrived at the end of 1840.
His first service lay in the then wild Khasia Hills, whither he was detached for the purpose of devising means for the transport of the local coal to the plains. In spite of the depressing character of the climate (Cherrapunjee boasts the highest rainfall on record), Yule thoroughly enjoyed himself, and always looked back with special pleasure on the time he spent here. He was unsuccessful in the object of his mission, the obstacles to cheap transport offered by the dense forests and mighty precipices proving insurmountable, but he gathered a wealth of interesting observations on the country and people, a very primitive Mongolian race, which he subsequently embodied in two excellent and most interesting papers (the first he ever published).[27]
In the following year, 1842, Yule was transferred to the xxxvirrigation canals of the north-west with head-quarters at Kurnaul. Here he had for chief Captain (afterwards General Sir William) Baker, who became his dearest and most steadfast friend. Early in 1843 Yule had his first experience of field service. The death without heir of the Khytul Rajah, followed by the refusal of his family to surrender the place to the native troops sent to receive it, obliged Government to send a larger force against it, and the canal officers were ordered to join this. Yule was detailed to serve under Captain Robert Napier (afterwards F.-M. Lord Napier of Magdala). Their immediate duty was to mark out the route for a night march of the troops, barring access to all side roads, and neither officer having then had any experience of war, they performed the duty “with all the elaborate care of novices.” Suddenly there was an alarm, a light detected, and a night attack awaited, when the danger resolved itself into Clerk Sahib’s khansamah with welcome hot coffee![28] Their hopes were disappointed, there was no fighting, and the Fort of Khytul was found deserted by the enemy. It “was a strange scene of confusion—all the paraphernalia and accumulation of odds and ends of a wealthy native family lying about and inviting loot. I remember one beautiful crutch-stick of ebony with two rams’ heads in jade. I took it and sent it in to the political authority, intending to buy it when sold. There was a sale, but my stick never appeared. Somebody had a more developed taste in jade.... Amid the general rummage that was going on, an officer of British Infantry had been put over a part of the palace supposed to contain treasure, and they—officers and all—were helping themselves. Henry Lawrence was one of the politicals under George Clerk. When the news of this affair came to him I was present. It was in a white marble loggia in the palace, where was a white marble chair or throne on a basement. Lawrence was sitting on this throne in great excitement. He wore an Afghan choga, a sort of dressing-gown garment, and this, and his thin locks, and thin beard were xxxvistreaming in the wind. He always dwells in my memory as a sort of pythoness on her tripod under the afflatus.”[29]
During his Indian service, Yule had renewed and continued by letters his suit to Miss White, and persistency prevailing at last, he soon after the conclusion of the Khytul affair applied for leave to go home to be married. He sailed from Bombay in May, 1843, and in September of the same year was married, at Bath, to the gifted and large-hearted woman who, to the end, remained the strongest and happiest influence in his life.[30]
Yule sailed for India with his wife in November 1843. The next two years were employed chiefly in irrigation work, and do not call for special note. They were very happy years, except in the one circumstance that the climate having seriously affected his wife’s health, and she having been brought to death’s door, partly by illness, but still more by the drastic medical treatment of those days, she was imperatively ordered back to England by the doctors, who forbade her return to India.
Having seen her on board ship, Yule returned to duty on the canals. The close of that year, December, 1845, brought some variety to his work, as the outbreak of the first Sikh War called nearly all the canal officers into the field. “They went up to the front by long marches, passing through no stations, and quite unable to obtain any news of what had occurred, though on the 21st December the guns of Ferozshah were distinctly heard in their camp at Pehoa, at a distance of 115 miles south-east from the field, and some days later they came successively on the fields of Moodkee and of Ferozshah itself, with all the recent traces of battle. When the party of irrigation officers reached head-quarters, the arrangements for attacking the Sikh army in its entrenchments at Sobraon were beginning (though suspended till weeks later for the arrival of the tardy siege guns), and the opposed forces were lying in sight of each other.”[31]
Yule’s share in this campaign was limited to the sufficiently arduous task of bridging the Sutlej for the advance of the British army. It is characteristic of the man that for this xxxviireason he always abstained from wearing his medal for the Sutlej campaign.
His elder brother, Robert Yule, then in the 16th Lancers, took part in that magnificent charge of his regiment at the battle of Aliwal (Jan. 28, 1846) which the Great Duke is said to have pronounced unsurpassed in history. From particulars gleaned from his brother and others present in the action, Henry Yule prepared a spirited sketch of the episode, which was afterwards published as a coloured lithograph by M‘Lean (Haymarket).
At the close of the war, Yule succeeded his friend Strachey as Executive Engineer of the northern division of the Ganges Canal, with his head-quarters at Roorkee, “the division which, being nearest the hills and crossed by intermittent torrents of great breadth and great volume when in flood, includes the most important and interesting engineering works.”[32]
At Roorkee were the extensive engineering workshops connected with the canal. Yule soon became so accustomed to the din as to be undisturbed by the noise, but the unpunctuality and carelessness of the native workmen sorely tried his patience, of which Nature had endowed him with but a small reserve. Vexed with himself for letting temper so often get the better of him, Yule’s conscientious mind devised a characteristic remedy. Each time that he lost his temper, he transferred a fine of two rupees (then about five shillings) from his right to his left pocket. When about to leave Roorkee, he devoted this accumulation of self-imposed fines to the erection of a sun-dial, to teach the natives the value of time. The late Sir James Caird, who told this legend of Roorkee as he heard it there in 1880, used to add, with a humorous twinkle of his kindly eyes, “It was a very handsome dial.”[33]
From September, 1845, to March, 1847, Yule was much occupied intermittently, in addition to his professional work, by service on a Committee appointed by Government “to investigate the causes of the unhealthiness which has existed at Kurnal, and other portions of the country along the line of the Delhi Canal,” and further, to report “whether an injurious xxxviiieffect on the health of the people of the Doab is, or is not, likely to be produced by the contemplated Ganges Canal.”
“A very elaborate investigation was made by the Committee, directed principally to ascertaining what relation subsisted between certain physical conditions of the different districts, and the liability of their inhabitants to miasmatic fevers.” The principal conclusion of the Committee was, “that in the extensive epidemic of 1843, when Kurnaul suffered so seriously ... the greater part of the evils observed had not been the necessary and unavoidable results of canal irrigation, but were due to interference with the natural drainage of the country, to the saturation of stiff and retentive soils, and to natural disadvantages of site, enhanced by excess of moisture. As regarded the Ganges Canal, they were of opinion that, with due attention to drainage, improvement rather than injury to the general health might be expected to follow the introduction of canal irrigation.”[34] In an unpublished note written about 1889, Yule records his ultimate opinion as follows: “At this day, and after the large experience afforded by the Ganges Canal, I feel sure that a verdict so favourable to the sanitary results of canal irrigation would not be given.” Still the fact remains that the Ganges Canal has been the source of unspeakable blessings to an immense population.
The Second Sikh War saw Yule again with the army in the field, and on 13th Jan. 1849, he was present at the dismal ‘Victory’ of Chillianwallah, of which his most vivid recollection seemed to be the sudden apparition of Henry Lawrence, fresh from London, but still clad in the legendary Afghan cloak.
On the conclusion of the Punjab campaign, Yule, whose health had suffered, took furlough and went home to his wife. For the next three years they resided chiefly in Scotland, though paying occasional visits to the Continent, and about 1850 Yule bought a house in Edinburgh. There he wrote “The African Squadron vindicated” (a pamphlet which was afterwards re-published in French), translated Schiller’s Kampf mit dem Drachen into English verse, delivered Lectures on Fortification at the, now long defunct, Scottish Naval and Military Academy, wrote on Tibet for his friend Blackwood’s xxxixMagazine, attended the 1850 Edinburgh Meeting of the British Association, wrote his excellent lines, “On the Loss of the Birkenhead,” and commenced his first serious study of Marco Polo (by whose wondrous tale, however, he had already been captivated as a boy in his father’s library—in Marsden’s edition probably). But the most noteworthy literary result of these happy years was that really fascinating volume, entitled Fortification for Officers of the Army and Students of Military History, a work that has remained unique of its kind. This was published by Blackwood in 1851, and seven years later received the honour of (unauthorised) translation into French. Yule also occupied himself a good deal at this time with the practice of photography, a pursuit to which he never after reverted.
In the spring of 1852, Yule made an interesting little semi-professional tour in company with a brother officer, his accomplished friend, Major R. B. Smith. Beginning with Kelso, “the only one of the Teviotdale Abbeys which I had not as yet seen,” they made their way leisurely through the north of England, examining with impartial care abbeys and cathedrals, factories, brick-yards, foundries, timber-yards, docks, and railway works. On this occasion Yule, contrary to his custom, kept a journal, and a few excerpts may be given here, as affording some notion of his casual talk to those who did not know him.
At Berwick-on-Tweed he notes the old ramparts of the town: “These, erected in Elizabeth’s time, are interesting as being, I believe, the only existing sample in England of the bastioned system of the 16th century.... The outline of the works seems perfect enough, though both earth and stone work are in great disrepair. The bastions are large with obtuse angles, square orillons, and double flanks originally casemated, and most of them crowned with cavaliers.” On the way to Durham, “much amused by the discussions of two passengers, one a smooth-spoken, semi-clerical looking person; the other a brusque well-to-do attorney with a Northumbrian burr. Subject, among others, Protection. The Attorney all for ‘cheap bread’— ‘You wouldn’t rob the poor man of his loaf,’ and so forth. ‘You must go with the stgheam, sir, you must go with the stgheam.’ ‘I never did, Mr. Thompson, and I never will,’ said the other in an oily manner, singularly inconsistent with the xlsentiment.” At Durham they dined with a dignitary of the Church, and Yule was roasted by being placed with his back to an enormous fire. “Coals are cheap at Durham,” he notes feelingly, adding, “The party we found as heavy as any Edinburgh one. Smith, indeed, evidently has had little experience of really stupid Edinburgh parties, for he had never met with anything approaching to this before.” (Happy Smith!) But thanks to the kindness and hospitality of the astronomer, Mr. Chevalier, and his gifted daughter, they had a delightful visit to beautiful Durham, and came away full of admiration for the (then newly established) University, and its grand locale. They went on to stay with an uncle by marriage of Yule’s, in Yorkshire. At dinner he was asked by his host to explain Foucault’s pendulum experiment. “I endeavoured to explain it somewhat, I hope, to the satisfaction of his doubts, but not at all to that of Mr. G. M., who most resolutely declined to take in any elucidation, coming at last to the conclusion that he entirely differed with me as to what North meant, and that it was useless to argue until we could agree about that!” They went next to Leeds, to visit Kirkstall Abbey, “a mediæval fossil, curiously embedded among the squalid brickwork and chimney stalks of a manufacturing suburb. Having established ourselves at the hotel, we went to deliver a letter to Mr. Hope, the official assignee, a very handsome, aristocratic-looking gentleman, who seemed as much out of place at Leeds as the Abbey.” At Leeds they visited the flax mills of Messrs. Marshall, “a firm noted for the conscientious care they take of their workpeople.... We mounted on the roof of the building, which is covered with grass, and formerly was actually grazed by a few sheep, until the repeated inconvenience of their tumbling through the glass domes put a stop to this.” They next visited some tile and brickworks on land belonging to a friend. “The owner of the tile works, a well-to-do burgher, and the apparent model of a West Riding Radical, received us in rather a dubious way: ‘There are a many people has come and brought introductions, and looked at all my works, and then gone and set up for themselves close by. Now des you mean to say that you be really come all the way from Bengul?’ ‘Yes, indeed we have, and we are going all the way back again, though we didn’t exactly come from there to look at your brickworks.’ ‘Then you’re not in xlithe brick-making line, are you?’ ‘Why we’ve had a good deal to do with making bricks, and may have again; but we’ll engage that if we set up for ourselves, it shall be ten thousand miles from you.’ This seemed in some degree to set his mind at rest....”
“A dismal day, with occasional showers, prevented our seeing Sheffield to advantage. On the whole, however, it is more cheerful and has more of a country-town look than Leeds—a place utterly without beauty of aspect. At Leeds you have vast barrack-like factories, with their usual suburbs of squalid rows of brick cottages, and everywhere the tall spiracles of the steam, which seems the pervading power of the place. Everything there is machinery—the machine is the intelligent agent, it would seem, the man its slave, standing by to tend it and pick up a broken thread now and then. At Sheffield ... you might go through most of the streets without knowing anything of the kind was going on. And steam here, instead of being a ruler, is a drudge, turning a grindstone or rolling out a bar of steel, but all the accuracy and skill of hand is the Man’s. And consequently there was, we thought, a healthier aspect about the men engaged. None of the Rodgers remain who founded the firm in my father’s time. I saw some pairs of his scissors in the show-room still kept under the name of Persian scissors.”[35]
From Sheffield Yule and his friend proceeded to Boston, “where there is the most exquisite church tower I have ever seen,” and thence to Lincoln, Peterborough, and Ely, ending their tour at Cambridge, where Yule spent a few delightful days.
In the autumn the great Duke of Wellington died, and Yule witnessed the historic pageant of his funeral. His furlough was now nearly expired, and early in December he again embarked for India, leaving his wife and only child, of a few xliiweeks old, behind him. Some verses dated “Christmas Day near the Equator,” show how much he felt the separation.
Shortly after his return to Bengal, Yule received orders to proceed to Aracan, and to examine and report upon the passes between Aracan and Burma, as also to improve communications and select suitable sites for fortified posts to hold the same. These orders came to Yule quite unexpectedly late one Saturday evening, but he completed all preparations and started at daybreak on the following Monday, 24th Jan. 1853.
From Calcutta to Khyook Phyoo, Yule proceeded by steamer, and thence up the river in the Tickler gunboat to Krenggyuen. “Our course lay through a wilderness of wooded islands (50 to 200 feet high) and bays, sailing when we could, anchoring when neither wind nor tide served ... slow progress up the river. More and more like the creeks and lagoons of the Niger or a Guiana river rather than anything I looked for in India. The densest tree jungle covers the shore down into the water. For miles no sign of human habitation, but now and then at rare intervals one sees a patch of hillside rudely cleared, with the bare stems of the burnt trees still standing.... Sometimes, too, a dark tunnel-like creek runs back beneath the thick vault of jungle, and from it silently steals out a slim canoe, manned by two or three wild-looking Mugs or Kyens (people of the Hills), driving it rapidly along with their short paddles held vertically, exactly like those of the Red men on the American rivers.”
At the military post of Bokhyong, near Krenggyuen, he notes (5th Feb.) that “Captain Munro, the adjutant, can scarcely believe that I was present at the Duke of Wellington’s funeral, of which he read but a few days ago in the newspapers, and here am I, one of the spectators, a guest in this wild spot among the mountains—2½ months since I left England.”
Yule’s journal of his arduous wanderings in these border wilds is full of interest, but want of space forbids further quotation. From a note on the fly-leaf it appears that from the time of quitting the gun-boat at Krenggyuen to his arrival at Toungoop he covered about 240 miles on foot, and that under immense difficulties, even as to food. He commemorated his tribulations in some cheery humorous verse, but ultimately fell seriously ill of the local fever, aided doubtless by previous exposure and privation. His servants successively fell ill, xliiisome died and others had to be sent back, food supplies failed, and the route through those dense forests was uncertain; yet under all difficulties he seems never to have grumbled or lost heart. And when things were nearly at the worst, Yule restored the spirits of his local escort by improvising a wappenshaw, with a Sheffield gardener’s knife, which he happened to have with him, for prize! When at last Yule emerged from the wilds and on 25th March marched into Prome, he was taken for his own ghost! “Found Fraser (of the Engineers) in a rambling phoongyee house, just under the great gilt pagoda. I went up to him announcing myself, and his astonishment was so great that he would scarcely shake hands!” It was on this occasion at Prome that Yule first met his future chief Captain Phayre—“a very young-looking man—very cordial,” a description no less applicable to General Sir Arthur Phayre at the age of seventy!
After some further wanderings, Yule embarked at Sandong, and returned by water, touching at Kyook Phyoo and Akyab, to Calcutta, which he reached on 1st May—his birthday.
The next four months were spent in hard work at Calcutta. In August, Yule received orders to proceed to Singapore, and embarked on the 29th. His duty was to report on the defences of the Straits Settlements, with a view to their improvement. Yule’s recommendations were sanctioned by Government, but his journal bears witness to the prevalence then, as since, of the penny-wise-pound-foolish system in our administration. On all sides he was met by difficulties in obtaining sites for batteries, etc., for which heavy compensation was demanded, when by the exercise of reasonable foresight, the same might have been secured earlier at a nominal price.
Yule’s journal contains a very bright and pleasing picture of Singapore, where he found that the majority of the European population “were evidently, from their tongues, from benorth the Tweed, a circumstance which seems to be true of four-fifths of the Singaporeans. Indeed, if I taught geography, I should be inclined to class Edinburgh, Glasgow, Dundee, and Singapore together as the four chief towns of Scotland.”
Work on the defences kept Yule in Singapore and its neighbourhood until the end of November, when he embarked for Bengal. On his return to Calcutta, Yule was appointed xlivDeputy Consulting Engineer for Railways at Head-quarters. In this post he had for chief his old friend Baker, who had in 1851 been appointed by the Governor-General, Lord Dalhousie, Consulting Engineer for Railways to Government. The office owed its existence to the recently initiated great experiment of railway construction under Government guarantee.
The subject was new to Yule, “and therefore called for hard and anxious labour. He, however, turned his strong sense and unbiased view to the general question of railway communication in India, with the result that he became a vigorous supporter of the idea of narrow gauge and cheap lines in the parts of that country outside of the main trunk lines of traffic.”[36]
The influence of Yule, and that of his intimate friends and ultimate successors in office, Colonels R. Strachey and Dickens, led to the adoption of the narrow (metre) gauge over a great part of India. Of this matter more will be said further on; it is sufficient at this stage to note that it was occupying Yule’s thoughts, and that he had already taken up the position in this question that he thereafter maintained through life. The office of Consulting Engineer to Government for Railways ultimately developed into the great Department of Public Works.
As related by Yule, whilst Baker “held this appointment, Lord Dalhousie was in the habit of making use of his advice in a great variety of matters connected with Public Works projects and questions, but which had nothing to do with guaranteed railways, there being at that time no officer attached to the Government of India, whose proper duty it was to deal with such questions. In August, 1854, the Government of India sent home to the Court of Directors a despatch and a series of minutes by the Governor-General and his Council, in which the constitution of the Public Works Department as a separate branch of administration, both in the local governments and the government of India itself, was urged on a detailed plan.”
In this communication Lord Dalhousie stated his desire to appoint Major Baker to the projected office of Secretary for the Department of Public Works. In the spring of 1855 these recommendations were carried out by the creation of the Department, xlvwith Baker as Secretary and Yule as Under Secretary for Public Works.
Meanwhile Yule’s services were called to a very different field, but without his vacating his new appointment, which he was allowed to retain. Not long after the conclusion of the second Burmese War, the King of Burma sent a friendly mission to the Governor-General, and in 1855 a return Embassy was despatched to the Court of Ava, under Colonel Arthur Phayre, with Henry Yule as Secretary, an appointment the latter owed as much to Lord Dalhousie’s personal wish as to Phayre’s good-will. The result of this employment was Yule’s first geographical book, a large volume entitled Mission to the Court of Ava in 1855, originally printed in India, but subsequently re-issued in an embellished form at home (see over leaf). To the end of his life, Yule looked back to this “social progress up the Irawady, with its many quaint and pleasant memories, as to a bright and joyous holiday.”[37] It was a delight to him to work under Phayre, whose noble and lovable character he had already learned to appreciate two years before in Pegu. Then, too, Yule has spoken of the intense relief it was to escape from the monotonous scenery and depressing conditions of official life in Bengal (Resort to Simla was the exception, not the rule, in these days!) to the cheerfulness and unconstraint of Burma, with its fine landscapes and merry-hearted population. “It was such a relief to find natives who would laugh at a joke,” he once remarked in the writer’s presence to the lamented E. C. Baber, who replied that he had experienced exactly the same sense of relief in passing from India to China.
Yule’s work on Burma was largely illustrated by his own sketches. One of these represents the King’s reception of the Embassy, and another, the King on his throne. The originals were executed by Yule’s ready pencil, surreptitiously within his cocked hat, during the audience.
From the latter sketch Yule had a small oil-painting executed under his direction by a German artist, then resident in Calcutta, which he gave to Lord Dalhousie.[38]
xlvi
The Government of India marked their approval of the Embassy by an unusual concession. Each of the members of the mission received a souvenir of the expedition. To Yule was given a very beautiful and elaborately chased small bowl, of nearly pure gold, bearing the signs of the Zodiac in relief.[39]
On his return to Calcutta, Yule threw himself heart and soul into the work of his new appointment in the Public Works Department. The nature of his work, the novelty and variety of the projects and problems with which this new branch of the service had to deal, brought Yule into constant, and eventually very intimate association with Lord Dalhousie, whom he accompanied on some of his tours of inspection. The two men thoroughly appreciated each other, and, from first to last, Yule experienced the greatest kindness from Lord Dalhousie. In this intimacy, no doubt the fact of being what French soldiers call pays added something to the warmth of their mutual regard: their forefathers came from the same airt, and neither was unmindful of the circumstance. It is much to be regretted that Yule preserved no sketch of Lord Dalhousie, nor written record of his intercourse with him, but the following lines show some part of what he thought:
“At this time [1849] there appears upon the scene that vigorous and masterful spirit, whose arrival to take up the government of India had been greeted by events so inauspicious. No doubt from the beginning the Governor-General was desirous to let it be understood that although new to India he was, and meant to be, master; ... Lord Dalhousie was by no means averse to frank dissent, provided in the manner it was never forgotten that he was Governor-General. Like his great predecessor Lord Wellesley, he was jealous of all familiarity and resented it.... The general sentiment of those who worked under that ἄναξ ανδρῶν was one of strong and admiring affection ... and we doubt if a Governor-General ever embarked on the Hoogly amid deeper feeling than attended him who, shattered by sorrow and xlviiphysical suffering, but erect and undaunted, quitted Calcutta on the 6th March 1856.”[40]
His successor was Lord Canning, whose confidence in Yule and personal regard for him became as marked as his predecessor’s.
In the autumn of 1856, Yule took leave and came home. Much of his time while in England was occupied with making arrangements for the production of an improved edition of his book on Burma, which so far had been a mere government report. These were completed to his satisfaction, and on the eve of returning to India, he wrote to his publishers[41] that the correction of the proof sheets and general supervision of the publication had been undertaken by his friend the Rev. W. D. Maclagan, formerly an officer of the Madras army (and now Archbishop of York).
Whilst in England, Yule had renewed his intimacy with his old friend Colonel Robert Napier, then also on furlough, a visitor whose kindly sympathetic presence always brought special pleasure also to Yule’s wife and child. One result of this intercourse was that the friends decided to return together to India. Accordingly they sailed from Marseilles towards the end of April, and at Aden were met by the astounding news of the outbreak of the Mutiny.
On his arrival in Calcutta Yule, who retained his appointment of Under Secretary to Government, found his work indefinitely increased. Every available officer was called into the field, and Yule’s principal centre of activity was shifted to the great fortress of Allahabad, forming the principal base of operations against the rebels. Not only had he to strengthen or create defences at Allahabad and elsewhere, but on Yule devolved the principal burden of improvising accommodation for the European troops then pouring into India, which ultimately meant providing for an army of 100,000 men. His task was made the more difficult by the long-standing chronic friction, then and long after, existing between the officers of the Queen’s and the Company’s services. But in a far more important matter he was always fortunate. As he subsequently recorded in a Note for Government: “Through all consciousness of mistakes and shortcomings, xlviiiI have felt that I had the confidence of those whom I served, a feeling which has lightened many a weight.”
It was at Allahabad that Yule, in the intervals of more serious work, put the last touches to his Burma book. The preface of the English edition is dated, “Fortress of Allahabad, Oct. 3, 1857,” and contains a passage instinct with the emotions of the time. After recalling the “joyous holiday” on the Irawady, he goes on: “But for ourselves, standing here on the margin of these rivers, which a few weeks ago were red with the blood of our murdered brothers and sisters, and straining the ear to catch the echo of our avenging artillery, it is difficult to turn the mind to what seem dreams of past days of peace and security; and memory itself grows dim in the attempt to repass the gulf which the last few months has interposed between the present and the time to which this narrative refers.”[42]
When he wrote these lines, the first relief had just taken place, and the second defence of Lucknow was beginning. The end of the month saw Sir Colin Campbell’s advance to the second—the real—relief of Lucknow. Of Sir Colin, Yule wrote and spoke with warm regard: “Sir Colin was delightful, and when in a good humour and at his best, always reminded me very much, both in manner and talk, of the General (i.e. General White, his wife’s father). The voice was just the same and the xlixquiet gentle manner, with its underlying keen dry humour. But then if you did happen to offend Sir Colin, it was like treading on crackers, which was not our General’s way.”
When Lucknow had been relieved, besieged, reduced, and finally remodelled by the grand Roads and Demolitions Scheme of his friend Napier, the latter came down to Allahabad, and he and Yule sought diversion in playing quoits and skittles, the only occasion on which either of them is known to have evinced any liking for games.
Before this time Yule had succeeded his friend Baker as de facto Secretary to Government for Public Works, and on Baker’s retirement in 1858, Yule was formally appointed his successor.[43] Baker and Yule had, throughout their association, worked in perfect unison, and the very differences in their characters enhanced the value of their co-operation; the special qualities of each friend mutually strengthened and completed each other. Yule’s was by far the more original and creative mind, Baker’s the more precise and, at least in a professional sense, the more highly-trained organ. In chivalrous sense of honour, devotion to duty, and natural generosity, the men stood equal; but while Yule was by nature impatient and irritable, and liable, until long past middle age, to occasional sudden bursts of uncontrollable anger, generally followed by periods of black depression and almost absolute silence,[44] Baker was the very reverse. Partly by natural temperament, but also certainly by severe self-discipline, his manner was invincibly placid and his temper imperturbable.[45] Yet none was more tenacious in maintaining whatever he judged right.
Baker, whilst large-minded in great matters, was extremely conventional in small ones, and Yule must sometimes have tried his feelings in this respect. The particulars of one such tragic occurrence have survived. Yule, who was colour-blind,[46] and in learly life whimsically obstinate in maintaining his own view of colours, had selected some cloth for trousers undeterred by his tailor’s timid remonstrance of “Not quite your usual taste, sir.” The result was that the Under-Secretary to Government startled official Calcutta by appearing in brilliant claret-coloured raiment. Baker remonstrated: “Claret-colour! Nonsense, my trousers are silver grey,” said Yule, and entirely declined to be convinced. “I think I did convince him at last,” said Baker with some pride, when long after telling the story to the present writer. “And then he gave them up?” “Oh, no,” said Sir William ruefully, “he wore those claret-coloured trousers to the very end.” That episode probably belonged to the Dalhousie period.
When Yule resumed work in the Secretariat at Calcutta at the close of the Mutiny, the inevitable arrears of work were enormous. This may be the proper place to notice more fully his action with respect to the choice of gauge for Indian railways already adverted to in brief. As we have seen, his own convictions led to the adoption of the metre gauge over a great part of India. This policy had great disadvantages not at first foreseen, and has since been greatly modified. In justice to Yule, however, it should be remembered that the conditions and requirements of India have largely altered, alike through the extraordinary growth of the Indian export, especially the grain, trade, and the development of new necessities for Imperial defence. These new features, however, did but accentuate defects inherent in the system, but which only prolonged practical experience made fully apparent.
At the outset the supporters of the narrow gauge seemed to have the stronger position, as they were able to show that the cost was much less, the rails employed being only about ⅔rds the weight of those required by the broad gauge, and many other subsidiary expenses also proportionally less. On the other lihand, as time passed and practical experience was gained, its opponents were able to make an even stronger case against the narrow gauge. The initial expenses were undoubtedly less, but the durability was also less. Thus much of the original saving was lost in the greater cost of maintenance, whilst the small carrying capacity of the rolling stock and loss of time and labour in shifting goods at every break of gauge, were further serious causes of waste, which the internal commercial development of India daily made more apparent. Strategic needs also were clamant against the dangers of the narrow gauge in any general scheme of Indian defence. Yule’s connection with the Public Works Department had long ceased ere the question of the gauges reached its most acute stage, but his interest and indirect participation in the conflict survived. In this matter a certain parental tenderness for a scheme which he had helped to originate, combined with his warm friendship for some of the principal supporters of the narrow gauge, seem to have influenced his views more than he himself was aware. Certainly his judgment in this matter was not impartial, although, as always in his case, it was absolutely sincere and not consciously biased.
In reference to Yule’s services in the period following the Mutiny, Lord Canning’s subsequent Minute of 1862 may here be fitly quoted. In this the Governor-General writes: “I have long ago recorded my opinion of the value of his services in 1858 and 1859, when with a crippled and overtaxed staff of Engineer officers, many of them young and inexperienced, the G.-G. had to provide rapidly for the accommodation of a vast English army, often in districts hitherto little known, and in which the authority of the Government was barely established, and always under circumstances of difficulty and urgency. I desire to repeat that the Queen’s army in India was then greatly indebted to Lieut.-Colonel Yule’s judgment, earnestness, and ability; and this to an extent very imperfectly understood by many of the officers who held commands in that army.
“Of the manner in which the more usual duties of his office have been discharged it is unnecessary for me to speak. It is, I believe, known and appreciated as well by the Home Government as by the Governor-General in Council.”
In the spring of 1859 Yule felt the urgent need of a rest, and liitook the, at that time, most unusual step of coming home on three months’ leave, which as the voyage then occupied a month each way, left him only one month at home. He was accompanied by his elder brother George, who had not been out of India for thirty years. The visit home of the two brothers was as bright and pleasant as it was brief, but does not call for further notice.
In 1860, Yule’s health having again suffered, he took short leave to Java. His journal of this tour is very interesting, but space does not admit of quotation here. He embodied some of the results of his observations in a lecture he delivered on his return to Calcutta.
During these latter years of his service in India, Yule owed much happiness to the appreciative friendship of Lord Canning and the ready sympathy of Lady Canning. If he shared their tours in an official capacity, the intercourse was much more than official. The noble character of Lady Canning won from Yule such wholehearted chivalrous devotion as, probably, he felt for no other friend save, perhaps in after days, Sir Bartle Frere. And when her health failed, it was to Yule’s special care that Lord Canning entrusted his wife during a tour in the Hills. Lady Canning was known to be very homesick, and one day as the party came in sight of some ilexes (the evergreen oak), Yule sought to cheer her by calling out pleasantly: “Look, Lady Canning! There are oaks!” “No, no, Yule, not oaks,” cried Sir C. B. “They are (solemnly) Ibexes.” “No, not Ibexes, Sir C., you mean Silexes,” cried Capt. ——, the A.D.C.; Lady Canning and Yule the while almost choking with laughter.
On another and later occasion, when the Governor-General’s camp was peculiarly dull and stagnant, every one yawning and grumbling, Yule effected a temporary diversion by pretending to tap the telegraph wires, and circulating through camp, what purported to be, the usual telegraphic abstract of news brought to Bombay by the latest English mail. The news was of the most astounding character, with just enough air of probability, in minor details, to pass muster with a dull reader. The effect was all he could wish—or rather more—and there was a general flutter in the camp. Of course the Governor-General and one or two others were in the secret, and mightily relished the diversion. But this pleasant and cheering intercourse was drawing to its liiimournful close. On her way back from Darjeeling, in November, 1861, Lady Canning (not then in Yule’s care) was unavoidably exposed to the malaria of a specially unhealthy season. A few days’ illness followed, and on 18th November, 1861, she passed calmly to
It was to Yule that Lord Canning turned in the first anguish of his loss, and on this faithful friend devolved the sad privilege of preparing her last resting-place. This may be told in the touching words of Lord Canning’s letter to his only sister, written on the day of Lady Canning’s burial, in the private garden at Barrackpoor[48]:—
“The funeral is over, and my own darling lies buried in a spot which I am sure she would have chosen of all others.... From the grave can be seen the embanked walk leading from the house to the river’s edge, which she made as a landing-place three years ago, and from within 3 or 4 paces of the grave there is a glimpse of the terrace-garden and its balustrades, which she made near the house, and of the part of the grounds with which she most occupied herself.... I left Calcutta yesterday ... and on arriving here, went to look at the precise spot chosen for the grave. I could see by the clear full moon ... that it was exactly right. Yule was there superintending the workmen, and before daylight this morning a solid masonry vault had been completely finished.
“Bowie [Military Secretary] and Yule have done all this for me. It has all been settled since my poor darling died. She liked Yule. They used to discuss together her projects of improvement for this place, architecture, gardening, the Cawnpore monument, etc., and they generally agreed. He knew her tastes well....”
The coffin, brought on a gun-carriage from Calcutta, “was carried by twelve soldiers of the 6th Regiment (Queen’s), the A.D.C.’s bearing the pall. There were no hired men or ordinary funeral attendants of any kind at any part of the ceremony, and no lookers-on.... Yule was the only person not of the household livstaff. Had others who had asked” to attend “been allowed to do so, the numbers would have been far too large.
“On coming near the end of the terrace walk I saw that the turf between the walk and the grave, and for several yards all round the grave, was strewed thick with palm branches and bright fresh-gathered flowers—quite a thick carpet. It was a little matter, but so exactly what she would have thought of.”[49]
And, therefore, Yule thought of this for her! He also recorded the scene two days later in some graceful and touching lines, privately printed, from which the following may be quoted:
Yule’s deep sympathy in this time of sorrow strengthened the friendship Lord Canning had long felt for him, and when the time approached for the Governor-General to vacate his high office, he invited Yule, who was very weary of India, to accompany him home, where his influence would secure Yule congenial employment. Yule’s weariness of India at this time was extreme. Moreover, after serving under such leaders as Lord Dalhousie and Lord Canning, and winning their full confidence and friendship, it was almost repugnant to him to begin afresh with new men and probably new measures, with which he might lvnot be in accord. Indeed, some little clouds were already visible on the horizon. In these circumstances, it is not surprising that Yule, under an impulse of lassitude and impatience, when accepting Lord Canning’s offer, also ‘burnt his boats’ by sending in his resignation of the service. This decision Yule took against the earnest advice of his anxious and devoted wife, and for a time the results justified all her misgivings. She knew well, from past experience, how soon Yule wearied in the absence of compulsory employment. And in the event of the life in England not suiting him, for even Lord Canning’s good-will might not secure perfectly congenial employment for his talents, she knew well that his health and spirits would be seriously affected. She, therefore, with affectionate solicitude, urged that he should adopt the course previously followed by his friend Baker, that is, come home on furlough, and only send in his resignation after he saw clearly what his prospects of home employment were, and what he himself wished in the matter.
Lord Canning and Yule left Calcutta late in March, 1862; at Malta they parted never to meet again in this world. Lord Canning proceeded to England, and Yule joined his wife and child in Rome. Only a few weeks later, at Florence, came as a thunderclap the announcement of Lord Canning’s unexpected death in London, on 17th June. Well does the present writer remember the day that fatal news came, and Yule’s deep anguish, not assuredly for the loss of his prospects, but for the loss of a most noble and magnanimous friend, a statesman whose true greatness was, both then and since, most imperfectly realised by the country for which he had worn himself out.[50] Shortly after Yule went to England,[51] where he was cordially received by Lord Canning’s representatives, who gave him a touching remembrance lviof his lost friend, in the shape of the silver travelling candlesticks, which had habitually stood on Lord Canning’s writing-table.[52] But his offer to write Lord Canning’s Life had no result, as the relatives, following the then recent example of the Hastings family, in the case of another great Governor-General, refused to revive discussion by the publication of any Memoir.
Nor did Yule find any suitable opening for employment in England, so after two or three months spent in visiting old friends, he rejoined his family in the Black Forest, where he sought occupation in renewing his knowledge of German. But it must be confessed that his mood both then and for long after was neither happy nor wholesome. The winter of 1862 was spent somewhat listlessly, partly in Germany and partly at the Hôtel des Bergues, Geneva, where his old acquaintance Colonel Tronchin was hospitably ready to open all doors. The picturesque figure of John Ruskin also flits across the scene at this time. But Yule was unoccupied and restless, and could neither enjoy Mr. Ruskin’s criticism of his sketches nor the kindly hospitality of his Genevan hosts. Early in 1863 he made another fruitless visit to London, where he remained four or five months, but found no opening. Though unproductive of work, this year brought Yule official recognition of his services in the shape of the C.B., for which Lord Canning had long before recommended him.[53]
On rejoining his wife and child at Mornex in Savoy, Yule found the health of the former seriously impaired. During his absence, the kind and able English Doctor at Geneva had felt obliged to inform Mrs. Yule that she was suffering from disease of the heart, and that her life might end suddenly at any moment. Unwilling to add to Yule’s anxieties, she made all necessary arrangements, but did not communicate this intelligence until he had done all he wished and returned, when she broke it to him very gently. Up to this year Mrs. Yule, though not strong and often ailing, had not allowed herself to be considered lviian invalid, but from this date doctor’s orders left her no choice in the matter.[54]
About this time, Yule took in hand the first of his studies of mediæval travellers. His translation of the Travels of Friar Jordanus was probably commenced earlier; it was completed during the leisurely journey by carriage between Chambéry and Turin, and the Dedication to Sir Bartle Frere written during a brief halt at Genoa, from which place it is dated. Travelling slowly and pleasantly by vetturino along the Riviera di Levante, the family came to Spezzia, then little more than a quiet village. A chance encounter with agreeable residents disposed Yule favourably towards the place, and a few days later he opened negotiations for land to build a house! Most fortunately for himself and all concerned these fell through, and the family continued their journey to Tuscany, and settled for the winter in a long rambling house, with pleasant garden, at Pisa, where Yule was able to continue with advantage his researches into mediæval travel in the East. He paid frequent visits to Florence, where he had many pleasant acquaintances, not least among them Charles Lever (“Harry Lorrequer”), with whom acquaintance ripened into warm and enduring friendship. At Florence he also made the acquaintance of the celebrated Marchese Gino Capponi, and of many other Italian men of letters. To this winter of 1863–64 belongs also the commencement of a lasting friendship with the illustrious Italian historian, Villari, at that time holding an appointment at Pisa. Another agreeable acquaintance, though less intimate, was formed with John Ball, the well-known President of the Alpine Club, then resident at Pisa, and with many others, among whom the name of a very cultivated German scholar, H. Meyer, specially recurs to memory.
lviii
In the spring of 1864, Yule took a spacious and delightful old villa, situated in the highest part of the Bagni di Lucca,[55] and commanding lovely views over the surrounding chestnut-clad hills and winding river.
Here he wrote much of what ultimately took form in Cathay and the Way Thither. It was this summer, too, that Yule commenced his investigations among the Venetian archives, and also visited the province of Friuli in pursuit of materials for the history of one of his old travellers, the Beato Odorico. At Verona—then still Austrian—he had the amusing experience of being arrested for sketching too near the fortifications. However, his captors had all the usual Austrian bonhomie and courtesy, and Yule experienced no real inconvenience. He was much more disturbed when, a day or two later, the old mother of one of his Venetian acquaintances insisted on embracing him on account of his supposed likeness to Garibaldi!
As winter approached, a warmer climate became necessary for Mrs. Yule, and the family proceeded to Sicily, landing at Messina in October, 1864. From this point, Yule made a very interesting excursion to the then little known group of the Lipari Islands, in the company of that eminent geologist, the late Robert Mallet, F.R.S., a most agreeable companion.
On Martinmas Day, the Yules reached the beautiful capital of Sicily, Palermo, which, though they knew it not, was to be their home—a very happy one—for nearly eleven years.
During the ensuing winter and spring, Yule continued the preparation of Cathay, but his appetite for work not being satisfied by this, he, when in London in 1865, volunteered to make an Index to the third decade of the Journal of the Royal Geographical Society, in exchange for a set of such volumes as he did not possess. That was long before any Index Society existed; but Yule had special and very strong views of his own as to what an Index should be, and he spared no labour to realise his ideal.[56] This proved a heavier task than he had anticipated, and he got very weary before the Index was completed.
lix
In the spring of 1866, Cathay and the Way Thither appeared, and at once took the high place which it has ever since retained. In the autumn of the same year Yule’s attention was momentarily turned in a very different direction by a local insurrection, followed by severe reprisals, and the bombardment of Palermo by the Italian Fleet. His sick wife was for some time under rifle as well as shell fire; but cheerfully remarking that “every bullet has its billet,” she remained perfectly serene and undisturbed. It was the year of the last war with Austria, and also of the suppression of the Monastic Orders in Sicily; two events which probably helped to produce the outbreak, of which Yule contributed an account to The Times, and subsequently a more detailed one to the Quarterly Review.[57]
Yule had no more predilection for the Monastic Orders than most of his countrymen, but his sense of justice was shocked by the cruel incidence of the measure in many cases, and also by the harshness with which both it and the punishment of suspected insurgents was carried out. Cholera was prevalent in Italy that year, but Sicily, which had maintained stringent quarantine, entirely escaped until large bodies of troops were landed to quell the insurrection, when a devastating epidemic immediately ensued, and re-appeared in 1867. In after years, when serving on the Army Sanitary Committee at the India Office, Yule more than once quoted this experience as indicating that quarantine restrictions may, in some cases, have more value than British medical authority is usually willing to admit.
In 1867, on his return from London, Yule commenced systematic work on his long projected new edition of the Travels of Marco Polo. It was apparently in this year that the scheme first took definite form, but it had long been latent in his mind. The Public Libraries of Palermo afforded him much good material, whilst occasional visits to the Libraries of Venice, Florence, Paris, and London, opened other sources. But his most important channel of supply came from his very extensive private correspondence, extending to nearly all parts of Europe and many centres in Asia. His work brought him many new and valued friends, indeed too many to mention, but amongst whom, as lxbelonging specially to this period, three honoured names must be recalled here: Commendatore (afterwards Baron) Cristoforo Negri, the large-hearted Founder and First President of the Geographical Society of Italy, from whom Yule received his first public recognition as a geographer, Commendatore Guglielmo Berchet (affectionately nicknamed il Bello e Buono), ever generous in learned help, who became a most dear and honoured friend, and the Hon. George P. Marsh, U.S. Envoy to the Court of Italy, a man, both as scholar and friend, unequalled in his nation, perhaps almost unique anywhere.
Those who only knew Yule in later years, may like some account of his daily life at this time. It was his custom to rise fairly early; in summer he sometimes went to bathe in the sea,[58] or for a walk before breakfast; more usually he would write until breakfast, which he preferred to have alone. After breakfast he looked through his notebooks, and before ten o’clock was usually walking rapidly to the library where his work lay. He would work there until two or three o’clock, when he returned home, read the Times, answered letters, received or paid visits, and then resumed work on his book, which he often continued long after the rest of the household were sleeping. Of course his family saw but little of him under these circumstances, but when he had got a chapter of Marco into shape, or struck out some new discovery of interest, he would carry it to his wife to read. She always took great interest in his work, and he had great faith in her literary instinct as a sound as well as sympathetic critic.
The first fruits of Yule’s Polo studies took the form of a review of Pauthier’s edition of Marco Polo, contributed to the Quarterly Review in 1868.
In 1870 the great work itself appeared, and received prompt generous recognition by the grant of the very beautiful gold medal of the Geographical Society of Italy,[59] followed in 1872 by the award of the Founder’s Medal of the Royal Geographical Society, while the Geographical and Asiatic Societies of Paris, the Geographical Societies of Italy and Berlin, the Academy of Bologna, and other learned bodies, enrolled him as an Honorary Member.
lxi
Reverting to 1869, we may note that Yule, when passing through Paris early in the spring, became acquainted, through his friend M. Charles Maunoir, with the admirable work of exploration lately performed by Lieut. Francis Garnier of the French Navy. It was a time of much political excitement in France, the eve of the famous Plébiscite, and the importance of Garnier’s work was not then recognised by his countrymen. Yule saw its value, and on arrival in London went straight to Sir Roderick Murchison, laid the facts before him, and suggested that no other traveller of the year had so good a claim to one of the two gold medals of the R.G.S. as this French naval Lieutenant. Sir Roderick was propitious, and accordingly in May the Patron’s medal was assigned to Garnier, who was touchingly grateful to Yule; whilst the French Minister of Marine marked his appreciation of Yule’s good offices by presenting him with the magnificent volumes commemorating the expedition.[60]
Yule was in Paris in 1871, immediately after the suppression of the Commune, and his letters gave interesting accounts of the extraordinary state of affairs then prevailing. In August, he served as President of the Geographical Section of the British Association at its Edinburgh meeting.
On his return to Palermo, he devoted himself specially to the geography of the Oxus region, and the result appeared next year in his introduction and notes to Wood’s Journey. Soon after his return to Palermo, he became greatly interested in the plans, about which he was consulted, of an English church, the gift to the English community of two of its oldest members, Messrs Ingham and Whitaker. Yule’s share in the enterprise gradually expanded, until he became a sort of volunteer clerk of the works, to the great benefit of his health, as this occupation during the next three years, whilst adding to his interests, also kept him longer in the open air than would otherwise have been the case. It was a real misfortune to Yule (and one of which he was himself at times conscious) that he had no taste for any out-of-door pursuits, neither for any form of natural science, nor for gardening, nor for lxiiany kind of sport nor games. Nor did he willingly ride.[61] He was always restless away from his books. There can be no doubt that want of sufficient air and exercise, reacting on an impaired liver, had much to do with Yule’s unsatisfactory state of health and frequent extreme depression. There was no lack of agreeable and intelligent society at Palermo (society that the present writer recalls with cordial regard), to which every winter brought pleasant temporary additions, both English and foreign, the best of whom generally sought Yule’s acquaintance. Old friends too were not wanting; many found their way to Palermo, and when such came, he was willing to show them hospitality and to take them excursions, and occasionally enjoyed these. But though the beautiful city and surrounding country were full of charm and interest, Yule was too much pre-occupied by his own special engrossing pursuits ever really to get the good of his surroundings, of which indeed he often seemed only half conscious.
By this time Yule had obtained, without ever having sought it, a distinct and, in some respects, quite unique position in geographical science. Although his Essay on the Geography of the Oxus Region (1872) received comparatively little public attention at home, it had yet made its mark once for all,[62] and from this time, if not earlier, Yule’s high authority in all questions of Central Asian geography was generally recognised. He had long ere this, almost unconsciously, laid the broad foundations of that “Yule method,” of which Baron von Richthofen has written so eloquently, declaring that not only in his own land, “but also in the literatures of France, Italy, Germany, and other countries, the powerful stimulating influence of the Yule method is visible.”[63] More than one writer has indeed boldly compared lxiiiCentral Asia before Yule to Central Africa before Livingstone!
Yule had wrought from sheer love of the work and without expectation of public recognition, and it was therefore a great surprise as well as gratification to him, to find that the demand for his Marco Polo was such as to justify the appearance of a second edition only a few years after the first. The preparation of this enlarged edition, with much other miscellaneous work (see subjoined bibliography), and the superintendence of the building of the church already named, kept him fully occupied for the next three years.
Amongst the parerga and miscellaneous occupations of Yule’s leisure hours in the period 1869–74, may be mentioned an interesting correspondence with Professor W. W. Skeat on the subject of William of Palerne and Sicilian examples of the Werwolf; the skilful analysis and exposure of Klaproth’s false geography;[64] the purchase and despatch of Sicilian seeds and young trees for use in the Punjab, at the request of the Indian Forestry Department; translations (prepared for friends) of tracts on the cultivation of Sumach and the collection of Manna as practised in Sicily; also a number of small services rendered to the South Kensington Museum, at the request of the late Sir Henry Cole. These latter included obtaining Italian and Sicilian bibliographic contributions to the Science and Art Department’s Catalogue of Books on Art, selecting architectural subjects to be photographed;[65] negotiating the purchase of the original drawings illustrative of Padre B. Gravina’s great work on the Cathedral of Monreale; and superintending the execution of a copy in mosaic of the large mosaic picture (in the Norman Palatine Chapel, Palermo,) of the Entry of our Lord into Jerusalem.
In the spring of 1875, just after the publication of the second lxivedition of Marco Polo, Yule had to mourn the loss of his noble wife. He was absent from Sicily at the time, but returned a few hours after her death on 30th April. She had suffered for many years from a severe form of heart disease, but her end was perfect peace. She was laid to rest, amid touching tokens of both public and private sympathy, in the beautiful camposanto on Monte Pellegrino. What her loss was to Yule only his oldest and closest friends were in a position to realise. Long years of suffering had impaired neither the soundness of her judgment nor the sweetness, and even gaiety, of her happy, unselfish disposition. And in spirit, as even in appearance, she retained to the very last much of the radiance of her youth. Nor were her intellectual gifts less remarkable. Few who had once conversed with her ever forgot her, and certainly no one who had once known her intimately ever ceased to love her.[66]
Shortly after this calamity, Yule removed to London, and on the retirement of his old friend, Sir William Baker, from the India Council early that autumn, Lord Salisbury at once selected him for the vacant seat. Nothing would ever have made him a party-man, but he always followed Lord Salisbury with conviction, and worked under him with steady confidence.
In 1877 Yule married, as his second wife, the daughter of an old friend,[67] a very amiable woman twenty years his junior, who made him very happy until her untimely death in 1881. From the time of his joining the India Council, his duties at the India Office of course occupied a great part of his time, but he also continued to do an immense amount of miscellaneous literary work, as may be seen by reference to the subjoined bibliography, lxv(itself probably incomplete). In Council he invariably “showed his strong determination to endeavour to deal with questions on their own merits and not only by custom and precedent.”[68] Amongst subjects in which he took a strong line of his own in the discussions of the Council, may be specially instanced his action in the matter of the cotton duties (in which he defended native Indian manufactures as against hostile Manchester interests); the Vernacular Press Act, the necessity for which he fully recognised; and the retention of Kandahar, for which he recorded his vote in a strong minute. In all these three cases, which are typical of many others, his opinion was overruled, but having been carefully and deliberately formed, it remained unaffected by defeat.
In all matters connected with Central Asian affairs, Yule’s opinion always carried great weight; some of his most competent colleagues indeed preferred his authority in this field to that of even Sir Henry Rawlinson, possibly for the reason given by Sir M. Grant Duff, who has epigrammatically described the latter as good in Council but dangerous in counsel.[69]
Yule’s courageous independence and habit of looking at all public questions by the simple light of what appeared to him right, yet without fads or doctrinairism, earned for him the respect of the successive Secretaries of State under whom he served, and the warm regard and confidence of his other colleagues. The value attached to his services in Council was sufficiently shown by the fact that when the period of ten years (for which members are usually appointed), was about to expire, Lord Hartington (now Duke of Devonshire), caused Yule’s appointment to be renewed for life, under a special Act of Parliament passed for this purpose in 1885.
His work as a member of the Army Sanitary Committee, brought him into communication with Miss Florence Nightingale, a privilege which he greatly valued and enjoyed, though he used to say: “She is worse than a Royal Commission to answer, and, in the most gracious charming manner possible, immediately finds out all I don’t know!” Indeed his devotion to the “Lady-in-Chief” was scarcely less complete than Kinglake’s.
lxvi
In 1880, Yule was appointed to the Board of Visitors of the Government Indian Engineering College at Cooper’s Hill, a post which added to his sphere of interests without materially increasing his work. In 1882, he was much gratified by being named an Honorary Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, more especially as it was to fill one of the two vacancies created by the deaths of Thomas Carlyle and Dean Stanley.
Yule had been President of the Hakluyt Society from 1877, and in 1885 was elected President also of the Royal Asiatic Society. He would probably also have been President of the Royal Geographical Society, but for an untoward incident. Mention has already been made of his constant determination to judge all questions by the simple touchstone of what he believed to be right, irrespective of personal considerations. It was in pursuance of these principles that, at the cost of great pain to himself and some misrepresentation, he in 1878 sundered his long connection with the Royal Geographical Society, by resigning his seat on their Council, solely in consequence of their adoption of what he considered a wrong policy. This severance occurred just when it was intended to propose him as President. Some years later, at the personal request of the late Lord Aberdare, a President in all respects worthy of the best traditions of that great Society, Yule consented to rejoin the Council, which he re-entered as a Vice-President.
In 1883, the University of Edinburgh celebrated its Tercentenary, when Yule was selected as one of the recipients of the honorary degree of LL.D. His letters from Edinburgh, on this occasion, give a very pleasant and amusing account of the festivity and of the celebrities he met. Nor did he omit to chronicle the envious glances cast, as he alleged, by some British men of science on the splendours of foreign Academic attire, on the yellow robes of the Sorbonne, and the Palms of the Institute of France! Pasteur was, he wrote, the one most enthusiastically acclaimed of all who received degrees.
I think it was about the same time that M. Renan was in England, and called upon Sir Henry Maine, Yule, and others at the India Office. On meeting just after, the colleagues compared notes as to their distinguished but unwieldy visitor. “It seems that le style n’est pas l’homme même in this instance,” lxviiquoth “Ancient Law” to “Marco Polo.” And here it may be remarked that Yule so completely identified himself with his favourite traveller that he frequently signed contributions to the public press as Marcus Paulus Venetus or M.P.V. His more intimate friends also gave him the same sobriquet, and once, when calling on his old friend, Dr. John Brown (the beloved chronicler of Rab and his Friends), he was introduced by Dr. John to some lion-hunting American visitors as “our Marco Polo.” The visitors evidently took the statement in a literal sense, and scrutinised Yule closely.[70]
In 1886 Yule published his delightful Anglo-Indian Glossary, with the whimsical but felicitous sub-title of Hobson-Jobson (the name given by the rank and file of the British Army in India to the religious festival in celebration of Hassan and Husaïn).
This Glossary was an abiding interest to both Yule and the present writer. Contributions of illustrative quotations came from most diverse and unexpected sources, and the arrival of each new word or happy quotation was quite an event, and gave such pleasure to the recipients as can only be fully understood by those who have shared in such pursuits. The volume was dedicated in affecting terms to his elder brother, Sir George Yule, who, unhappily, did not survive to see it completed.
In July 1885, the two brothers had taken the last of many happy journeys together, proceeding to Cornwall and the Scilly Isles. A few months later, on 13th January 1886, the end came suddenly to the elder, from the effects of an accident at his own door.[71]
It may be doubted if Yule ever really got over the shock of this loss, though he went on with his work as usual, and served that year as a Royal Commissioner on the occasion of the Indian and Colonial Exhibition of 1886.
From 1878, when an accidental chill laid the foundations of an exhausting, though happily quite painless, malady, Yule’s strength had gradually failed, although for several years longer his general health and energies still appeared unimpaired to a casual observer. The condition of public affairs also, in some lxviiidegree, affected his health injuriously. The general trend of political events from 1880 to 1886 caused him deep anxiety and distress, and his righteous wrath at what he considered the betrayal of his country’s honour in the cases of Frere, of Gordon, and of Ireland, found strong, and, in a noble sense, passionate expression in both prose and verse. He was never in any sense a party man, but he often called himself “one of Mr. Gladstone’s converts,” i.e. one whom Gladstonian methods had compelled to break with liberal tradition and prepossessions.
Nothing better expresses Yule’s feeling in the period referred to than the following letter, written in reference to the R. E. Gordon Memorial,[72] but of much wider application: “Will you allow me an inch or two of space to say to my brother officers, ‘Have nothing to do with the proposed Gordon Memorial.’
“That glorious memory is in no danger of perishing and needs no memorial. Sackcloth and silence are what it suggests to those who have guided the action of England; and Englishmen must bear the responsibility for that action and share its shame. It is too early for atoning memorials; nor is it possible for those who take part in them to dissociate themselves from a repulsive hypocrisy.
“Let every one who would fain bestow something in honour of the great victim, do, in silence, some act of help to our soldiers or their families, or to others who are poor and suffering.
“In later days our survivors or successors may look back with softened sorrow and pride to the part which men of our corps have played in these passing events, and Charles Gordon far in the front of all; and then they may set up our little tablets, or what not—not to preserve the memory of our heroes, but to maintain the integrity of our own record of the illustrious dead.”
Happily Yule lived to see the beginning of better times for his country. One of the first indications of that national awakening was the right spirit in which the public, for the most part, received Lord Wolseley’s stirring appeal at the close of 1888, and Yule was so much struck by the parallelism between Lord Wolseley’s warning and some words of his own contained lxixin the pseudo-Polo fragment (see above, end of Preface), that he sent Lord Wolseley the very last copy of the 1875 edition of Marco Polo, with a vigorous expression of his sentiments.
That was probably Yule’s last utterance on a public question. The sands of life were now running low, and in the spring of 1889, he felt it right to resign his seat on the India Council, to which he had been appointed for life. On this occasion Lord Cross, then Secretary of State for India, successfully urged his acceptance of the K.C.S.I., which Yule had refused several years before.
In the House of Lords, Viscount Cross subsequently referred to his resignation in the following terms. He said: “A vacancy on the Council had unfortunately occurred through the resignation from ill-health of Sir Henry Yule, whose presence on the Council had been of enormous advantage to the natives of the country. A man of more kindly disposition, thorough intelligence, high-minded, upright, honourable character, he believed did not exist; and he would like to bear testimony to the estimation in which he was held, and to the services which he had rendered in the office he had so long filled.”[73]
This year the Hakluyt Society published the concluding volume of Yule’s last work of importance, the Diary of Sir William Hedges. He had for several years been collecting materials for a full memoir of his great predecessor in the domain of historical geography, the illustrious Rennell.[74] This work was well advanced as to preliminaries, but was not sufficiently developed for early publication at the time of Yule’s death, and ere it could be completed its place had been taken by a later enterprise.
During the summer of 1889, Yule occupied much of his leisure by collecting and revising for re-issue many of his miscellaneous writings. Although not able to do much at a time, this desultory work kept him occupied and interested, and gave him much pleasure during many months. It was, however, never completed. Yule went to the seaside for a few weeks lxxin the early summer, and subsequently many pleasant days were spent by him among the Surrey hills, as the guest of his old friends Sir Joseph and Lady Hooker. Of their constant and unwearied kindness, he always spoke with most affectionate gratitude. That autumn he took a great dislike to the English climate; he hankered after sunshine, and formed many plans, eager though indefinite, for wintering at Cintra, a place whose perfect beauty had fascinated him in early youth. But increasing weakness made a journey to Portugal, or even the South of France, an alternative of which he also spoke, very inexpedient, if not absolutely impracticable. Moreover, he would certainly have missed abroad the many friends and multifarious interests which still surrounded him at home. He continued to take drives, and occasionally called on friends, up to the end of November, and it was not until the middle of December that increasing weakness obliged him to take to his bed. He was still, however, able to enjoy seeing his friends—some to the very end, and he had a constant stream of visitors, mostly old friends, but also a few newer ones, who were scarcely less welcome. He also kept up his correspondence to the last, three attached brother R.E.’s, General Collinson, General Maclagan, and Major W. Broadfoot, taking it in turn with the present writer to act as his amanuensis.
On Friday, 27th December, Yule received a telegram from Paris, announcing his nomination that day as Corresponding Member of the Institute of France (Académie des Inscriptions), one of the few distinctions of any kind of which it can still be said that it has at no time lost any of its exalted dignity.
An honour of a different kind that came about the same time, and was scarcely less prized by him, was a very beautiful letter of farewell and benediction from Miss Florence Nightingale,[75] which he kept under his pillow and read many times. On the 28th, he dictated to the present writer his acknowledgment, also by telegraph, of the great honour done him by the Institute. The message was in the following words: “Reddo gratias, lxxiIllustrissimi Domini, ob honores tanto nimios quanto immeritos! Mihi robora deficiunt, vita collabitur, accipiatis voluntatem pro facto. Cum corde pleno et gratissimo moriturus vos, Illustrissimi Domini, saluto.Yule.”
Sunday, 29th December, was a day of the most dense black fog, and he felt its oppression, but was much cheered by a visit from his ever faithful friend, Collinson, who, with his usual unselfishness, came to him that day at very great personal inconvenience.
On Monday, 30th December, the day was clearer, and Henry Yule awoke much refreshed, and in a peculiarly happy and even cheerful frame of mind. He said he felt so comfortable. He spoke of his intended book, and bade his daughter write about the inevitable delay to his publisher: “Go and write to John Murray,” were indeed his last words to her. During the morning he saw some friends and relations, but as noon approached his strength flagged, and after a period of unconsciousness, he passed peacefully away in the presence of his daughter and of an old friend, who had come from Edinburgh to see him, but arrived too late for recognition. Almost at the same time that Yule fell asleep, his “stately message,”[76] was being read under the great Dome in Paris. Some two hours after Yule had passed away, F.-M. Lord Napier of Magdala, called on an errand of friendship, and at his desire was admitted to see the last of his early friend. When Lord Napier came out, he said to the present writer, in his own reflective way: “He looks as if he had just settled to some great work.” With these suggestive words of the great soldier, who was so soon, alas, to follow his old friend to the work of another world, this sketch may fitly close.
The following excellent verses (of unknown authorship) on Yule’s death, subsequently appeared in the Academy:[77]
The same idea had been previously embodied, in very felicitous language, by the late General Sir William Lockhart, in a letter which that noble soldier addressed to the present writer a few days after Yule’s death. And Yule himself would have taken pleasure in the idea of those meetings with his old travellers, which seemed so certain to his surviving friends.[78]
He rests in the old cemetery at Tunbridge Wells, with his second wife, as he had directed. A great gathering of friends attended the first part of the burial service which was held in London on 3rd January, 1890. Amongst those present were witnesses of every stage of his career, from his boyish days at the High School of Edinburgh downwards. His daughter, of course, was there, led by the faithful, peerless friend who was so soon to follow him into the Undiscovered Country.[79] She and his youngest nephew, with two cousins and a few old friends, followed his remains over the snow to the graveside. The epitaph subsequently inscribed on the tomb was penned by Yule himself, but is by no means representative of his powers in a kind of composition in which he had so often excelled in the service of others. As a composer of epitaphs and other monumental inscriptions few of our time have surpassed, if any have equalled him, in his best efforts.
lxxiiiSIR GEORGE UDNY YULE, C.B., K.C.S.I.[80]
George Udny Yule, born at Inveresk in 1813, passed through Haileybury into the Bengal Civil Service, which he entered at the age of 18 years. For twenty-five years his work lay in Eastern Bengal. He gradually became known to the Government for his activity and good sense, but won a far wider reputation as a mighty hunter, alike with hog-spear and double barrel. By 1856 the roll of his slain tigers exceeded four hundred, some of them of special fame; after that he continued slaying his tigers, but ceased to count them. For some years he and a few friends used annually to visit the plains of the Brahmaputra, near the Garrow Hills—an entirely virgin country then, and swarming with large game. Yule used to describe his once seeing seven rhinoceroses at once on the great plain, besides herds of wild buffalo and deer of several kinds. One of the party started the theory that Noah’s Ark had been shipwrecked there! In those days George Yule was the only man to whom the Maharajah of Nepaul, Sir Jung Bahadur, conceded leave to shoot within his frontier.
Yule was first called from his useful obscurity in 1856. The year before, the Sonthals in insurrection disturbed the long unbroken peace of the Delta. These were a numerous non-Aryan, uncivilised, but industrious race, driven wild by local mismanagement, and the oppressions of Hindoo usurers acting through the regulation courts. After the suppression of their rising, Yule was selected by Sir F. Halliday, who knew his man, to be Commissioner of the Bhagulpoor Division, containing some six million souls, and embracing the hill country of the Sonthals. He obtained sanction to a code for the latter, which removed these people entirely from the Court system, and its tribe of leeches, and abolished all intermediaries between the Sahib and the Sonthal peasant. Through these measures, and his personal influence, aided by picked assistants, he was able to effect, with extraordinary rapidity, not only their entire pacification, but such a beneficial change in their material condition, that they have risen from a state of barbarous penury to comparative prosperity and comfort.
George Yule was thus engaged when the Mutiny broke out, and it soon made itself felt in the districts under him. To its suppression within his limits, he addressed himself with characteristic vigour. Thoroughly trusted by every class—by his Government, by those under him, by planters and by Zemindars—he organised a little force, comprising a small detachment of the 5th Regiment, a party of British sailors, mounted volunteers from the districts, etc., and of this he became practically the captain. Elephants were collected from all quarters to spare the legs of his infantry and sailors; while dog-carts were turned into limbers for the small three-pounders of the seamen. And with this little army George Yule scoured the Trans-Gangetic districts, leading it against bodies of the Mutineers, routing them upon more than one occasion, and out-manœuvring them by lxxivhis astonishing marches, till he succeeded in driving them across the Nepaul frontier. No part of Bengal was at any time in such danger, and nowhere was the danger more speedily and completely averted.
After this Yule served for two or three years as Chief Commissioner of Oudh, where in 1862 he married Miss Pemberton, the daughter of a very able father, and the niece of Sir Donald MacLeod, of honoured and beloved memory. Then for four or five years he was Resident at Hyderabad, where he won the enduring friendship of Sir Salar Jung. “Everywhere he showed the same characteristic firm but benignant justice. Everywhere he gained the lasting attachment of all with whom he had intimate dealings—except tigers and scoundrels.”
Many years later, indignant at the then apparently supine attitude of the British Government in the matter of the Abyssinian captives, George Yule wrote a letter (necessarily published without his name, as he was then on the Governor-General’s Council), to the editor of an influential Indian paper, proposing a private expedition should be organised for their delivery from King Theodore, and inviting the editor (Dr. George Smith) to open a list of subscriptions in his paper for this purpose, to which Yule offered to contribute £2000 by way of beginning. Although impracticable in itself, it is probable that, as in other cases, the existence of such a project may have helped to force the Government into action. The particulars of the above incident were printed by Dr. Smith in his Memoir of the Rev. John Wilson, but are given here from memory.
From Hyderabad he was promoted in 1867 to the Governor-General’s Council, but his health broke down under the sedentary life, and he retired and came home in 1869.
After some years of country life in Scotland, where he bought a small property, he settled near his brother in London, where he was a principal instrument in enabling Sir George Birdwood to establish the celebration of Primrose Day (for he also was “one of Mr. Gladstone’s converts”). Sir George Yule never sought ‘London Society’ or public employment, but in 1877 he was offered and refused the post of Financial Adviser to the Khedive under the Dual control. When his feelings were stirred he made useful contributions to the public press, which, after his escape from official trammels, were always signed. The very last of these (St. James Gazette, 24th February 1885) was a spirited protest against the snub administered by the late Lord Derby, as Secretary of State, to the Colonies, when they had generously offered assistance in the Soudan campaign. He lived a quiet, happy, and useful life in London, where he was the friend and unwearied helper of all who needed help. He found his chief interests in books and flowers, and in giving others pleasure. Of rare unselfishness and sweet nature, single in mind and motive, fearing God and knowing no other fear, he was regarded by a large number of people with admiring affection. He met his death by a fall on the frosty pavement at his door, in the very act of doing a kindness. An interesting sketch of Sir George Yule’s Indian career, by one who knew him thoroughly, is to be found in Sir Edward Braddon’s Thirty Years of Shikar. An account of his share in the origin of Primrose Day appeared in the St. James’ Gazette during 1891.
Though Yules of sorts are still to be found in Scotland, the present writer is the only member of the Fentoun Tower family now left in the country, and of the few remaining out of it most are to be found in the Army List.
In the tablet which he erected to her memory in the family burial-place of St. Andrew’s, Gulane, her husband described her thus:—“A woman singular in endowments, in suffering, and in faith; to whom to live was Christ, to die was gain.”
A BIBLIOGRAPHY OF SIR HENRY YULE’S WRITINGS
- 1842 Notes on the Iron of the Kasia Hills. (Jour. Asiatic Soc. Bengal, XI. Part II. July–Dec. 1842, pp. 853–857.)Reprinted in Proceedings of the Museum of Economic Geology, 1852.
- 1844 Notes on the Kasia Hills and People. By Lieut. H. Yule. (Jour. Asiatic Soc. Bengal, XII. Part II. July–Dec. 1844, pp. 612–631.)
- 1846 A Canal Act of the Emperor Akbar, with some notes and remarks on the History of the Western Jumna Canals. By Lieut. Yule. (Jour. Asiatic Society Bengal, XV. 1846, pp. 213–223.)
- 1850 The African Squadron vindicated. By Lieut. H. Yule. Second Edition. London, J. Ridgway, 1850, 8vo, pp. 41.Had several editions. Reprinted in the Colonial Magazine of March, 1850.
- —— L’Escadre Africaine vengée. Par le lieutenant H. Yule. Traduit du Colonial Magazine de Mars, 1850. (Revue Coloniale, Mai, 1850.)
- 1851 Fortification for Officers of the Army and Students of Military History, with Illustrations and Notes. By Lieut. H. Yule, Blackwood, MDCCCLI. 8vo, pp. xxii.–210. (There had been a previous edition privately printed.)
- —— La Fortification mise à la portée des Officiers de l’Armée et des personnes qui se livrent à l’étude de l’histoire militaire (avec Atlas). Par H. Yule. Traduit de l’Anglais par M. Sapia, Chef de Bataillon d’Artillerie de Marine et M. Masselin, Capitaine du Génie. Paris, J. Corréard, 1858, 8vo, pp. iii.–263, and Atlas.
- 1851 The Loss of the Birkenhead (Verses). (Edinburgh Courant, Dec. 1851.)Republished in Henley’s Lyra Heroica, a Book of Verse for Boys. London, D. Nutt, 1890.
- 1852 Tibet. (Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine, 1852.)
- 1856 Narrative of Major Phayre’s Mission to the Court of Ava, with Notices of the Country, Government, and People. Compiled by Capt. H. Yule. Printed for submission to the Government of India. Calcutta, J. Thomas, ... 1856, 4to, pp. xxix. + 1 f. n. ch. p. l. er. + pp. 315 + pp. cxiv. + pp. iv. and pp. 70.The last pp. iv.–70 contain: Notes on the Geological features of the banks of the River Irawadee and on the Country north of the Amarapoora, by Thomas Oldham ... Calcutta, 1856.
- —— A Narrative of the Mission sent by the Governor-General of India to the Court of Ava in 1855, with Notices of the Country, Government, and People. By Capt. H. Yule. With Numerous Illustrations. London, Smith, Elder & Co., 1858, 4to.
- 1857 On the Geography of Burma and its Tributary States, in illustration of a New Map of those Regions. (Journal, R.G.S., XXVII. 1857, pp. 54–108.)
- —— Notes on the Geography of Burma, in illustration of a Map of that lxxviCountry. (Proceedings R.G.S., vol. i. 1857, pp. 269–273.)
- 1857 An Account of the Ancient Buddhist Remains at Pagân on the Iráwadi. By Capt. H. Yule. (Jour. Asiatic Society, Bengal, XXVI. 1857, pp. 1–51.)
- 1861 A few notes on Antiquities near Jubbulpoor. By Lieut.-Col. H. Yule. (Journal Asiatic Society, Bengal, XXX. 1861, pp. 211–215.)
- —— Memorandum on the Countries between Thibet, Yunân, and Burmah. By the Very Rev. Thomine D’Mazure (sic), communicated by Lieut.-Col. A. P. Phayre (with notes and a comment by Lieut.-Col. H. Yule). With a Map of the N. E. Frontier, prepared in the Office of the Surveyor-Gen. of India, Calcutta, Aug. 1861. (Jour. Asiatic Soc. Bengal, XXX. 1861, pp. 367–383.)
- 1862 Notes of a brief Visit to some of the Indian Remains in Java. By Lieut.-Col. H. Yule. (Jour. Asiatic Society, Bengal, XXXI. 1862, pp. 16–31.)
- —— Sketches of Java. A Lecture delivered at the Meeting of the Bethune Society, Calcutta, 13th Feb. 1862.
- —— Fragments of Unprofessional Papers gathered from an Engineer’s portfolio after twenty-three years of service. Calcutta, 1862.Ten copies printed for private circulation.
- 1863 Mirabilia descripta. The Wonders of the East. By Friar Jordanus, of the Order of Preachers and Bishop of Columbum in India the Greater (circa 1330). Translated from the Latin original, as published at Paris in 1839, in the Recueil de Voyages et de Mémoires, of the Society of Geography, with the addition of a Commentary, by Col. H. Yule, London.Printed for the Hakluyt Society, M.DCCC.LXIII, 8vo, p. iv.–xvii.–68.
- —— Report on the Passes between Arakan and Burma [written in 1853]. (Papers on Indian Civil Engineering, vol. i. Roorkee.)
- 1866 Notices of Cathay. (Proceedings, R.G.S., X. 1866, pp. 270–278.)
- —— Cathay and the Way Thither, being a Collection of Mediæval Notices of China. Translated and Edited by Col. H. Yule. With a Preliminary Essay on the Intercourse between China and the Western Nations previous to the Discovery of the Cape route. London, printed for the Hakluyt Society. M.DCCC.LXVI. 2 vols. 8vo.
- 1866 The Insurrection at Palermo. (Times, 29th Sep., 1866.)
- —— Lake People. (The Athenæum, No. 2042, 15th Dec. 1866, p. 804.)Letter dated Palermo, 3rd Dec. 1866.
- 1867 General Index to the third ten Volumes of the Journal of the Royal Geographical Society. Compiled by Col. H. Yule. London, John Murray, M.DCCCLXVII, 8vo, pp. 228.
- —— A Week’s Republic at Palermo. (Quarterly Review, Jan. 1867.)
- —— On the Cultivation of Sumach (Rhus coriaria), in the Vicinity of Colli, near Palermo. By Prof. Inzenga. Translated by Col. H. Yule. Communicated by Dr. Cleghorn. From the Trans. Bot. Society, vol. ix., 1867–68, ppt. 8vo, p. 15.Original first published in the Annali di Agricoltura Siciliana, redatti per l’Istituzione del Principe di Castelnuovo. Palermo, 1852.
- 1868 Marco Polo and his Recent Editors. (Quarterly Review, vol. 125, July and Oct. 1868, pp. 133 and 166.)
- 1870 An Endeavour to Elucidate Rashiduddin’s Geographical Notices of India. (Journal R. Asiatic Society, N.S. iv. 1870, pp. 340–356.)
- —— Some Account of the Senbyú Pagoda at Mengún, near the Burmese Capital, in a Memorandum by Capt. E. H. Sladen, Political Agent at Mandalé; with Remarks on the Subject, by Col. H. Yule. (Ibid. pp. 406–429.)
- —— Notes on Analogies of Manners between the Indo-Chinese and the Races of the Malay Archipelago. (Report Fortieth Meeting British Association, Liverpool, Sept. 1870, p. 178.)
- 1871 The Book of Ser Marco Polo, the Venetian, Concerning the Kingdoms and Marvels of the East. Newly translated and edited with notes. By Col. H. Yule. In two volumes. With Maps and other Illustrations. London, John Murray, 1871, 2 vols. 8vo.
- —— The Book of Ser Marco Polo, the Venetian, concerning the Kingdoms and Marvels of the East. Newly translated and edited, with Notes, Maps, and other Illustrations. By lxxviiCol. H. Yule. Second edition. London, John Murray, 1875, 2 vols. 8vo.
- 1871 Address by Col. H. Yule (Report Forty-First Meeting British Association, Edinburgh, Aug. 1871, pp. 162–174.)
- 1872 A Journey to the Source of the River Oxus. By Captain John Wood, Indian Navy. New edition, edited by his Son. With an Essay on the Geography of the Valley of the Oxus. By Col. H. Yule. With maps. London, John Murray, 1872. In–8, pp. xc.–280.
- —— Papers connected with the Upper Oxus Regions. (Journal, xlii. 1872, pp. 438–481.)
- —— Letter [on Yule’s edition of Wood’s Oxus]. (Ocean Highways, Feb. 1874, p. 475.)Palermo, 9th Jan. 1874.
- 1873 Letter [about the route of M. Polo through Southern Kerman]. (Ocean Highways, March, 1873, p. 385.)Palermo, 11th Jan. 1873.
- —— On Northern Sumatra and especially Achin. (Ocean Highways, Aug. 1873, pp. 177–183.)
- —— Notes on Hwen Thsang’s Account of the Principalities of Tokharistan, in which some previous Geographical Identifications are reconsidered. (Jour. Royal Asiatic Society, N.S. vi. 1873, pp. 92–120 and p. 278.)
- 1874 Francis Garnier (In Memoriam). (Ocean Highways, pp. 487–491.) March, 1874.
- —— Remarks on Mr. Phillips’s Paper [Notices of Southern Mangi]. (Journal, XLIV. 1874, pp. 103–112.)Palermo, 22nd Feb. 1874.
- —— [Sir Frederic Goldsmid’s] “Telegraph and Travel.” (Geographical Magazine, April, 1874, p. 34; Oct. 1874, pp. 300–303.)
- —— Geographical Notes on the Basins of the Oxus and the Zarafshán. By the late Alexis Fedchenko. (Geog. Mag., May, 1874, pp. 46–54.)
- —— [Mr. Ashton Dilke on the Valley of the Ili.] (Geog. Mag., June, 1874, p. 123.)Palermo, 16th May, 1874.
- —— The Atlas Sinensis and other Sinensiana. (Geog. Mag., 1st July, 1847, pp. 147–148.)
- —— Letter [on Belasaghun]. (Geog. Mag., 1st July, 1874, p. 167; Ibid. 1st Sept. 1874, p. 254.)Palermo, 17th June, 1874; 8th Aug. 1874.
- 1874 Bala Sagun and Karakorum. By Eugene Schuyler. With note by Col. Yule. (Geog. Mag., 1st Dec. 1874, p. 389.)
- —— M. Khanikoff’s Identifications of Names in Clavijo. (Ibid. pp. 389–390.)
- 1875 Notes [to the translation by Eugene Schuyler of Palladius’s version of The Journey of the Chinese Traveller, Chang Fe-hui]. (Geog. Mag., 1st Jan. 1875, pp. 7–11.)
- —— Some Unscientific Notes on the History of Plants. (Geog. Mag., 1st Feb. 1875, pp. 49–51.)
- —— Trade Routes to Western China. (Geog. Mag., April, 1875, pp. 97–101.)
- —— Garden of Transmigrated Souls [Friar Odoric]. (Geog. Mag., 1st May, 1875, pp. 137–138.)
- —— A Glance at the Results of the Expedition to Hissar. By Herr P. Lerch. (Geog. Mag., 1st Nov. 1875, pp. 334–339.)
- —— Kathay or Cathay. (Johnson’s American Cyclopædia.)
- —— Achín. (Encycl. Brit. 9th edition, 1875, I. pp. 95–97.)
- —— Afghânistân. (Ibid. pp. 227–241.)
- —— Andaman Islands. (Ibid. II. 1875, pp. 11–13.)
- —— India [Ancient]. (Map No. 31, 1874, in An Atlas of Ancient Geography, edited by William Smith and George Grove. London, John Murray, 1875.)
- 1876 Mongolia, the Tangut Country, and the Solitudes of Northern Tibet, being a Narrative of Three Years’ Travel in Eastern High Asia. By Lieut.-Col. N. Prejevalsky, of the Russian Staff Corps; Mem. of the Imp. Russ. Geog. Soc. Translated by E. Delmar Morgan, F.R.G.S. With Introduction and Notes by Col. H. Yule. With Maps and Illustrations. London, Sampson Low, 1876, 8vo.
- —— Tibet ... Edited by C. R. Markham. Notice of. (Times, 1876, ——?)
- —— Eastern Persia. Letter. (The Athenæum, No. 2559, 11th Nov. 1876.)
- —— Review of H. Howorth’s History of the Mongols, Part I. (The Athenæum, No. 2560, 18th Nov. 1876, pp. 654–656.) Correspondence. (Ibid. No. 2561, 25th Nov. 1876.)
- —— Review of T. E. Gordon’s Roof of the World. (The Academy, 15th July, 1876, pp. 49–50.)
- lxxviii1876 Cambodia. (Encycl. Brit. IV. 1876, pp. 723–726.)
- 1877 Champa. (Geog. Mag., 1st March, 1877, pp. 66–67.)Article written for the Encycl. Brit. 9th edition, but omitted for reasons which the writer did not clearly understand.
- —— Quid, si Mundus evolvatur? (Spectator, 24th March, 1877.)Written in 1875.—Signed Marcus Paulus Venetus.
- —— On Louis de Backer’s L’Extrême-Orient au Moyen-Age. (The Athenæum, No. 2598, 11th Aug. 1877, pp. 174–175.)
- —— On P. Dabry de Thiersant’s Catholicisme en Chine. (The Athenæum, No. 2599, 18th Aug. 1877, pp. 209–210.)
- —— Review of Thomas de Quincey, His Life and Writings. By H. A. Page. (Times, 27th Aug. 1877.)
- —— Companions of Faust. Letter on the Claims of P. Castaldi. (Times, Sept. 1877.)
- 1878 The late Col. T. G. Montgomerie, R.E. (Bengal). (R. E. Journal, April, 1878.) 8vo, pp. 8.
- —— Mr. Henry M. Stanley and the Royal Geographical Society; being the Record of a Protest. By Col. H. Yule and H. M. Hyndman B.A., F.R.G.S. London: Bickers and Son, 1878, 8vo, pp. 48.
- —— Review of Burma, Past and Present; with Personal Reminiscences of the Country. By Lieut.-Gen. Albert Fytche. (The Athenæum, No. 2634, 20th April, 1878, pp. 499–500.)
- —— Kayal. (The Athenæum, No. 2634, 20th April, 1878, p. 515.)Letter dated April, 1878.
- —— Missions in Southern India. (Letter to Pall Mall Gazette, 20th June, 1878.)
- —— Mr. Stanley and his Letters of 1875. (Letter to Pall Mall Gazette, 30th Jan. 1878.)
- —— Review of Richthofen’s China, Bd. I. (The Academy, 13th April, 1878, pp. 315–316.)
- —— [A foreshadowing of the Phonograph.] (The Athenæum, No. 2636, 4th May, 1878.)
- 1879 A Memorial of the Life and Services of Maj.-Gen. W. W. H. Greathed, C.B., Royal Engineers (Bengal), (1826–1878). Compiled by a Friend and Brother Officer. London, printed for private circulation, 1879, 8vo, pp. 57.
- —— Review of Gaur: its Ruins and Inscriptions. By John Henry Ravenshaw. (The Athenæum, No. 2672, 11th Jan. 1879, pp. 42–44.)
- —— Wellington College. (Letter to Pall Mall Gazette, 14th April, 1879.)
- —— Dr. Holub’s Travels. (The Athenæum, No. 2710, 4th Oct. 1879, pp. 436–437.)
- —— Letter to Comm. Berchet, dated 2nd Dec. 1878. (Archivio Veneto XVII. 1879, pp. 360–362.)Regarding some documents discovered by the Ab. Cav. V. Zanetti.
- —— Gaur. (Encyclop. Brit. X. 1879, pp. 112–116.)
- —— Ghazni. (Ibid. pp. 559–562.)
- —— Gilgit. (Ibid. pp. 596–599.)
- —— Singular Coincidences. (The Athenæum, No. 2719, 6th Dec. 1879.)
- 1880 [Brief Obituary Notice of] General W. C. Macleod. (Pall Mall Gazette, 10th April, 1880.)
- —— [Obituary Notice of] Gen. W. C. Macleod. (Proc. R. Geog. Soc., June, 1880.)
- —— An Ode in Brown Pig. Suggested by reading Mr. Lang’s Ballades in Blue China. [Signed Marcus Paulus Venetus.] (St. James’ Gazette, 17th July, 1880.)
- —— Notes on Analogies of Manners between the Indo-Chinese Races and the Races of the Indian Archipelago. By Col. Yule (Journ. Anthrop. Inst. of Great Britain and Ireland, vol. ix., 1880, pp. 290–301.)
- —— Sketches of Asia in the Thirteenth Century and of Marco Polo’s Travels, delivered at Royal Engineer Institute, 18th Nov. 1880.[This Lecture, with slight modification, was also delivered on other occasions both before and after. Doubtful if ever fully reported.]
- —— Dr. Holub’s Collections. (The Athenæum, No. 2724, 10th Jan. 1880.)
- —— Prof. Max Müller’s Paper at the Royal Asiatic Society. (The Athenæum, No. 2731, 28th Feb. 1880, p. 285.)
- —— The Temple of Buddha Gaya. (Review of Dr. Rajendralála Mitra’s Buddha Gaya.) (Sat. Rev., 27th March, 1870.)
- —— Mr. Gladstone and Count Karolyi. (Letter to The Examiner, 22nd May, 1880, signed Tristram Shandy.)
- lxxix—— Stupa of Barhut. [Review of Cunningham’s work.] (Sat. Rev., 5th June, 1880.)
- —— From Africa: Southampton, Fifth October, 1880.[Verses to Sir Bartle Frere.] (Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine, Nov. 1880.)
- —— Review of H. Howorth’s History of the Mongols, Part II. (The Athenæum, No. 2762, 2nd Oct. 1880, pp. 425–427.)
- —— Verboten ist, a Rhineland Rhapsody. (Printed for private circulation only.)
- —— Hindú-Kúsh. (Encyclop. Brit. XI. 1880, pp. 837–839.)
- —— The River of Golden Sand, the Narrative of a Journey through China and Eastern Tibet to Burmah, With Illustrations and ten Maps from Original Surveys. By Capt. W. Gill, Royal Engineers. With an Introductory Essay. By Col. H. Yule, London, John Murray, ... 1880, 2 vols. 8vo, pp. 95–420, 11–453.
- —— The River of Golden Sand: Being the Narrative of a Journey through China and Eastern Tibet to Burmah. By the late Capt. W. Gill, R.E. Condensed by Edward Colborne Baber, Chinese Secretary to H.M.’s Legation at Peking. Edited, with a Memoir and Introductory Essay, by Col. H. Yule. With Portrait, Map, and Woodcuts. London, John Murray, 1883, 8vo., pp. 141–332.
- —— Memoir of Captain W. Gill, R.E., and Introductory Essay as prefixed to the New Edition of the “River of Golden Sand.” By Col. H. Yule. London, John Murray, ... 1884, 8vo. [Paged 19–141.]
- 1881 [Notice on William Yule] in Persian Manuscripts in the British Museum. By Sir F. J. Goldsmid.(The Athenæum, No. 2813, 24th Sept. 1881, pp. 401–403.)
- —— Il Beato Odorico di Pordenone, ed i suoi Viaggi: Cenni dettati dal Col. Enrico Yule, quando s’inaugurava in Pordenone il Busto di Odorico il giorno, 23° Settembre, MDCCCLXXXI, 8vo. pp. 8.
- —— Hwen T’sang. (Encyclop. Brit. XII. 1881, pp. 418–419.)
- —— Ibn Batuta. (Ibid. pp. 607–609.)
- —— Kâfiristân. (Ibid. XIII. 1881, pp. 820–823.)
- —— Major James Rennell, F.R.S., of the Bengal Engineers. [Reprinted from the Royal Engineers’ Journal], 8vo., pp. 16.(Dated 7th Dec. 1881.)
- 1881 Notice of Sir William E. Baker. (St. James’ Gazette, 27th Dec. 1881.)
- —— Parallels [Matthew Arnold and de Barros]. (The Athenæum, No. 2790, 16th April, 1881, pp. 536.)
- 1882 Memoir of Gen. Sir William Erskine Baker, K.C.B., Royal Engineers (Bengal). Compiled by two old friends, brother officers and pupils. London. Printed for private circulation, 1882, 8vo., pp. 67.By H. Y[ule] and R. M. [Gen. R. Maclagan].
- —— Etymological Notes. (The Athenæum, No. 2837, 11th March, 1882; No. 2840, 1st April, 1882, p. 413.)
- —— Lhása. (Encyclop. Brit. XIV. 1882, pp. 496–503.)
- —— Wadono. (The Athenæum, No. 2846, 13th May, 1882, p. 602.)
- —— Dr. John Brown. (The Athenæum, No. 2847, 20th May, 1882, pp. 635–636.)
- —— A Manuscript of Marco Polo. (The Athenæum, No. 2851, 17th June, 1882, pp. 765–766.)[About Baron Nordenskiöld’s Facsimile Edition.]
- —— Review of Ancient India as described by Ktesias the Knidian, etc. By J. W. M’Crindle. (The Athenæum, No. 2860, 19th Aug. 1882, pp. 237–238.)
- —— The Silver Coinage of Thibet. (Review of Terrien de Lacouperie’s Paper.) (The Academy, 19th Aug. 1882, pp 140–141.)
- —— Review of The Indian Balhara and the Arabian Intercourse with India. By Edward Thomas. (The Athenæum, No. 2866, 30th Sept. 1882, pp. 428–429.)
- —— The Expedition of Professor Palmer, Capt. Gill, and Lieut. Charrington. (Letter in The Times, 16th Oct. 1882.)
- —— Obituary Notice of Dr. Arthur Burnell. (Times, 20th Oct. 1882.)
- —— Capt. William Gill, R.E. [Notice of]. (The Times, 31st Oct. 1882.)See supra, first col. of this page.
- —— Notes on the Oldest Records of the Sea Route to China from Western Asia. By Col. Yule. Proc. of the Royal Geographical Society, and Monthly Record of Geography, Nov. No. 1882, 8vo.Proceedings, N.S. IV. 1882, pp. lxxx649–660. Read at the Geographical Section, Brit. Assoc., Southampton Meeting, augmented and revised by the author.
- 1883 Lord Lawrence. [Review of Life of Lord Lawrence. By R. Bosworth Smith.] (Quarterly Review, vol. 155, April, 1883, pp. 289–326.)
- —— Review of Across Chrysé. By A. R. Colquhoun. (The Athenæum, No. 2900, 26th May, 1883, pp. 663–665.)
- —— La Terra del Fuoco e Carlo Darwin. (Extract from Letter published by the Fanfulla, Rome 2nd June, 1883.)
- —— How was the Trireme rowed? (The Academy, 6th Oct. 1883, p. 237.)
- —— Across Chrysé. (The Athenæum, No. 2922, 27th Oct. 1883.)
- —— Political Fellowship in the India Council. (Letter in The Times, 15th Dec. 1883.) [Heading was not Yule’s.]
- —— Maldive Islands. (Encyclop. Brit. XV. 1883, pp. 327–332.)
- —— Mandeville. (Ibid. pp. 473–475.)
- 1884 A Sketch of the Career of Gen. John Reid Becher, C.B., Royal Engineers (Bengal). By an old friend and brother officer. Printed for private circulation, 1884, 8vo, pp. 40.
- —— Ruc Quills. (The Academy, No. 620, 22nd March, 1884, pp. 204–205.) Reprinted in present ed. of Marco Polo, vol. ii. p. 596.
- —— Lord Canning. (Letter in The Times, 2nd April, 1884.)
- —— Sir Bartle Frere [Letter respecting Memorial of]. (St. James’ Gazette, 27th July, 1884.)
- —— Odoric. (Encyclop. Brit. XVIII. 1884, pp. 728–729.)
- —— Ormus. (Ibid. pp. 856–858.)
- 1885 Memorials of Gen. Sir Edward Harris Greathed, K.C.B. Compiled by the late Lieut.-Gen. Alex. Cunningham Robertson, C.B. Printed for private circulation. (With a prefatory notice of the compiler.) London, Harrison & Sons, ... 1885, 8vo, pp. 95.The Prefatory Notice of Gen. A. C. Robertson is by H. Yule, June, 1885, p. iii.–viii.
- —— Anglo-Indianisms. (Letter in the St. James’ Gazette, 30th July, 1885.)
- —— Obituary Notice of Col. Grant Allan, Madras Army. (From the Army and Navy Gazette, 22nd Aug. 1885.)
- —— Shameless Advertisements. (Letter in The Times, 28th Oct. 1885.)
- 1886 Marco Polo. (Encyclop. Brit. XIX. 1885, pp. 404–409.)
- —— Prester John. (Ibid. pp. 714–718.)
- —— Brief Notice of Sir Edward Clive Bayley. Pages ix.–xiv. [Prefixed to The History of India as told by its own Historians: Gujarat. By the late Sir Edward Clive Bayley.] London, Allen, 1886, 8vo.
- —— Sir George Udny Yule. In Memoriam (St. James’ Gazette, 18th Jan. 1886.)
- —— Cacothanasia. [Political Verse, Signed Μηνιν ἈΕΙΔΕ.] (St. James’ Gazette, 1st Feb. 1886.)
- —— William Kay, D.D. [Notice of]. (Letter to The Guardian, 3rd Feb. 1886.)
- —— Col. George Thomson, C.B., R.E. (Royal Engineers’ Journal, 1886.)
- —— Col. George Thomson, C.B. [Note]. (St. James’ Gazette, 16th Feb. 1886.)
- —— Hidden Virtues [A Satire on W. E. Gladstone]. (Letter to the St. James’ Gazette, 21st March, 1886. Signed M. P. V.)
- —— Burma, Past and Present. (Quart. Rev. vol. 162, Jan. and April, 1886, pp. 210–238.)
- —— Errors of Facts, in two well-known Pictures.(The Athenæum, No. 3059, 12th June, 1886, p. 788.)
- —— [Obituary Notice of] Lieut.-Gen. Sir Arthur Phayre, C.B., K.C.S.I., G.C.M.G. (Proc. R.G.S., N.S. 1886, VIII. pp. 103–112.)
- —— “Lines suggested by a Portrait in the Millais Exhibition.”Privately printed and (though never published) widely circulated. These powerful verses on Gladstone are those several times referred to by Sir Mountstuart Grant Duff, in his published Diaries.
- —— Introductory Remarks on The Rock-Cut Caves and Statues of Bamian. By Capt. the Hon. M. G. Talbot. (Journ. R. As. Soc. N.S. XVIII. 1886, pp. 323–329.)
- —— Opening Address. (Ibid. pp. i.–v.)
- —— Opening Address. (Ibid. xix. pp. i.–iii.)
- —— Hobson-Jobsoniana. By H. Yule (Asiatic Quarterly Review, vol. i. 1886, pp. 119–140.)
- —— Hobson-Jobson: Being a Glossary of Anglo-Indian Colloquial Words and Phrases, and of Kindred Terms; etymological, historical, geographical, and discursive. By Col. H. Yule, and the late Arthur Coke lxxxiBurnell, Ph.D., C.I.E., author of “The Elements of South Indian Palaeography,” etc., London, John Murray, 1886. (All rights reserved), 8vo, p. xliii.–870. Preface, etc.A new edition is in preparation under the editorship of Mr. William Crooke (1902).
- 1886 John Bunyan. (Letter in St. James’ Gazette, circa 31st Dec. 1886. Signed M. P. V.)
- —— Rennell. (Encyclop. Brit. XX. 1886, pp. 398–401.)
- —— Rubruquis (Ibid. XXI. 1886, pp. 46–47.)
- 1887 Lieut.-Gen. W. A. Crommelen, C.B., R.E. (Royal Engineers’ Journal, 1887.)
- —— [Obituary Notice] Col. Sir J. U. Bateman Champain. (Times, 2nd Feb. 1887).
- —— “Pulping Public Records.” (Notes and Queries, 19th March, 1887.)
- —— A Filial Remonstrance (Political Verses). Signed M. P. V. (St. James’ Gazette, 8th Aug. 1887.)
- —— Memoir of Major-Gen. J. T. Boileau, R.E., F.R.S. By C. R. Low, I.N., F.R.G.S. With a Preface by Col. H. Yule, C.B., London, Allen, 1887.
- —— The Diary of William Hedges, Esq. (afterwards Sir William Hedges), during his Agency in Bengal; as well as on his voyage out and return overland (1681–1687). Transcribed for the Press, with Introductory Notes, etc., by R. Barlow, Esq., and illustrated by copious extracts from unpublished records, etc., by Col. H. Yule. Pub. for Hakluyt Society. London, 1887–1889, 3 vols. 8vo.
- 1888 Concerning some little known Travellers in the East. (Asiatic Quarterly Review, V. 1888, pp. 312–335.)No. I.—George Strachan.
- —— Concerning some little known Travellers in the East. (Asiatic Quarterly Review, VI. 1888, pp. 382–398.)No. II.—William, Earl of Denbigh; Sir Henry Skipwith; and others.
- —— Notes on the St. James’s of the 6th Jan. [A Budget of Miscellaneous interesting criticism.] (Letter to St. James’ Gazette, 9th Jan. 1888.)
- —— Deflections of the Nile. (Letter in The Times, 15th Oct. 1888.)
- —— The History of the Pitt Diamond, being an excerpt from Documentary Contributions to a Biography of Thomas Pitt, prepared for issue [in Hedges’ Diary] by the Hakluyt Society. London, 1888, 8vo. pp. 23.Fifty Copies printed for private circulation.
- 1889 The Remains of Pagan. By H. Yule. (Trübner’s Record, 3rd ser. vol. i. pt. i. 1889, p. 2.)To introduce notes by Dr. E Forchammer.
- —— A Coincident Idiom. By H. Yule. (Trübner’s Record, 3rd ser. vol. i. pt. iii. pp. 84–85.)
- —— The Indian Congress [a Disclaimer]. (Letter to The Times, 1st Jan. 1889.)
- —— Arrowsmith, the Friend of Thomas Poole. (Letter in The Academy, 9th Feb. 1889, p. 96.)
Biographies of Sir Henry Yule.
- —— Colonel Sir Henry Yule, K.C.S.I., C.B., LL.D., R.E. By General Robert Maclagan, R.E. (Proceed. Roy. Geog. Soc. XII. 1890, pp. 108–113.)
- —— Colonel Sir Henry Yule, K.C.S.I., C.B., LL.D., R.E., etc. (With a Portrait). By E. Delmar Morgan. (Scottish Geographical Magazine, VI. 1890, pp. 93–98.) Contains a very good Bibliography.
- —— Col. Sir H. Yule, R.E., C.B., K.C.S.I., by Maj.-Gen. T. B. Collinson, R.E., Royal Engineers’ Journal, March, 1890. [This is the best of the Notices of Yule which appeared at the time of his death.]
- —— Sir Henry Yule, K.C.S.I, C.B., LL.D., R.E., by E. H. Giglioli. Roma, 1890, ppt. 8vo, pp. 8.Estratto dal Bollettino della Società Geografica Italiana, Marzo, 1890.
- —— Sir Henry Yule. By J. S. C[otton]. (The Academy, 11th Jan. 1890, No. 923, pp. 26–27.)
- —— Sir Henry Yule. (The Athenæum, No. 3245, 4th Jan. 1900, p. 17; No. 3246, 11th Jan. p. 53; No. 3247, 18th Jan. p. 88.)
- —— In Memoriam. Sir Henry Yule. By D. M. (The Academy, 29th March, 1890, p. 222.)See end of Memoir in present work.
- —— Le Colonel Sir Henry Yule. Par M. Henri Cordier. Extrait du Journal Asiatique. Paris, Imprimerie nationale, MDCCCXC, in–8, pp. 26.
- —— The same, Bulletin de la Société de Géographie. Par M. Henri Cordier. 1890, 8vo, pp. 4.Meeting 17th Jan. 1890.
- lxxxii1889 Baron F. von Richthofen. (Verhandlungen der Gesellschaft für Erdkunde zu Berlin, xvii. 2.)
- —— Colonel Sir Henry Yule, R.E., C.B., K.C.S.I. Memoir by General R. Maclagan, Journ. R. Asiatic Society, 1890.
- —— Memoir of Colonel Sir Henry Yule, R.E., C.B., K.C.S.I., LL.D., etc. By Coutts Trotter. (Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1891. p. xliii. to p. lvi.)
- 1889 Sir Henry Yule (1820–1889). By Coutts Trotter. (Dict. of National Biography, lxiii. pp. 405–407.)
- 1903 Memoir of Colonel Sir Henry Yule, R.E., C.B., K.C.S.I., Corr. Inst. France, by his daughter, Amy Frances Yule, L.A. Soc. Ant. Scot., etc. Written for third edition of Yule’s Marco Polo. Reprinted for private circulation only.
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]
SYNOPSIS OF CONTENTS.
| Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements |
1
|
|
| § 1. Obscurities, etc. 2. Ramusio his earliest Biographer; his Account of Polo. 3. He vindicates Polo’s Geography. 4. Compares him with Columbus. 5. Recounts a Tradition of the Traveller’s Return to Venice. 6. Recounts Marco’s Capture by the Genoese. 7. His statements about Marco’s liberation and marriage. 8. His account of the Family Polo and its termination. | ||
| Sketch of the State of the East at the Time of the Journeys of the Polo Family |
8
|
|
| § 9. State of the Levant. 10. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe. 11. China. 12. India and Indo-China. | ||
| The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers till their final Return from the East |
13
|
|
| § 13. Alleged origin of the Polos. 14. Claims to Nobility. 15. The Elder Marco Polo. 16. Nicolo and Maffeo Polo commence their Travels. 17. Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan. 18. Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene. 19. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco. (See App. L. 1.) 20. Marco’s Employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his Journeys. 21. Circumstances of the departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court. 22. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there. | ||
| lxxxivDigression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at S. Giovanni Grisostomo |
26
|
|
| § 23. Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo. 24. Relics of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. 24a. Recent corroboration as to traditional site of the Casa Polo. | ||
| Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages |
31
|
|
| § 25. Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys; a separate Oar to every Man. 26. Change of System in 16th Century. 27. Some details of 13th-Century Galleys. 28. Fighting Arrangements. 29. Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet. 30. Music and miscellaneous particulars. | ||
| The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese |
41
|
|
| § 31. Growing Jealousies and Outbreaks between the Republics. 32. Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294. 33. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic. 34. The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola. 35. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a Prisoner. 36. Marco Polo in Prison dictates his Book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian Prisoners. 37. Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests. | ||
| Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels |
55
|
|
| § 38. Rusticiano, perhaps a Prisoner from Meloria. 39. A Person known from other sources. 40. Character of his Romance Compilations. 41. Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner. 42. Further particulars regarding Rusticiano. | ||
| Notices of Marco Polo’s History after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa |
64
|
|
| § 43. Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his Brother Maffeo. 44. Documentary Notices of Polo at this time. The Sobriquet of Milione. 45. Polo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. 46. His Marriage, and his Daughters. Marco as a Merchant. 47. His Last Will; and Death. 48. Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo. 49. Further History of the Polo Family. 49 bis. Reliques of Marco Polo. | ||
| Marco Polo’s Book; and the Language in which it was first written |
80
|
|
| § 50. General Statement of what the Book contains. 51. Language of the original Work. 52. Old French Text of the Société de Géographie. 53. Conclusive proof that the Old French Text is the source of all the others. 54. Greatly diffused employment of French in that age. | ||
| lxxxvVarious Types of Text of Marco Polo’s Book |
90
|
|
| § 55. Four Principal Types of Text. First, that of the Geographic or Oldest French. 56. Second, the Remodelled French Text; followed by Pauthier. 57. The Bern MS. and two others form a sub-class of this type. 58. Third, Friar Pipino’s Latin. 59. The Latin of Grynæus, a Translation at Fifth Hand. 60. Fourth, Ramusio’s Italian. 61. Injudicious Tamperings in Ramusio. 62. Genuine Statements peculiar to Ramusio. 63. Hypothesis of the Sources of the Ramusian Version. 64. Summary in regard to Text of Polo. 65. Notice of a curious Irish Version. | ||
| Some Estimate of the Character of Polo and His Book |
104
|
|
| § 66. Grounds of Polo’s Pre-eminence among Mediæval Travellers. 67. His true claims to glory. 68. His personal attributes seen but dimly. 69. Absence of scientific notions. 70. Map constructed on Polo’s data. 71. Singular omissions of Polo in regard to China; historical inaccuracies. 72. Was Polo’s Book materially affected by the Scribe Rusticiano? 73. Marco’s reading embraced the Alexandrian Romances. Examples. 74. Injustice long done to Polo. Singular Modern Example. | ||
| Contemporary Recognition of Polo and his Book |
116
|
|
| § 75. How far was there diffusion of his Book in his own day? 76. Contemporary References to Polo. T. de Cepoy; Pipino; Jacopo d’Acqui; Giov. Villani. 77. Pietro d’Abano; Jean le Long of Ypres. 78. Curious borrowings from Polo in the Romance of Bauduin de Sebourc. 78 bis. Chaucer and Marco Polo. | ||
| Nature of Polo’s Influence on Geographical Knowledge |
129
|
|
| § 79. Tardy operation, and causes thereof. 80. General characteristics of Mediæval Cosmography. 81. Roger Bacon as a Geographer. 82. Arab Geography. 83. Marino Sanudo the Elder. 84. The Catalan Map of 1375, the most complete mediæval embodiment of Polo’s Geography. 85. Fra Mauro’s Map. Confusions in Cartography of the 16th Century from the endeavour to combine new and old information. 86. Gradual disappearance of Polo’s nomenclature. 87. Alleged introduction of Block-printed Books into Europe by Marco Polo in connexion with the fiction of the invention of Printing by Castaldi of Feltre. 88. Frequent opportunities for such introduction in the Age following Polo’s. | ||
| Explanations regarding the Basis adopted for the Present Translation |
141
|
|
| § 89. Texts followed by Marsden and by Pauthier. 90. Eclectic Formation of the English Text of this Translation. 91. Mode of rendering Proper Names. |
lxxxvi

|
|
Preliminary Address of Rusticiano of Pisa |
1
|
| —How the Two Brothers Polo set forth from Constantinople to traverse the World |
2
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “The Great Sea.” The Port of Soldaia. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers went on beyond Soldaia |
4
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site and Ruins of Sarai. 2. City of Bolghar. 3. Alau Lord of the Levant (i.e. Hulaku). 4. Ucaca on the Volga. 5. River Tigeri. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers, after crossing a Desert, came to the City of Bocara, and fell in with certain Envoys there |
9
|
|
| Notes.—1. “Bocara a City of Persia.” 2. The Great Kaan’s Envoys. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers took the Envoys’ counsel, and went to the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Two Brothers arrived at the Court of the Great Kaan |
11
|
|
| —How the Great Kaan asked all about the manners of the Christians, and particularly about the Pope of Rome |
12
|
|
| Note.—Apostoille. The name Tartar. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan sent the two Brothers as his Envoys to the Pope |
13
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Great Kaan’s Letter. 2. The Seven Arts. 3. Religious Indifference of the Mongol Princes. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan gave them a Tablet of Gold, Bearing his Orders in their behalf |
15
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Tablet. 2. The Port of Ayas. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers came to the City of Acre; and thence to Venice |
17
|
|
| Notes.—1. Names of the deceased Pope and of the Legate. 2. Negropont. 3. Mark’s age. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers again departed from Venice, on their Way back to the Great Kaan, and took with them Mark, the Son of Messer Nicolo |
19
|
|
| Note.—Oil from the Holy Sepulchre. | ||
| —lxxxviiHow the Two Brothers set out from Acre, and Mark along with them |
20
|
|
| Note.—Pope Gregory X. and his Election. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers presented themselves before the new Pope |
22
|
|
| Notes.—1. William of Tripoli. 2. Powers conceded to Missionary Friars. 3. Bundúḳdár and his Invasion of Armenia; his character. 4. The Templars in Cilician Armenia. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo, accompanied by Mark, travelled to the Court of the Great Kaan |
25
|
|
| Note.—The City of Kemenfu, Summer Residence of Kúblái. | ||
| —How Messer Nicolo and Messer Maffeo Polo and Marco presented themselves before the Great Kaan |
26
|
|
| Notes.—1. Verbal. 2. “Vostre Homme.” | ||
| —How the Lord sent Mark on an Embassy of his |
27
|
|
| Notes.—1. The four Characters learned by Marco, what? 2. Ramusio’s addition. 3. Nature of Marco’s employment. | ||
| —How Mark returned from the Mission whereon he had been sent |
30
|
|
| —How Messer Nicolo, Messer Maffeo, and Messer Marco, asked Leave of the Great Kaan to go their way |
31
|
|
| Notes.—1. Risks to Foreigners on a change of Sovereign. 2. The Lady Bolgana. 3. Passage from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Two Brothers and Messer Marco took Leave of the Great Kaan, and returned to their own Country |
34
|
|
| Notes.—1. Mongol Royal Messengers. 2. Mongol communication with the King of England. 3. Mediæval Ships of China. 4. Passage from China to Sumatra. 5. Mortality among the party. 6. The Lady Cocachin in Persian History. 7. Death of the Kaan. 8. The Princess of Manzi. |

| —Here the Book begins; and first it speaks of the Lesser Hermenia |
41
|
|
| Notes.—1. Little Armenia. 2. Meaning of Chasteaux. 3. Sickliness of Cilician Coast. 4. The phrase “fra terre.” | ||
| —lxxxviiiConcerning the Province of Turcomania |
43
|
|
| Notes.—1. Brutality of the people. 2. Application of name Turcomania. Turcoman Hordes. | ||
| —Description of the Greater Hermenia |
45
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erzingan. Buckrams, what were they? 2. Erzrum. 3. Baiburt. 4. Ararat. 5. Oil wells of Baku. | ||
| —Of Georgiania and the Kings thereof |
50
|
|
| Notes.—1. Georgian Kings. 2. The Georgians. 3. The Iron Gates and Wall of Alexander. 4. Box forests. 5. Goshawks. 6. Fish Miracle. 7. Sea of Ghel or Ghelan. Names ending in -án. 8. Names of the Caspian, and navigation thereon. 9. Fish in the Caspian. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Mausul |
60
|
|
| Notes.—1. Atabeks of Mosul. 2. Nestorian and Jacobite Christians. 3. Mosolins. 4. The Kurds. 5. Mush and Mardin. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Baudas, and how it was taken |
63
|
|
| Notes.—1. Baudas, or Baghdad. 2. Island of Kish. 3. Basra. 4. Baldachins and other silk textures; Animal patterns. 5, 6. Hulákú’s Expedition. 7. The Death of the Khalíf Mosta’sim. 8. Froissart. | ||
| —How the Calif of Baudas took counsel to slay all the Christians in his Land |
68
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. “Ses Regisles et ses Casses.” | ||
| —How the Christians were in great dismay because of what the Calif had said |
70
|
|
| Note.—The word “cralantur.” | ||
| —How the One-eyed Cobler was desired to pray for the Christians |
71
|
|
| —How the Prayer of the One-eyed Cobler caused the Mountain to move |
72
|
|
| Note.—The Mountain Miracle. | ||
| —Of the Noble City of Tauris |
74
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tabriz. 2. Cremesor. 3. Traffic at Tabriz. 4. The Torizi. 5. Character of City and People. | ||
| —Of the Monastery of Saint Barsamo on the Borders of Tauris |
77
|
|
| Note.—The Monastery of Barsauma. | ||
| —Of the Great Country of Persia; with some account of the Three Kings |
78
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kala’ Atishparastán. 2. The Three Kings. | ||
| —How the Three Kings returned to their own Country |
79
|
|
| Notes.—1. The three mystic Gifts. 2. The Worshipped Fire. 3. Sávah and Ávah. The Legend in Mas’udi. Embellishments of the Story of the Magi. | ||
| —lxxxixOf the Eight Kingdoms of Persia, and how they are named |
83
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Eight Kingdoms. 2. Export of Horses, and Prices. 3. Persian Brigands. 4. Persian wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Great City of Yasdi |
88
|
|
| Notes.—1. Yezd. 2. Yezd to Kerman. The Woods spoken of. | ||
| —Concerning the Kingdom of Kerman |
90
|
|
| Notes.—1. City and Province of Kerman. 2. Turquoises. 3. Ondanique or Indian Steel. 4. Manufactures of Kerman. 5. Falcons. | ||
| —Of the City of Camadi and its Ruins; also touching the Carauna Robbers |
97
|
|
| Notes.—1. Products of the warmer plains. 2. Humped oxen and fat-tailed sheep. 3. Scarani. 4. The Karaunahs and Nigudarian Bands. 5. Canosalmi. | ||
| —Of the Descent to the City of Hormos |
107
|
|
| Notes.—1. Site of Old Hormuz and Geography of the route from Kerman to Hormuz. 2. Dates and Fish Diet. 3. Stitched Vessels. “One rudder,” why noticed as peculiar. 4. Great heat at Hormuz. 5. The Simúm. 6. History of Hormuz, and Polo’s Ruomedan Acomat. 7. Second Route between Hormuz and Kerman. | ||
| —Of the Wearisome and Desert Road that has now to be Travelled |
123
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kerman to Kúbenán. 2. Desert of Lút. 3. Subterraneous Canals. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Cobinan and the things that are made there |
125
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kuh-Banán. 2. Production of Tútíá. | ||
| —Of a certain Desert that continues for eight days’ Journey |
127
|
|
| Notes.—1. Deserts of Khorasan. 2. The Arbre Sol or Arbre Sec. | ||
| —Concerning the Old Man of the Mountain |
139
|
|
| Note.—The Assassins, Hashíshîn, or Muláhidah. | ||
| —How the Old Man used to train his Assassins |
142
|
|
| Notes.—1. The story widely spread. Notable murders by the Sectaries. 2. Their different branches. | ||
| —How the Old Man came by His End |
145
|
|
| Note.—History of the apparent Destruction of the Sect by Hulákú; its survival to the present time. Castles of Alamut and Girdkuh. | ||
| —Concerning the City of Sapurgan |
149
|
|
| Note.—Shibrgân, and the route followed. Dried Melons. | ||
| —Of the City of Balc |
151
|
|
| Notes.—1. Balkh. 2. Country meant by Dogana. 3. Lions in the Oxus Valley. | ||
| —xcOf Taican, and the Mountains of Salt. Also of the Province of Casem |
153
|
|
| Notes.—1. Talikan. 2. Mines of Rock-salt. 3. Ethnological characteristics. 4. Kishm. 5. Porcupines. 6. Cave dwellings. 7. Old and New Capitals of Badakhshan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Badashan |
157
|
|
| Notes.—1. Dialects of Badakhshan. Alexandrian lineage of the Princes. 2. Badakhshan and the Balas Ruby. 3. Azure Mines. 4. Horses of Badakhshan. 5. Naked Barley. 6. Wild sheep. 7. Scenery of Badakhshan. 8. Repeated devastation of the Country from War. 9. Amplitude of feminine garments. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pashai. |
164
|
|
| Note.—On the country intended by this name. | ||
| —Of the Province of Keshimur |
166
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kashmir language. 2. Kashmir Conjurers. (See App. L. 2.) 3. Importance of Kashmir in History of Buddhism. 4. Character of the People. 5. Vicissitudes of Buddhism in Kashmir. 6. Buddhist practice as to slaughter of animals. 7. Coral. | ||
| —Of the Great River of Badashan; and Plain of Pamier |
170
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Upper Oxus and Wakhan. The title Nono. (See App. L. 3.) 2. The Plateau of Pamir. (See App. L. 4 and 5.) The Great Wild Sheep. Fire at great altitudes. 3. Bolor. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Cascar |
180
|
|
| Note.—Kashgar. | ||
| —Of the Great City of Samarcan |
183
|
|
| Notes.—1. Christians in Samarkand. 2. Chagatai’s relation to Kúblái mis-stated. 3. The Miracle of the Stone. | ||
| —Of the Province of Yarcan |
187
|
|
| Note.—Yarkand. Goître prevalent there. | ||
| —Of a Province called Cotan |
188
|
|
| Notes.—1. Government. 2. “Adoration of Mahommet.” 3. Khotan. | ||
| —Of the Province of Pein |
191
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Pein (App. L. 6.) 2. The Yu or Jade. 3. Temporary marriages. | ||
| —Of the Province of Charchan |
194
|
|
| Note.—Position of Charchan and Lop. | ||
| —Of the City of Lop, and the Great Desert |
196
|
|
| Notes.—1. Geographical discrepancy. 2. Superstitions as to Deserts: their wide diffusion. The Sound of Drums on certain sandy acclivities. 3. Sha-chau to Lob-nor. | ||
| —xciConcerning the Great Province of Tangut |
203
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tangut. 2. Buddhism encountered here. 3. Kalmak superstition, the “Heaven’s Ram.” 4. Chinese customs described here. 5. Mongol disposal of the Dead. 6. Superstitious practice of avoiding to carry out the dead by the house-door; its wide diffusion. | ||
| —Of the Province of Camul |
209
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kamul. 2. Character of the people. 3. Shameless custom. 4. Parallel. | ||
| —Of the Province of Chingintalas |
212
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Country intended. 2. Ondanique. 3. Asbestos Mountain. 4. The four elements. 5 and 6. The Story of the Salamander. Asbestos fabrics. | ||
| —Of the Province of Sukchur |
217
|
|
| Notes.—1. Explanatory. 2. The City of Suhchau. 3. Rhubarb country. 4. Poisonous pasture. | ||
| —Of the City of Campichu |
219
|
|
| Notes.—1. The City of Kanchau. 2. Recumbent Buddhas. 3. Buddhist Days of Special Worship. 4. Matrimonial Customs. 5. Textual. | ||
| —Of the City of Etzina |
223
|
|
| Notes.—1. Position of Yetsina. 2. Textual. 3. The Wild Ass of Mongolia. | ||
| —Of the City of Caracoron |
226
|
|
| Notes.—1. Karakorum. 2. Tartar. 3. Chorcha. 4. Prester John. | ||
| —Of Chinghis, and how he became the First Kaan of the Tartars |
238
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Relations between Chinghiz and Aung Khan, the Prester John of Polo. | ||
| —How Chinghis mustered his People to march against Prester John |
240
|
|
| —How Prester John marched to meet Chinghis |
241
|
|
| Notes.—1. Plain of Tanduc. 2. Divination by Twigs and Arrows. | ||
| —The Battle between Chinghis Kaan and Prester John. Death of Chinghis |
244
|
|
| Note.—Real circumstances and date of the Death of Chinghiz. | ||
| —Of Those who did Reign after Chinghis Kaan, and of the Customs of the Tartars |
245
|
|
| Notes.—1. Origin of the Cambuscan of Chaucer. 2. Historical Errors. 3. The Place of Sepulture of Chinghiz. 4. Barbarous Funeral Superstition. | ||
| —Concerning the Customs of the Tartars |
251
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Huts. 2. Tartar Waggons. 3. Pharaoh’s Rat. 4. Chastity of the Women. 5. Polygamy and Marriage Customs. | ||
| —xciiConcerning the God of the Tartars |
256
|
|
| Notes.—1. The old Tartar idols. 2. Kumiz. | ||
| —Concerning the Tartar Customs of War |
260
|
|
| Notes.—1. Tartar Arms. 2. The Decimal Division of their Troops. 3. Textual. 4. Blood-drinking. 5. Kurút, or Tartar Curd. 6. The Mongol military rapidity and terrorism. 7. Corruption of their Nomade simplicity. | ||
| —Concerning the Administering of Justice among the Tartars |
266
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cudgel. 2. Punishment of Theft. 3. Marriage of the Dead. 4. Textual. | ||
| —Sundry Particulars on the Plain beyond Caracoron |
269
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Bargu, the Mecrit, the Reindeer, and Chase of Water-fowl. 3. The bird Barguerlac, the Syrrhaptes. 4. Gerfalcons. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Erguiul, and Province of Sinju |
274
|
|
| Notes.—1. Erguiul. 2. Siningfu. 3. The Yak. 4. The Musk Deer. 5. Reeves’s Pheasant. | ||
| —Of the Kingdom of Egrigaia |
281
|
|
| Notes.—1. Egrigaia. 2. Calachan. 3. White Camels, and Camlets: Siclatoun. | ||
| —Concerning the Province of Tenduc, and the Descendants of Prester John |
284
|
|
| Notes.—1. The name and place Tenduc. King George. 2. Standing Marriage Compact. The title Gurgán. 3. Azure. 4. The terms Argon and Guasmul. The Dungens. 5. The Rampart of Gog and Magog. 6. Tartary cloths. 7. Siuen-hwa fu. | ||
| —Concerning the Kaan’s Palace of Chagannor |
296
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace. 2. The word Sesnes. 3. Chagan-nor. 4. The five species of Crane described by Polo. 5. The word Cator. | ||
| —Of the City of Chandu, and the Kaan’s Palace there |
298
|
|
| Notes.—1. Two Roads. 2. Chandu, properly Shangtu. 3. Leopards. 4. The Bamboo Palace. Uses of the Bamboo. 5. Kúblái’s Annual Migration to Shangtu. 6. The White Horses. The Oirad Tribe. 7. The Mare’s Milk Festival. 8. Weather Conjuring. 9. Ascription of Cannibalism to Tibetans, etc. 10. The term Bacsi. 11. Magical Feats ascribed to the Lamas. 12. Lamas. 13. Vast extent of Lama Convents. 14. Married Lamas. 15. Bran. 16. Patarins. 17. The Ascetics called Sensin. 18. Textual. 19. Tao-sze Idols. |
xciii

| —Of Cublay Kaan, the Great Kaan now reigning, and of his Great Puissance |
331
|
|
| Note.—Eulogies of Kúblái. | ||
| —Concerning the Revolt of Nayan, who was Uncle to the Great Kaan Cublay |
332
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology. 2. Kúblái’s Age. 3. His Wars. 4. Nayan and his true relationship to Kúblái. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan marched against Nayan |
335
|
|
| Note.—Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —Of the Battle that the Great Kaan fought with Nayan |
336
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Bretesche. 2. Explanatory. 3. The Nakkára. 4. Parallel Passages. 5. Verbal. 6. The Story of Nayan. (See App. L. 7.) | ||
| —How the Great Kaan caused Nayan to be put to Death |
343
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Shedding of Royal blood avoided. 2. Chorcha, Kaoli, Barskul, Sikintinju. 3. Jews in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan went back to the City of Cambaluc |
348
|
|
| Note.—Passage from Ramusio respecting the Kaan’s views of Religion. Remarks. | ||
| —How the Kaan rewarded the Valour of his Captains |
350
|
|
| Notes.—1. Parallel from Sanang Setzen. 2. The Golden Honorary Tablets or Paizah of the Mongols. 3. Umbrellas. 4. The Gerfalcon Tablets. | ||
| —Concerning the Person of the Great Kaan |
356
|
|
| Notes.—1. Colour of his Eyes. 2. His Wives. 3. The Kungurat Tribe. Competitive Examination in Beauty. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Kaan’s Sons |
359
|
|
| Notes.—1. Kúblái’s intended Heir. 2. His other Sons. | ||
| —Concerning the Palace of the Great Kaan |
362
|
|
| Notes.—1. Palace Wall. 2. The word Tarcasci. 3. Towers. 4. Arsenals of the Palace. 5. The Gates. 6. Various Readings. 7. Barracks. 8. Wide diffusion of the kind of Palace here described. 9. Parallel description. 10. “Divine” Park. 11. Modern account of the Lake, etc. 12. “Roze de l’açur.” 13. The Green Mount. 14. Textual. 15. Bridge. | ||
| —xcivConcerning the City of Cambaluc |
374
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chronology, etc., of Peking. 2. The City Wall. 3. Changes in the Extent of the City. 4. Its ground plan. 5. Aspect. 6. Public Towers. 7. Addition from Ramusio. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan maintains a Guard of Twelve Thousand Horse, which are called Keshican |
379
|
|
| Note.—The term Quescican. | ||
| —The Fashion of the Great Kaan’s Table at his High Feasts |
381
|
|
| Notes.—1. Order of the Tables. 2. The word Vernique. 3. The Buffet of Liquors. 4. The superstition of the Threshold. 5. Chinese Etiquettes. 6. Jugglers at the Banquet. | ||
| —Concerning the Great Feast held by the Grand Kaan every year on his Birthday |
386
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Chinese Year. 2. “Beaten Gold.” 3. Textual. Festal changes of costume. 4. Festivals. | ||
| —Of the Great Festival which the Kaan holds on New Year’s Day |
390
|
|
| Notes.—1. The White Month. 2. Mystic value of the number 9. 3. Elephants at Peking. 4. Adoration of Tablets. K’o-tow. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Thousand Barons who receive Robes of Cloth of Gold from the Emperor on the Great Festivals, thirteen changes a-piece |
394
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The words Camut and Borgal. 3. Tame Lions. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan enjoineth his People to supply him with Game |
396
|
|
| Note.—Parallel Passage. | ||
| —Of the Lions and Leopards and Wolves that the Kaan keeps for the Chase |
397
|
|
| Notes.—1. The Cheeta or Hunting Leopard. 2. Lynxes. 3. The Tiger, termed Lion by Polo. 4. The Búrgút Eagle. | ||
| —Concerning the Two Brothers who have charge of the Kaan’s Hounds |
400
|
|
| Note.—The Masters of the Hounds, and their title. | ||
| —How the Emperor goes on a Hunting Expedition |
402
|
|
| Notes.—1. Direction of the Tour. 2. Hawking Establishments. 3. The word Tosḳáúl. 4. The word Bularguchi. 5. Kúblái’s Litter. 6. Kachar Modun. 7. The Kaan’s Great Tents. 8. The Sable and Ermine. 9. Pétis de la Croix. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan, on returning from his Hunting Expedition, holds a Great Court and Entertainment |
410
|
|
| Note.—This chapter peculiar to the 2nd Type of MSS. | ||
| —xcvConcerning the City of Cambaluc, and its Great Traffic and Population |
412
|
|
| Notes.—1. Suburbs of Peking. 2. The word Fondaco. | ||
| —[Concerning the Oppressions of Achmath the Bailo, and the Plot that was formed against Him] |
415
|
|
| Notes.—1. Chapter peculiar to Ramusio. 2. Kúblái’s Administration. The Rise of Ahmad. 3. The term Bailo. 4. The Conspiracy against Ahmad as related by Gaubil from the Chinese. 5. Marco’s presence and upright conduct commemorated in the Chinese Annals. The Kaan’s prejudice against Mahomedans. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causeth the Bark of Trees, made into something like Paper, to pass for Money over all his Country |
423
|
|
| Note.—Chinese Paper Currency. | ||
| —Concerning the Twelve Barons who are set over all the Affairs of the Great Kaan |
430
|
|
| Note.—The Ministers of the Mongol Dynasty. The term Sing. | ||
| —How the Kaan’s Posts and Runners are sped through many Lands and Provinces |
433
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. The word Yam. 3. Government Hostelries. 4. Digression from Ramusio. 5. Posts Extraordinary. 6. Discipline of the Posts. 7. Antiquity of Posts in China, etc. | ||
| —How the Emperor bestows Help on his People, when they are afflicted with Dearth or Murrain |
439
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s remissions, and justice. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Trees to be Planted by the Highways |
440
|
|
| Note.—Kúblái’s Avenues. | ||
| —Concerning the Rice-Wine drunk by the People of Cathay |
441
|
|
| Note.—Rice-wine. | ||
| —Concerning the Black Stones that are dug in Cathay, and are burnt for Fuel |
442
|
|
| Note.—Distribution and Consumption of Coal in China. | ||
| —How the Great Kaan causes Stores of Corn to be made, to help his People withal in time of Dearth |
443
|
|
| Note.—The Chinese Public Granaries. | ||
| —Of the Charity of the Emperor to the Poor |
444
|
|
| Note.—Buddhist influence, and Chinese Charities. | ||
| —xcvi[Concerning the Astrologers in the City of Cambaluc] |
446
|
|
| Notes.—1. The word Tacuin.—The Chinese Almanacs. The Observatory. 2. The Chinese and Mongol Cycle. | ||
| —[Concerning the Religion of the Cathayans; their views as to the Soul; and their Customs] |
456
|
|
| Notes.—1. Textual. 2. Do. 3. Exceptions to the general charge of Irreligion brought against the Chinese. 4. Politeness. 5. Filial Piety. 6. Pocket Spitoons. |
EXPLANATORY LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS TO VOLUME I.

| Portrait of Sir Henry Yule. From the Painting by Mr. T. B. Wirgman, in the Royal Engineers’ Mess House at Chatham. | |
| Illuminated Title, with Medallion representing the Polos Arriving at Venice after 26 years’ absence, and being refused admittance to the Family Mansion; as related by Ramusio, p. 4 of Introductory Essay. Drawn by Signor Quinto Cenni, No. 7 Via Solferino, Milan; from a Design by the Editor. | |
| Doorway of the House of Marco Polo in the Corte Sabbionera at Venice (see p. 27). Woodcut from a drawing by Signor L. Rosso, Venice. | |
| Corte del Milione, Venice. | |
| Malibran Theatre, Venice. | |
| Entrance to the Corte del Milione, Venice. From photographs taken for the present editor, by Signor Naya. | |
| Figures from St. Sabba’s, sent to Venice. From a photograph of Signor Naya. | |
| Church of San Matteo, at Genoa. | |
| Palazzo di S. Giorgio, at Genoa. | |
| Miracle of S. Lorenzo. From the Painting by V. Carpaccio. | |
| Facsimile of the Will of Marco Polo, preserved in St. Mark’s Library. Lithographed from a photograph specially taken by Bertani at Venice. | |
| Pavement in front of S. Lorenzo. | |
| Mosaic Portrait of Marco Polo, at Genoa. | |
| The Pseudo Marco Polo at Canton. | |
| Porcelain Incense-Burner, from the Louvre. | |
| Temple of 500 Genii, at Canton, after a drawing by Félix Régamey. | |
| Probable view of Marco Polo’s own Geography: a Map of the World, formed as far as possible from the Traveller’s own data. Drawn by the Editor. | |
| Part of the Catalan Map of 1375. | |
| xcviiiMarco Polo’s Itineraries, No. I. Western Asia. This includes also “Sketch showing the chief Monarchies of Asia, in the latter part of the 13th century.” | |
| Map illustrating the geographical position of the City of Sarai. | |
| Plan of part of the remains of the same city. Reduced from a Russian plan published by M. Grigorieff. | |
| Reduced Facsimile of the Buddhist Inscription of the Mongol Era, on the Archway at Kiu-yong kwan in the Pass of Nan-k’au, north-west of Peking, showing the characters in use under the Mongol Dynasty. Photogravure from the Recueil des documents de l’Époque Mongole, by H.H. Prince Roland Bonaparte. See an Article by Mr. Wylie in the J. R. A. S. for 1870, p. 14. | |
| Plan of Ayas, the Laias of Polo. From an Admiralty Chart. | |
| Plan of position of Diláwar, the supposed site of the Dilavar of Polo. Ext. from a Survey by Lt.-Col. D. G. Robinson, R.E. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. II. Routes between Kerman and Hormuz. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries, No. III. Regions on and near the Upper Oxus. | |
| Heading, in the old Chinese seal-character, of an Inscription on a Memorial raised by Kúblái Kaan to a Buddhist Ecclesiastic, in the vicinity of his summer-palace at Shangtu in Mongolia. Reduced from a facsimile obtained on the spot by Dr. S. W. Bushell, 1872, and by him lent to the Editor. | |
| The Cho-khang. The grand Temple of Buddha at Lhasa, from The Journey to Lhasa, by Sarat Chandra Das, by kind permission of the Royal Geographical Society. | |
| “Table d’Or de Commandement;” the Païza of the Mongols, from a specimen found in Siberia. Reduced to one-half the scale of the original, from an engraving in a paper by I. J. Schmidt in the Bulletin de la Classe Historico-Philologique de l’Acad. Imp. des Sciences, St.-Pétersbourg, tom. iv. No. 9. | |
| Second Example of a Mongol Païza with superscription in the Uighúr character, found near the Dnieper River, 1845. From Trans. of the Oriental Section, Imp. Soc. of Archæology of St. Petersburg, vol. v. The Inscription on this runs: “By the strength of Eternal Heaven, and thanks to Its Great Power, the Man who obeys not the order of Abdullah shall be guilty, shall die.” | |
| Plan of Peking as it is, and as it was about A.D. 1290. | |
| Bank-note of the Ming Dynasty, on one-half the scale of the original. Reduced from a genuine note in the possession of the British Museum. Was brought back from Peking after the siege of the Legations in 1900. | |
| Mongol “Compendium Instrument.” | |
| Mongol Armillary Sphere. | |
| Observatory Terrace. | |
| Observatory Instruments of the Jesuits. All these from photographs kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| Marco Polo’s Itineraries. No. IV. Eastern Asia. This includes also Sketch Map of the Ruins of Shangtu, after Dr. Bushell; and Enlarged Sketch of the Passage of the Hwang-ho or Karamoran on the road to Si-ngan fu (see vol. ii. pp. 25–27) from the data of Baron von Richthofen. | |
xcix
| A Mediæval Ship. | |
| Coat of Arms of Sir Henry Yule. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Priuli. | |
| Arms of the Polo family, according to Marco Barbaro. (See p. 7, note.) | |
| Autograph of Hethum or Hayton I. King of (Cilician) Armenia; copied from Codice Diplomatico del Sacro Militare Ordine Gerosolemitano, I. 135. The signature is attached to a French document without date, granting the King’s Daughter “Damoiselle Femie” (Euphemia) in marriage to Sire Julian, son of the Lady of Sayete (Sidon). The words run: Thagávor Haiwetz (“Rex Armenorum”), followed by the King’s cypher or monogram; but the initial letter is absent, probably worn off the original document. | |
| The Piazzetta at Venice in the 14th century. From a portion of the Frontispiece Miniature of the MS. of Marco Polo in the Bodleian. (Borrowed from the National Miscellany, published by J. H. Parker, Oxford, for 1853–55; and see Street’s Brick and Marble, etc., 1855, pp. 150–151.) [See vol. ii. p. 529.] | |
| Three extracts from Maps of Venice, showing the site of the Ca’ Polo at three different periods, (1) From the great woodcut Map or View of Venice, dated 1500, and commonly called Albert Dürer’s. (2) From a Plan by Cav. Ludovico Ughi, 1729. (3) From the Modern Official Plan of the City. | |
| Diagram of arrangement of oars in galleys. | |
| Extract from a fresco by Spinello Aretini, in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a Galley-fight (perhaps imaginary) between the Venetians and the fleet of the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and illustrating the arrangements of mediæval galleys. Drawn from a very dim and imperfect photograph, after personal study of the original, by the Editor. | |
| Extract from a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Ducal Palace at Venice, representing the same Galley-fight. After an engraving in the Theatrum Venetum. | |
| Marco Polo’s Galley going into action at Curzola. Drawn by Signor Q. Cenni, from a design by the Editor. | |
| Map to illustrate the Sea-fight at Curzola, where Marco Polo was taken prisoner. | |
| Seal of the Pisan Prisoners in Genoa, after the battle of Meloria (1284). From Manni, Osservazioni Storiche sopra Sigilli Antichi, tom. xii. Engraved by T. Adeney. | |
| The Convent and Church of S. Lorenzo, the burial-place of Marco Polo, as it existed in the 15th century. From the Map of 1500 (see above). Engraved by the same. | |
| Arms of the Trevisan family, according to Priuli. | |
| Tailed Star near the Antarctic, as Marco Polo drew it for Pietro d’Abano. From the Conciliator of Pietro d’Abano. |
| Remains of the Castle of Soldaia or Sudák. After Dubois de Montpereux, Voyage autour du Caucase, Atlas, 3d s. Pl. 64. | |
| Ruins of Bolghar. After Demidoff, Voyage dans la Russie Méridionale, Pl. 75. | |
| The Great Kaan delivering a Golden Tablet to the two elder Polos. From a miniature in the Livre des Merveilles du Monde (Fr. 2810) in the Library at Paris, fol. 3 verso. | |
| Castle of Ayas. After Langlois, Voyage en Cilicie. | |
| Plan of Acre as it was when lost (A.D. 1291). Reduced and translated from the contemporary plan in the Secreta Fidelium Crucis of Marino Sanudo the Elder, engraved in Bongars, Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. | |
| Portrait of Pope Gregory X. After J. B. de Cavaleriis Pontificum Romanorum Effigies, etc. Romæ, 1580. | |
| Ancient Chinese War Vessel. From the Chinese Encyclopædia called San-Thsai-Thou-Hoei, in the Paris Library. |
| Coin of King Hetum I. and Queen Isabel of Cilician Armenia. From an original in the British Museum. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Castle of Baiburt. After Texier, L’Arménie, Pl. 3. | |
| Mediæval Georgian Fortress. From a drawing by Padre Cristoforo di Castelli of the Theatine Mission, made in 1634, and now in the Communal Library at Palermo. The name of the place has been eaten away, and I have not yet been able to ascertain it. | |
| View of Derbend. After a cut from a drawing by M. Moynet in the Tour du Monde, vol. i. | |
| Coin of Badruddín Lolo of Mosul (A.H. 620). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 164. By Adeney. | |
| Gházán Khan’s Mosque at Tabriz. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Kashmir Scarf with animals, etc. After photograph from the scarf in the Indian Museum. | |
| Humped Oxen from the Assyrian Sculptures at Kouyunjik. From Rawlinson’s Ancient Monarchies. | |
| Portrait of a Hazára. From a Photograph, kindly taken for the purpose, by M.-Gen. C. P. Keyes, C.B., Commanding the Panjáb Frontier Force. | |
| Illustrations of the use of the double rudder in the Middle Ages. 7 figures, viz., No. 1, The Navicella of Giotto in the Porch of St. Peter’s. From Eastlake’s H. of Painting; Nos. 2 and 3, from Pertz, Scriptores, tom. xviii. after a Genoese Chronicle; No. 4, Sketch from fresco of Spinello Aretini at Siena; No. 5, Seal of Port of Winchelsea, from Sussex Archæological Collections, vol. i. 1848; No. 6, Sculpture on Leaning Tower at Pisa, after Jal, Archéologie Navale; No. 7, from the Monument of Peter Martyr, the persecutor of the Lombard Patarini, in the Church of St. Eustorgius at Milan, after Le Tombe ed i Monumenti Illustri d’Italia, Mil. 1822–23. | |
| ciThe Arbre Sec, and Arbres du Soleil et de la Lune. From a miniature in the Prose Romance of Alexander, in the Brit. Museum MS. called the Shrewsbury Book (Reg. xv. e. 6). | |
| The Chinár or Oriental Plane, viz., that called the Tree of Godfrey of Boulogne at Buyukdéré, near Constantinople. Borrowed from Le Monde Végétal of Figuier. | |
| Portrait of H. H. Agha Khán Meheláti, late representative of the Old Man of the Mountain. From a photograph by Messrs. Shepherd and Bourne. | |
| Ancient Silver Patera of debased Greek Art, formerly in the possession of the Princes of Badakhshan, now in the India Museum. | |
| Ancient Buddhist Temple at Pandrethan in Káshmir. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| Horns of the Ovis Poli, or Great Sheep of Pamir. Drawn by the Editor from the specimen belonging to the Royal Asiatic Society. | |
| Figure of the Ovis Poli or Great Sheep of Pamir. From a drawing by Mr. Severtsof in a Russian publication. | |
| Head of a native of Kashgar. After Verchaguine. From the Tour du Monde. | |
| View of Kashgar. From Mr. R. Shaw’s Tartary. | |
| View of Samarkand. From a Sketch by Mr. D. Ivanoff, engraved in a Russian Illustrated Paper (kindly sent by Mr. I. to the editor). | |
| Colossal Figure; Buddha entering Nirvana. Sketched by the Editor at Pagán in Burma. | |
| Great Lama Monastery, viz., that at Jehol. After Staunton’s Narrative of Lord Macartney’s Embassy. | |
| The Kyang, or Wild Ass of Mongolia. After a plate by Wolf in the Journal of the Royal Zoological Society. | |
| The Situation of Karákorum. | |
| Entrance to the Erdeni Tso, Great Temple. From Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Death of Chinghiz Khan. From a Miniature in the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| Dressing up a Tent, from Marcel Monnier’s Tour d’Asie, by kind permission of M. Plon. | |
| Mediæval Tartar Huts and Waggons. Drawn by Sig. Quinto Cenni, on a design compiled by the Editor from the descriptions of mediæval and later travellers. | |
| Tartar Idols and Kumis Churn. Drawn by the Editor after data in Pallas and Zaleski (Vie des Steppes Kirghiz). | |
| The Syrrhaptes Pallasii; Bargherlac of Marco Polo. From a plate by Wolf in the Ibis for April, 1860. | |
| Reeves’s Pheasant. After an engraving in Wood’s Illustrated Natural History. | |
| The Rampart of Gog and Magog. From a photograph of the Great Wall of China. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking and the Pekingese. | |
| A Pavilion at Yuen-Ming-Yuen, to illustrate the probable style of Kúblái Kaan’s Summer Palace. Borrowed from Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Chinese Conjuring Extraordinary. Extracted from an engraving in Edward Melton’s Zeldzaame Reizen, etc. Amsterdam, 1702. | |
| A Monastery of Lamas. Borrowed from the Tour du Monde. | |
| A Tibetan Bacsi. Sketched from the life by the Editor. |
| ciiNakkaras. From a Chinese original in the Lois des Empereurs Mandchous (Thai-Thsing-Hoei-Tien-Thou), in the Paris Library. | |
| Nakkaras. After one of the illustrations in Blochmann’s edition of the Ain-i-Akbari. | |
| Seljukian Coin, with the Lion and the Sun (A.H. 640). After Marsden’s Numismata Orientalia, No. 98. Engraved by Adeney. | |
| Sculptured Gerfalcon from the Gate of Iconium. Copied from Hammer’s Falknerklee. | |
| Portrait of the Great Kaan Kúblái. From a Chinese engraving in the Encyclopædia called San Thsai-Thou-Hoei; in the Paris Library. | |
| Ideal Plan of the Ancient Palaces of the Mongol Emperors at Khanbaligh, according to Dr. Bretschneider. | |
| Palace at Khan-baligh. From the Livre des Merveilles. | |
| The Winter Palace at Peking. Borrowed from Fergusson’s History of Architecture. | |
| View of the “Green Mount.” From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| The Yüan ch’eng. From a photograph kindly lent to the present Editor by Count de Semallé. | |
| South Gate of the “Imperial City” at Peking. From an original sketch belonging to the late Dr. W. Lockhart. | |
| The Búrgút Eagle. After Atkinson’s Oriental and Western Siberia. | |
| The Tents of the Emperor K’ien-lung. From a drawing in the Staunton Collection in the British Museum. | |
| Plain of Cambaluc; the City in the distance; from the hills on the north-west. From a photograph. Borrowed from Dr. Rennie’s Peking. | |
| The Great Temple of Heaven at Peking. From Michie’s Siberian Overland Route. | |
| Marble Archway erected under the Mongol Dynasty at Kiu-Yong Kwan in the Nan-k’au Pass, N.W. of Peking. From a photograph in the possession of the present Editor. |

INTRODUCTORY NOTICES.

I. Obscurities in the History of his Life and Book. Ramusio’s Statements.
1. With all the intrinsic interest of Marco Polo’s Book it may perhaps be doubted if it would have continued to exercise such Obscurities of Polo’s Book, and personal History.fascination on many minds through successive generations were it not for the difficult questions which it suggests. It is a great book of puzzles, whilst our confidence in the man’s veracity is such that we feel certain every puzzle has a solution.
And such difficulties have not attached merely to the identification of places, the interpretation of outlandish terms, or the illustration of obscure customs; for strange entanglements have perplexed also the chief circumstances of the Traveller’s life and authorship. The time of the dictation of his Book and of the execution of his Last Will have been almost the only undisputed epochs in his biography. The year of his birth has been contested, and the date of his death has not been recorded; the critical occasion of his capture by the Genoese, to which we seem to owe the happy fact that he did not go down mute to the tomb of his fathers, has been made the subject of chronological difficulties; there are in the various texts of his story variations hard to account for; the very tongue in which it was written down has furnished a question, solved only in our own age, and in a most unexpected manner.
2
2. The first person who attempted to gather and string the Ramusio, his earliest biographer. His account of Polo.facts of Marco Polo’s personal history was his countryman, the celebrated John Baptist Ramusio. His essay abounds in what we now know to be errors of detail, but, prepared as it was when traditions of the Traveller were still rife in Venice, a genuine thread runs through it which could never have been spun in later days, and its presentation seems to me an essential element in any full discourse upon the subject.
Ramusio’s preface to the Book of Marco Polo, which opens the second volume of his famous Collection of Voyages and Travels, and is addressed to his learned friend Jerome Fracastoro, after referring to some of the most noted geographers of antiquity, proceeds:[1]—
“Of all that I have named, Ptolemy, as the latest, possessed the greatest extent of knowledge. Thus, towards the North, his knowledge carries him beyond the Caspian, and he is aware of its being shut in all round like a lake,—a fact which was unknown in the days of Strabo and Pliny, though the Romans were already lords of the world. But though his knowledge extends so far, a tract of 15 degrees beyond that sea he can describe only as Terra Incognita; and towards the South he is fain to apply the same character to all beyond the Equinoxial. In these unknown regions, as regards the South, the first to make discoveries have been the Portuguese captains of our own age; but as regards the North and North-East the discoverer was the Magnifico Messer Marco Polo, an honoured nobleman of Venice, nearly 300 years since, as may be read more fully in his own Book. And in truth it makes one marvel to consider the immense extent of the journeys made, first by the Father and Uncle of the said Messer Marco, when they proceeded continually towards the East-North-East, all the way to the Court of the Great Can and the Emperor of the Tartars; and afterwards again by the three of them when, on their return homeward, they traversed the Eastern and Indian Seas. Nor is that all, for one marvels also how the aforesaid gentleman was able to give such an orderly description of all that he had seen; seeing that such an accomplishment was possessed by very few in his day, and he had had a large part of his nurture among those uncultivated Tartars, without any regular training in the art of composition. His Book indeed, owing to the endless errors and inaccuracies that had crept into it, had come for many years to be regarded as fabulous; and the opinion prevailed that the names of cities and provinces contained therein were all fictitious and imaginary, without any ground in fact, or were (I might rather say) mere dreams.
3
3. “Howbeit, during the last hundred years, persons acquainted with Persia have begun to recognise the existence of Cathay. Ramusio vindicates Polo’s Geography.The voyages of the Portuguese also towards the North-East, beyond the Golden Chersonese, have brought to knowledge many cities and provinces of India, and many islands likewise, with those very names which our Author applies to them; and again, on reaching the Land of China, they have ascertained from the people of that region (as we are told by Sign. John de Barros, a Portuguese gentleman, in his Geography) that Canton, one of the chief cities of that kingdom, is in 30⅔° of latitude, with the coast running N.E. and S.W.; that after a distance of 275 leagues the said coast turns towards the N.W.; and that there are three provinces along the sea-board, Mangi, Zanton, and Quinzai, the last of which is the principal city and the King’s Residence, standing in 46° of latitude. And proceeding yet further the coast attains to 50°.[2] Seeing then how many particulars are in our day becoming known of that part of the world concerning which Messer Marco has written, I have deemed it reasonable to publish his book, with the aid of several copies written (as I judge) more than 200 years ago, in a perfectly accurate form, and one vastly more faithful than that in which it has been heretofore read. And thus the world shall not lose the fruit that may be gathered from so much diligence and industry expended upon so honourable a branch of knowledge.”
4. Ramusio, then, after a brief apologetic parallel of the marvels related by Polo with those related by the Ancients and by the modern discoverers in the West, such as Columbus and Cortes, proceeds:—
“And often in my own mind, comparing the land explorations of these our Venetian gentlemen with the sea explorations of the aforesaid Signor Don Christopher, I have asked myself which of the two were really the more marvellous. Ramusio compares Polo with Columbus.And if patriotic prejudice delude me not, methinks good reason might be adduced for setting the land journey above the sea voyage. Consider only what a height of courage was needed to undertake and carry through so difficult an enterprise, over a route of such desperate length and hardship, whereon it was sometimes necessary to carry food for the supply of man and beast, not for days only but for months together. Columbus, on the other hand, going by sea, readily carried with him all necessary provision; and after a voyage of some 30 or 40 days was conveyed by the wind whither he desired to go, whilst the Venetians again took a whole year’s time to pass all those great deserts and mighty rivers. Indeed that the difficulty of travelling to Cathay was so much greater than that of reaching the New World, and the route so much longer and more perilous, may be gathered from the fact that, since those gentlemen twice made this 4journey, no one from Europe has dared to repeat it,[3] whereas in the very year following the discovery of the Western Indies many ships immediately retraced the voyage thither, and up to the present day continue to do so, habitually and in countless numbers. Indeed those regions are now so well known, and so thronged by commerce, that the traffic between Italy, Spain, and England is not greater.”
5. Ramusio goes on to explain the light regarding the first part or prologue of Marco Polo’s book that he had derived Recounts a tradition of the travellers’ return to Venice.from a recent piece of luck which had made him partially acquainted with the geography of Abulfeda, and to make a running commentary on the whole of the preliminary narrative until the final return of the travellers to Venice:—
“And when they got thither the same fate befel them as befel Ulysses, who, when he returned, after his twenty years’ wanderings, to his native Ithaca, was recognized by nobody. Thus also those three gentlemen who had been so many years absent from their native city were recognized by none of their kinsfolk, who were under the firm belief that they had all been dead for many a year past, as indeed had been reported. Through the long duration and the hardships of their journeys, and through the many worries and anxieties that they had undergone, they were quite changed in aspect, and had got a certain indescribable smack of the Tartar both in air and accent, having indeed all but forgotten their Venetian tongue. Their clothes too were coarse and shabby, and of a Tartar cut. They proceeded on their arrival to their house in this city in the confine of St. John Chrysostom, where you may see it to this day. The house, which was in those days a very lofty and handsome palazzo, is now known by the name of the Corte del Millioni for a reason that I will tell you presently. Going thither they found it occupied by some of their relatives, and they had the greatest difficulty in making the latter understand who they should be. For these good people, seeing them to be in countenance so unlike what they used to be, and in dress so shabby, flatly refused to believe that they were those very gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo whom they had been looking upon for ever so many years as among the dead.[4] So these three gentlemen,—this is a story I have often heard when I was a youngster from the illustrious Messer Gasparo Malpiero, a gentleman of very great age, and a Senator of eminent virtue and integrity, whose house was on the Canal of Santa Marina, exactly at the corner over the mouth of the Rio di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, and just midway among the buildings of the aforesaid Corte del Millioni, and he said he had heard the story from his own father and grandfather, and from other old men among the neighbours,—the three gentlemen, I say, devised a scheme by which they should at once bring about their recognition 5by their relatives, and secure the honourable notice of the whole city; and this was it:—
“They invited a number of their kindred to an entertainment, which they took care to have prepared with great state and splendour in that house of theirs; and when the hour arrived for sitting down to table they came forth of their chamber all three clothed in crimson satin, fashioned in long robes reaching to the ground such as people in those days wore within doors. And when water for the hands had been served, and the guests were set, they took off those robes and put on others of crimson damask, whilst the first suits were by their orders cut up and divided among the servants. Then after partaking of some of the dishes they went out again and came back in robes of crimson velvet, and when they had again taken their seats, the second suits were divided as before. When dinner was over they did the like with the robes of velvet, after they had put on dresses of the ordinary fashion worn by the rest of the company.[5] These proceedings caused much wonder and amazement among the guests. But when the cloth had been drawn, and all the servants had been ordered to retire from the dining hall, Messer Marco, as the youngest of the three, rose from table, and, going into another chamber, brought forth the three shabby dresses of coarse stuff which they had worn when they first arrived. Straightway they took sharp knives and began to rip up some of the seams and welts, and to take out of them jewels of the greatest value in vast quantities, such as rubies, sapphires, carbuncles, diamonds and emeralds, which had all been stitched up in those dresses in so artful a fashion that nobody could have suspected the fact. For when they took leave of the Great Can they had changed all the wealth that he had bestowed upon them into this mass of rubies, emeralds, and other jewels, being well aware of the impossibility of carrying with them so great an amount in gold over a journey of such extreme length and difficulty. Now this exhibition of such a huge treasure of jewels and precious stones, all tumbled out upon the table, threw the guests into fresh amazement, insomuch that they seemed quite bewildered and dumbfounded. And now they recognized that in spite of all former doubts these were in truth those honoured and worthy gentlemen of the Ca’ Polo that they claimed to be; and so all paid them the greatest honour and reverence. And when the story got wind in Venice, straightway the whole city, gentle and simple, flocked to the house to embrace them, and to make much of them, with every conceivable demonstration of affection and respect. On Messer Maffio, who was the eldest, they conferred the honours of an office that was of great dignity in those days; whilst the young men came daily to visit and converse with the ever polite and gracious Messer Marco, and to ask him questions about Cathay and the Great Can, all which he answered with such kindly courtesy that every man felt himself in a manner his debtor. And as it happened that in the story, which he was constantly called on to repeat, of the magnificence of the Great Can, he would speak of his revenues as 6amounting to ten or fifteen millions of gold; and in like manner, when recounting other instances of great wealth in those parts, would always make use of the term millions, so they gave him the nickname of Messer Marco Millioni: a thing which I have noted also in the Public Books of this Republic where mention is made of him.[6] The Court of his House, too, at S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, has always from that time been popularly known as the Court of the Millioni.
6. “Not many months after the arrival of the travellers at Venice, news came that Lampa Doria, Captain of the Genoese Fleet, had advanced with 70 galleys to the Island of Curzola, upon which orders were issued by the Prince of the Most Illustrious Signory for the arming of 90 galleys with all the expedition possible, Recounts Marco’s capture by the Genoese.and Messer Marco Polo for his valour was put in charge of one of these. So he with the others, under the command of the Most Illustrious Messer Andrea Dandolo, Procurator of St. Mark’s, as Captain General, a very brave and worthy gentleman, set out in search of the Genoese Fleet. They fought on the September feast of Our Lady, and, as is the common hazard of war, our fleet was beaten, and Polo was made prisoner. For, having pressed on in the vanguard of the attack, and fighting with high and worthy courage in defence of his country and his kindred, he did not receive due support, and being wounded, he was taken, along with Dandolo, and immediately put in irons and sent to Genoa.
“When his rare qualities and marvellous travels became known there, the whole city gathered to see him and to speak with him, and he was no longer entreated as a prisoner but as a dear friend and honoured gentleman. Indeed they showed him such honour and affection that at all hours of the day he was visited by the noblest gentlemen of the city, and was continually receiving presents of every useful kind. Messer Marco finding himself in this position, and witnessing the general eagerness to hear all about Cathay and the Great Can, which indeed compelled him daily to repeat his story till he was weary, was advised to put the matter in writing. So having found means to get a letter written to his father here at Venice, in which he desired the latter to send the notes and memoranda which he had brought home with him, after the receipt of these, and assisted by a Genoese gentleman, who was a great friend of his, and who took great delight in learning about the various regions of the world, and used on that account to spend many hours daily in the prison with him, he wrote this present book (to please him) in the Latin tongue.
“To this day the Genoese for the most part write what they have to write in that language, for there is no possibility of expressing their natural dialect with the pen.[7] Thus then it came to pass that the Book was put forth at first by Messer Marco in Latin; but as many copies were taken, and as it was rendered into our vulgar tongue, all Italy became filled with it, so much was this story desired and run after.
7
7. “The captivity of Messer Marco greatly disturbed the minds of Messer Maffio and his father Messer Nicolo. They had decided, whilst still on their travels, Ramusio’s account of Marco’s liberation and marriage.that Marco should marry as soon as they should get to Venice; but now they found themselves in this unlucky pass, with so much wealth and nobody to inherit it. Fearing that Marco’s imprisonment might endure for many years, or, worse still, that he might not live to quit it (for many assured them that numbers of Venetian prisoners had been kept in Genoa a score of years before obtaining liberty); seeing too no prospect of being able to ransom him,—a thing which they had attempted often and by various channels,—they took counsel together, and came to the conclusion that Messer Nicolo, who, old as he was, was still hale and vigorous, should take to himself a new wife. This he did; and at the end of four years he found himself the father of three sons, Stefano, Maffio, and Giovanni. Not many years after, Messer Marco aforesaid, through the great favour that he had acquired in the eyes of the first gentlemen of Genoa, and indeed of the whole city, was discharged from prison and set free. Returning home he found that his father had in the meantime had those three other sons. Instead of taking this amiss, wise and discreet man that he was, he agreed also to take a wife of his own. He did so accordingly, but he never had any son, only two girls, one called Moreta and the other Fantina.
“When at a later date his father died, like a good and dutiful son he caused to be erected for him a tomb of very honourable kind for those days, being a great sarcophagus cut from the solid stone, which to this day may be seen under the portico before the Church of S. Lorenzo in this city, on the right hand as you enter, with an inscription denoting it to be the tomb of Messer Nicolo Polo of the contrada of S. Gio. Chrisostomo. The arms of his family consist of a Bend with three birds on it, and the colours, according to certain books of old histories in which you see all the coats of the gentlemen of this city emblazoned, are the field azure, the bend argent, and the three birds sable. These last are birds of that kind vulgarly termed Pole,[8] or, as the Latins call them, Gracculi.
8. “As regards the after duration of this noble and worthy family, I 8find that Messer Andrea Polo of San Felice had three sons, the first of whom was Messer Marco, the second Maffio, the third Nicolo. Ramusio’s account of the Family Polo and its termination.The two last were those who went to Constantinople first, and afterwards to Cathay, as has been seen. Messer Marco the elder being dead, the wife of Messer Nicolo who had been left at home with child, gave birth to a son, to whom she gave the name of Marco in memory of the deceased, and this is the Author of our Book. Of the brothers who were born from his father’s second marriage, viz. Stephen, John, and Matthew, I do not find that any of them had children, except Matthew. He had five sons and one daughter called Maria; and she, after the death of her brothers without offspring, inherited in 1417 all the property of her father and her brothers. She was honourably married to Messer Azzo Trevisano of the parish of Santo Stazio in this city, and from her sprung the fortunate and honoured stock of the Illustrious Messer Domenico Trevisano, Procurator of St. Mark’s, and valorous Captain General of the Sea Forces of the Republic, whose virtue and singular good qualities are represented with augmentation in the person of the Most Illustrious Prince Ser Marc’Antonio Trevisano, his son.[9]
“Such has been the history of this noble family of the Ca’ Polo, which lasted as we see till the year of our Redemption 1417, in which year died childless Marco Polo, the last of the five sons of Maffeo, and so it came to an end. Such be the chances and changes of human affairs!”


They are under this name made the object of a similitude by Dante (surely a most unhappy one) in reference to the resplendent spirits flitting on the celestial stairs in the sphere of Saturn:—
There is some difference among authorities as to the details of the Polo blazon. According to a MS. concerning the genealogies of Venetian families written by Marco Barbaro in 1566, and of which there is a copy in the Museo Civico, the field is gules, the bend or. And this I have followed in the cut. But a note by S. Stefani of Venice, with which I have been favoured since the cut was made, informs me that a fine 15th-century MS. in his possession gives the field as argent, with no bend, and the three birds sable with beaks gules, disposed thus ∵.
II. Sketch of the State of the East at the time of the Journeys of the Polo Family.
9. The story of the travels of the Polo family opens in 1260.
Christendom had recovered from the alarm into which it 9had been thrown some 18 years before when the Tartar cataclysm had threatened to engulph it.State of the Levant. The Tartars themselves were already becoming an object of curiosity rather than of fear, and soon became an object of hope, as a possible help against the old Mahomedan foe. The frail Latin throne in Constantinople was still standing, but tottering to its fall. The successors of the Crusaders still held the Coast of Syria from Antioch to Jaffa, though a deadlier brood of enemies than they had yet encountered was now coming to maturity in the Dynasty of the Mamelukes, which had one foot firmly planted in Cairo, the other in Damascus. The jealousies of the commercial republics of Italy were daily waxing greater. The position of Genoese trade on the coasts of the Aegean was greatly depressed, through the predominance which Venice had acquired there by her part in the expulsion of the Greek Emperors, and which won for the Doge the lofty style of Lord of Three-Eighths of the Empire of Romania. But Genoa was biding her time for an early revenge, and year by year her naval strength and skill were increasing. Both these republics held possessions and establishments in the ports of Syria, which were often the scene of sanguinary conflicts between their citizens. Alexandria was still largely frequented in the intervals of war as the great emporium of Indian wares, but the facilities afforded by the Mongol conquerors who now held the whole tract from the Persian Gulf to the shores of the Caspian and of the Black Sea, or nearly so, were beginning to give a great advantage to the caravan routes which debouched at the ports of Cilician Armenia in the Mediterranean and at Trebizond on the Euxine. Tana (or Azov) had not as yet become the outlet of a similar traffic; the Venetians had apparently frequented to some extent the coast of the Crimea for local trade, but their rivals appear to have been in great measure excluded from this commerce, and the Genoese establishments which so long flourished on that coast, are first heard of some years after a Greek dynasty was again in possession of Constantinople.[1]
10. In Asia and Eastern Europe scarcely a dog might bark without Mongol leave, from the borders of Poland and the Gulf 10of Scanderoon to the Amur and the Yellow Sea. The various Mongol Sovereignties in Asia and Eastern Europe.The vast empire which Chinghiz had conquered still owned a nominally supreme head in the Great Kaan,[2] but practically it was splitting up into several great monarchies under the descendants of the four sons of Chinghiz, Juji, Chaghatai, Okkodai, and Tuli; and wars on a vast scale were already brewing between them. Hulaku, third son of Tuli, and brother of two Great Kaans, Mangku and Kúblái, had become practically independent as ruler of Persia, Babylonia, Mesopotamia, and Armenia, though he and his sons, and his sons’ sons, continued to stamp the name of the Great Kaan upon their coins, and to use the Chinese seals of state which he bestowed upon them. The Seljukian Sultans of Iconium, whose dominion bore the proud title of Rúm (Rome), were now but the struggling bondsmen of the Ilkhans. The Armenian 11Hayton in his Cilician Kingdom had pledged a more frank allegiance to the Tartar, the enemy of his Moslem enemies.
Barka, son of Juji, the first ruling prince of the House of Chinghiz to turn Mahomedan, reigned on the steppes of the Volga, where a standing camp, which eventually became a great city under the name of Sarai, had been established by his brother and predecessor Batu.
The House of Chaghatai had settled upon the pastures of the Ili and the valley of the Jaxartes, and ruled the wealthy cities of Sogdiana.
Kaidu, the grandson of Okkodai who had been the successor of Chinghiz in the Kaanship, refused to acknowledge the transfer of the supreme authority to the House of Tuli, and was through the long life of Kúblái a thorn in his side, perpetually keeping his north-western frontier in alarm. His immediate authority was exercised over some part of what we should now call Eastern Turkestan and Southern Central Siberia; whilst his hordes of horsemen, force of character, and close neighbourhood brought the Khans of Chaghatai under his influence, and they generally acted in concert with him.
The chief throne of the Mongol Empire had just been ascended by Kúblái, the most able of its occupants after the Founder. Before the death of his brother and predecessor Mangku, who died in 1259 before an obscure fortress of Western China, it had been intended to remove the seat of government from Kara Korum on the northern verge of the Mongolian Desert to the more populous regions that had been conquered in the further East, and this step, which in the end converted the Mongol Kaan into a Chinese Emperor,[3] was carried out by Kúblái.
11. For about three centuries the Northern provinces of China had been detached from native rule, and subject to foreign dynasties; first to the Khitan, China.a people from the basin of the Sungari River, and supposed (but doubtfully) to have been akin to the Tunguses, whose rule subsisted for 200 years, and originated the name of Khitai, Khata, or Cathay, by which for nearly 1000 years China has been known to the nations of Inner Asia, and to those 12whose acquaintance with it was got by that channel.[4] The Khitan, whose dynasty is known in Chinese history as the Liao or “Iron,” had been displaced in 1123 by the Chúrchés or Niu-chen, another race of Eastern Tartary, of the same blood as the modern Manchus, whose Emperors in their brief period of prosperity were known by the Chinese name of Tai-Kin, by the Mongol name of the Altun Kaans, both signifying “Golden.” Already in the lifetime of Chinghiz himself the northern Provinces of China Proper, including their capital, known as Chung-tu or Yen-King, now Peking, had been wrenched from them, and the conquest of the dynasty was completed by Chinghiz’s successor Okkodai in 1234.
Southern China still remained in the hands of the native dynasty of the Sung, who had their capital at the great city now well known as Hang-chau fu. Their dominion was still substantially untouched, but its subjugation was a task to which Kúblái before many years turned his attention, and which became the most prominent event of his reign.
12. In India the most powerful sovereign was the Sultan of Delhi, Nassir-uddin Mahmud of the Turki House of Iltitmish;[5] but, India, and Indo-China.though both Sind and Bengal acknowledged his supremacy, no part of Peninsular India had yet been invaded, and throughout the long period of our Traveller’s residence in the East the Kings of Delhi had their hands too full, owing to the incessant incursions of the Mongols across the Indus, to venture on extensive campaigning in the south. Hence the Dravidian Kingdoms of Southern India were as yet untouched by foreign conquest, and the accumulated gold of ages lay in their temples and treasuries, an easy prey for the coming invader.
In the Indo-Chinese Peninsula and the Eastern Islands a variety of kingdoms and dynasties were expanding and contracting, of which we have at best but dim and shifting glimpses. That they were advanced in wealth and art, far 13beyond what the present state of those regions would suggest, is attested by vast and magnificent remains of Architecture, nearly all dating, so far as dates can be ascertained, from the 12th to the 14th centuries (that epoch during which an architectural afflatus seems to have descended on the human race), and which are found at intervals over both the Indo-Chinese continent and the Islands, as at Pagán in Burma, at Ayuthia in Siam, at Angkor in Kamboja, at Borobodor and Brambánan in Java. All these remains are deeply marked by Hindu influence, and, at the same time, by strong peculiarities, both generic and individual.

[Mr. Rockhill writes (Rubruck, p. 108, note): “The title Khan, though of very great antiquity, was only used by the Turks after A.D. 560, at which time the use of the word Khatun came in use for the wives of the Khan, who himself was termed Ilkhan. The older title of Shan-yü did not, however, completely disappear among them, for Albiruni says that in his time the chief of the Ghuz Turks, or Turkomans, still bore the title of Jenuyeh, which Sir Henry Rawlinson (Proc. R. G. S., v. 15) takes to be the same word as that transcribed Shan-yü by the Chinese (see Ch’ien Han shu, Bk. 94, and Chou shu, Bk. 50, 2). Although the word Khakhan occurs in Menander’s account of the embassy of Zemarchus, the earliest mention I have found of it in a Western writer is in the Chronicon of Albericus Trium Fontium, where (571), under the year 1239, he uses it in the form Cacanus”—Cf. Terrien de Lacouperie, Khan, Khakan, and other Tartar Titles. Lond., Dec. 1888.—H. C.]
III. The Polo Family. Personal History of the Travellers down to their final Return from the East.
13. In days when History and Genealogy were allowed to draw largely on the imagination for the origines of states and families, Alleged origin of the Polos.it was set down by one Venetian Antiquary that among the companions of King Venetus, or of Prince Antenor of Troy, when they settled on the northern shores of the Adriatic, there was one Lucius Polus, who became the progenitor of our Traveller’s Family;[1] whilst another deduces it from Paolo the first Doge[2] (Paulus Lucas Anafestus of Heraclea, A.D. 696).
14
More trustworthy traditions, recorded among the Family Histories of Venice, but still no more it is believed than traditions, represent the Family of Polo as having come from Sebenico in Dalmatia, in the 11th century.[3] Before the end of the century they had taken seats in the Great Council of the Republic; for the name of Domenico Polo is said to be subscribed to a grant of 1094, that of Pietro Polo to an act of the time of the Doge Domenico Michiele in 1122, and that of a Domenico Polo to an acquittance granted by the Doge Domenico Morosini and his Council in 1153.[4]
The ascertained genealogy of the Traveller, however, begins only with his grandfather, who lived in the early part of the 13th century.
Two branches of the Polo Family were then recognized, distinguished by the confini or Parishes in which they lived, as Polo of S. Geremia, and Polo of S. Felice. Andrea Polo of S. Felice was the father of three sons, Marco, Nicolo, and Maffeo. And Nicolo was the Father of our Marco.
14. Till quite recently it had never been precisely ascertained whether the immediate family of our Traveller belonged to the Nobles of Venice properly so called, Claims to be styled noble.who had seats in the Great Council and were enrolled in the Libro d’Oro. Ramusio indeed styles our Marco Nobile and Magnifico, and Rusticiano, the actual scribe of the Traveller’s recollections, calls him “sajes et noble citaiens de Venece,” but Ramusio’s accuracy and Rusticiano’s precision were scarcely to be depended on. Very recently, however, since the subject has been discussed with accomplished students of the Venice Archives, proofs have been found establishing Marco’s personal claim to nobility, inasmuch as both in judicial decisions and in official resolutions of the Great Council, he is designated Nobilis Vir, a formula which would never have been used in such documents (I am assured) had he not been technically noble.[5]
15
15. Of the three sons of Andrea Polo of S. Felice, Marco seems to have been the eldest, and Maffeo the youngest.[6] Marco the Elder.They were all engaged in commerce, and apparently in a partnership, which to some extent held good even when the two younger had been many years absent in the Far East.[7] Marco seems to have been established for a time at Constantinople,[8] and also to have had a house (no doubt of business) at Soldaia, in the Crimea, where his son and daughter, Nicolo and Maroca by name, were living in 1280. This year is the date of the Elder Marco’s Will, executed at Venice, and when he was “weighed down by bodily ailment.” Whether he survived for any length of time we do not know.
16. Nicolo Polo, the second of the Brothers, had two legitimate sons, Marco, the Author of our Book, born in 1254,[9] and Maffeo, Nicolo and Maffeo commence their travels.of whose place in the family we shall have a few words to say presently. The story opens, as we have said, in 1260, when we find the two brothers, Nicolo and Maffeo the Elder, at Constantinople. How long they had been absent from Venice we are not distinctly told. Nicolo had left his wife there behind him; Maffeo apparently was a bachelor. In the year named they started on a trading venture to the Crimea, whence a succession of openings and chances, recounted in the Introductory chapters of Marco’s work, carried them far north along the Volga, and thence first to Bokhara, and then to the Court of the Great Kaan Kúblái in the Far East, on or within the borders of Cathay. That a great and civilized country so called existed in the extremity of Asia had already been reported in Europe by the Friars Plano Carpini (1246) and William Rubruquis (1253), who had not indeed reached its 16frontiers, but had met with its people at the Court of the Great Kaan in Mongolia; whilst the latter of the two with characteristic acumen had seen that they were identical with the Seres of classic fame.
17. Kúblái had never before fallen in with European gentlemen. He was delighted with these Venetians, Their intercourse with Kúblái Kaan.listened with strong interest to all that they had to tell him of the Latin world, and determined to send them back as his ambassadors to the Pope, accompanied by an officer of his own Court. His letters to the Pope, as the Polos represent them, were mainly to desire the despatch of a large body of educated missionaries to convert his people to Christianity. It is not likely that religious motives influenced Kúblái in this, but he probably desired religious aid in softening and civilizing his rude kinsmen of the Steppes, and judged, from what he saw in the Venetians and heard from them, that Europe could afford such aid of a higher quality than the degenerate Oriental Christians with whom he was familiar, or the Tibetan Lamas on whom his patronage eventually devolved when Rome so deplorably failed to meet his advances.
18. The Brothers arrived at Acre in April,[10] 1269, and found that no Pope existed, for Clement IV. was dead the year before, Their return home, and Marco’s appearance on the scene.and no new election had taken place. So they went home to Venice to see how things stood there after their absence of so many years.
The wife of Nicolo was no longer among the living, but he found his son Marco a fine lad of fifteen.
The best and most authentic MSS. tell us no more than this. But one class of copies, consisting of the Latin version made by our Traveller’s contemporary, Francesco Pipino, and of the numerous editions based indirectly upon it, represents that Nicolo had left Venice when Marco was as yet unborn, and consequently had never seen him till his return from the East in 1269.[11]
17
We have mentioned that Nicolo Polo had another legitimate son, by name Maffeo, and him we infer to have been younger than Marco, because he is named last (Marcus et Matheus) in the Testament of their uncle Marco the Elder. We do not know if they were by the same mother. They could not have been so if we are right in supposing Maffeo to have been the younger, and if Pipino’s version of the history be genuine. If however we reject the latter, as I incline to do, no ground remains for supposing that Nicolo went to the East much before we find him there viz., in 1260, and Maffeo may have been born of the same mother during the interval between 1254 and 1260. If on the other hand Pipino’s version be held to, we must suppose that Maffeo (who is named by his uncle in 1280, during his father’s second absence in the East) was born of a marriage contracted during Nicolo’s residence at home after his first journey, a residence which lasted from 1269 to 1271.[12]
18

19. The Papal interregnum was the longest known, at least since the dark ages. Those two years passed, and yet the Cardinals at Viterbo had come to no agreement. Second Journey of the Polo Brothers, accompanied by Marco.The brothers were unwilling to let the Great Kaan think them faithless, and perhaps they hankered after the virgin field of speculation that they had discovered; so they started again for the East, taking young Mark with them. At Acre they took counsel with an eminent churchman, Tedaldo (or Tebaldo) Visconti, Archdeacon 19of Liège, whom the Book represents to have been Legate in Syria, and who in any case was a personage of much gravity and influence. From him they got letters to authenticate the causes of the miscarriage of their mission, and started for the further East. But they were still at the port of Ayas on the Gulf of Scanderoon, which was then becoming one of the chief points of arrival and departure for the inland trade of Asia, when they were overtaken by the news that a Pope was at last elected, and that the choice had fallen upon their friend Archdeacon Tedaldo. They immediately returned to Acre, and at last were able to execute the Kaan’s commission, and to obtain a reply. But instead of the hundred able teachers of science and religion whom Kúblái is said to have asked for, the new Pope, Gregory X., could supply but two Dominicans; and these lost heart and drew back when they had barely taken the first step of the journey.
Judging from certain indications we conceive it probable that the three Venetians, whose second start from Acre took place about November 1271, proceeded by Ayas and Sivas, and then by Mardin, Mosul, and Baghdad, to Hormuz at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, with the view of going on by sea, but that some obstacle arose which compelled them to abandon this project and turn north again from Hormuz.[13] They then 20traversed successively Kerman and Khorasan, Balkh and Badakhshan, whence they ascended the Panja or upper Oxus to the Plateau of Pamir, a route not known to have been since followed by any European traveller except Benedict Goës, till the spirited expedition of Lieutenant John Wood of the Indian Navy in 1838.[14] Crossing the Pamir highlands the travellers descended upon Kashgar, whence they proceeded by Yarkand and Khotan, and the vicinity of Lake Lob, and eventually across the Great Gobi Desert to Tangut, the name then applied by Mongols and Persians to territory at the extreme North-west of China, both within and without the Wall. Skirting the 21northern frontier of China they at last reached the presence of the Kaan, who was at his usual summer retreat at Kai-ping fu, near the base of the Khingan Mountains, and nearly 100 miles north of the Great Wall at Kalgan. If there be no mistake in the time (three years and a half) ascribed to this journey in all the existing texts, the travellers did not reach the Court till about May of 1275.[15]
20. Kúblái received the Venetians with great cordiality, and took kindly to young Mark, who must have been by this time one-and-twenty. Marco’s employment by Kúblái Kaan; and his journeys.The Joenne Bacheler, as the story calls him, applied himself to the acquisition of the languages and written characters in chief use among the multifarious nationalities included in the Kaan’s Court and administration; and Kúblái after a time, seeing his discretion and ability, began to employ him in the public service. M. Pauthier has found a record in the Chinese Annals of the Mongol Dynasty, which states that in the year 1277, a certain Polo was nominated a second-class commissioner or agent attached to the Privy Council, a passage which we are happy to believe to refer to our young traveller.[16]
His first mission apparently was that which carried him through the provinces of Shan-si, Shen-si, and Sze-ch’wan, and the wild country on the East of Tibet, to the remote province of Yun-nan, called by the Mongols Karájàng, and which had been partially conquered by an army under Kúblái himself in 1253, before his accession to the throne.[17] Mark, during his stay at court, had observed the Kaan’s delight in hearing of strange countries, their marvels, manners, and oddities, and had heard 22his Majesty’s frank expressions of disgust at the stupidity of his commissioners when they could speak of nothing but the official business on which they had been sent. Profiting by these observations, he took care to store his memory or his note-books with all curious facts that were likely to interest Kúblái, and related them with vivacity on his return to Court. This first journey, which led him through a region which is still very nearly a terra incognita, and in which there existed and still exists, among the deep valleys of the Great Rivers flowing down from Eastern Tibet, and in the rugged mountain ranges bordering Yun-nan and Kwei-chau, a vast Ethnological Garden, as it were, of tribes of various race and in every stage of uncivilisation, afforded him an acquaintance with many strange products and eccentric traits of manners, wherewith to delight the Emperor.
Mark rose rapidly in favour, and often served Kúblái again on distant missions, as well as in domestic administration, but we gather few details as to his employments. At one time we know that he held for three years the government of the great city of Yang-chau, though we need not try to magnify this office, as some commentators have done, into the viceroyalty of one of the great provinces of the Empire; on another occasion we find him with his uncle Maffeo, passing a year at Kan-chau in Tangut; again, it would appear, visiting Kara Korum, the old capital of the Kaans in Mongolia; on another occasion in Champa or Southern Cochin China; and again, or perhaps as a part of the last expedition, on a mission to the Indian Seas, when he appears to have visited several of the southern states of India. We are not informed whether his father and uncle shared in such employments;[18] and the story of their services rendered to the Kaan in promoting the capture of the city of Siang-yang, by the construction of powerful engines of attack, is too much perplexed by difficulties of chronology to be cited with confidence. Anyhow they were gathering wealth, and after years of exile they began to dread what might follow old Kúblái’s death, and longed to carry their gear and their own grey heads safe home to the Lagoons. The aged Emperor 23growled refusal to all their hints, and but for a happy chance we should have lost our mediæval Herodotus.
21. Arghún Khan of Persia, Kúblái’s great-nephew, had in 1286 lost his favourite wife the Khatun Bulughán; and, mourning her sorely, Circumstances of the Departure of the Polos from the Kaan’s Court.took steps to fulfil her dying injunction that her place should be filled only by a lady of her own kin, the Mongol Tribe of Bayaut. Ambassadors were despatched to the Court of Kaan-baligh to seek such a bride. The message was courteously received, and the choice fell on the lady Kokáchin, a maiden of 17, “moult bele dame et avenant.” The overland road from Peking to Tabriz was not only of portentous length for such a tender charge, but was imperilled by war, so the envoys desired to return by sea. Tartars in general were strangers to all navigation; and the envoys, much taken with the Venetians, and eager to profit by their experience, especially as Marco had just then returned from his Indian mission, begged the Kaan as a favour to send the three Firinghis in their company. He consented with reluctance, but, having done so, fitted the party out nobly for the voyage, charging the Polos with friendly messages for the potentates of Europe, including the King of England. They appear to have sailed from the port of Zayton (as the Westerns called T’swan-chau or Chin-cheu in Fo-kien) in the beginning of 1292. It was an ill-starred voyage, involving long detentions on the coast of Sumatra, and in the South of India, to which, however, we are indebted for some of the best chapters in the book; and two years or upwards passed before they arrived at their destination in Persia.[19] The three hardy 24Venetians survived all perils, and so did the lady, who had come to look on them with filial regard; but two of the three envoys, and a vast proportion of the suite, had perished by the way.[20] Arghún Khan too had been dead even before they quitted China;[21] his brother Kaikhátú reigned in his stead; and his son Gházán succeeded to the lady’s hand. We are told by one who knew both the princes well that Arghún was one of the handsomest men of his time, whilst Gházán was, among all his host, one of the most insignificant in appearance. But in other respects the lady’s change was for the better. Gházán had some of the highest qualities of a soldier, a legislator and a king, adorned by many and varied accomplishments; though his reign was too short for the full development of his fame.
22. The princess, whose enjoyment of her royalty was brief, wept as she took leave of the kindly and noble Venetians. They pass by Persia to Venice. Their relations there.They went on to Tabriz, and after a long halt there proceeded homewards, reaching Venice, according to all the texts some time in 1295.[22]
We have related Ramusio’s interesting tradition, like a bit out of the Arabian Nights, of the reception that the Travellers met with from their relations, and of the means that they took to establish their position with those relations, and 25with Venetian society.[23] Of the relations, Marco the Elder had probably been long dead;[24] Maffeo the brother of our Marco was alive, and we hear also of a cousin (consanguineus) Felice Polo, and his wife Fiordelisa, without being able to fix their precise position in the family. We know also that Nicolo, who died before the end of the century, left behind him two illegitimate sons, Stefano and Zannino. It is not unlikely that these were born from some connection entered into during the long 26residence of the Polos in Cathay, though naturally their presence in the travelling company is not commemorated in Marco’s Prologue.[25]
The interpolation is older even than Pipino’s version, for we find in the rude Latin published by the Société de Géographie “quam cum Venetiis primo recessit praegnantem dimiserat.” But the statement is certainly an interpolation, for it does not exist in any of the older texts; nor have we any good reason for believing that it was an authorised interpolation. I suspect it to have been introduced to harmonise with an erroneous date for the commencement of the travels of the two brothers.
Lazari prints: “Messer Nicolò trovò che la sua donna era morta, e n’era rimasto un fanciullo di dodici anni per nome Marco, che il padre non avea veduto mai, perchè non era ancor nato quando egli partì.” These words have no equivalent in the French Texts, but are taken from one of the Italian MSS. in the Magliabecchian Library, and are I suspect also interpolated. The dodici is pure error (see p. 21 infra).
The matter is of some interest, because in the Will of the younger Maffeo, which is extant, he makes a bequest to his uncle (Avunculus) Jordan Trevisan. This seems an indication that his mother’s name may have been Trevisan. The same Maffeo had a daughter Fiordelisa. And Marco the Elder, in his Will (1280), appoints as his executors, during the absence of his brothers, the same Jordan Trevisan and his own sister-in-law Fiordelisa (“Jordanum Trivisanum de confinio S. Antonini: et Flordelisam cognatam meam”). Hence I conjecture that this cognata Fiordelisa (Trevisan?) was the wife of the absent Nicolo, and the mother of Maffeo. In that case of course Maffeo and Marco were the sons of different mothers. With reference to the above suggestion of Nicolo’s second marriage in 1269 there is a curious variation in a fragmentary Venetian Polo in the Barberini Library at Rome. It runs, in the passage corresponding to the latter part of ch. ix. of Prologue: “i qual do fratelli steteno do anni in Veniezia aspettando la elletion de nuovo Papa, nel qual tempo Mess. Nicolo si tolse moier et si la lasò graveda.” I believe, however, that it is only a careless misrendering of Pipino’s statement about Marco’s birth.
“To return to our travellers, who started on their second great journey in 1271, Sir Henry Yule, in his introduction,[A] makes them travel viâ Sivas to Mosul and Baghdád, and thence by sea to Hormuz, and this is the itinerary shown on his sketch map. This view I am unwilling to accept for more than one reason. In the first place, if, with Colonel Yule, we suppose that Ser Marco visited Baghdád, is it not unlikely that he should term the River Volga the Tigris,[B] and yet leave the river of Baghdád nameless? It may be urged that Marco believed the legend of the reappearance of the Volga in Kurdistán, but yet, if the text be read with care and the character of the traveller be taken into account, this error is scarcely explicable in any other way, than that he was never there.
“Again, he gives no description of the striking buildings of Baudas, as he terms it, but this is nothing to the inaccuracy of his supposed onward journey. To quote the text, ‘A very great river flows through the city, ... and merchants descend some eighteen days from Baudas, and then come to a certain city called Kisi,[C] where they enter the Sea of India.’ Surely Marco, had he travelled down the Persian Gulf, would never have given this description of the route, which is so untrue as to point to the conclusion that it was vague information given by some merchant whom he met in the course of his wanderings.
“Finally, apart from the fact that Baghdád, since its fall, was rather off the main caravan route, Marco so evidently travels east from Yezd and thence south to Hormuz, that unless his journey be described backwards, which is highly improbable, it is only possible to arrive at one conclusion, namely, that the Venetians entered Persia near Tabriz, and travelled to Sultania, Kashán, and Yezd. Thence they proceeded to Kermán and Hormuz, where, probably fearing the sea voyage, owing to the manifest unseaworthiness of the ships, which he describes as ‘wretched affairs,’ the Khorasán route was finally adopted. Hormuz, in this case, was not visited again until the return from China, when it seems probable that the same route was retraced to Tabriz, where their charge, the Lady Kokachin, ‘moult bele dame et avenant,’ was married to Gházan Khán, the son of her fiancé Arghun. It remains to add that Sir Henry Yule may have finally accepted this view in part, as in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography,[D] the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád.”
I may be allowed to answer that when Marco Polo started for the East, Baghdád was not rather off the main caravan route. The fall of Baghdád was not immediately followed by its decay, and we have proof of its prosperity at the beginning of the 14th century. Tauris had not yet the importance it had reached when the Polos visited it on their return journey. We have the will of the Venetian Pietro Viglioni, dated from Tauris, 10th December, 1264 (Archiv. Veneto, xxvi. 161–165), which shows that he was but a pioneer. It was only under Arghún Khan (1284–1291) that Tauris became the great market for foreign, especially Genoese, merchants, as Marco Polo remarks on his return journey; with Gházán and the new city built by that prince, Tauris reached a very high degree of prosperity, and was then really the chief emporium on the route from Europe to Persia and the far East. Sir Henry Yule had not changed his views, and if in the plate showing Probable View of Marco Polo’s own Geography, the itinerary is not shown as running to Baghdád, it is mere neglect on the part of the draughtsman.—H. C.]
The data are too slight for unexceptional precision, but the following adjustment will fairly meet the facts. Say that they sailed from Fo-kien in January 1292. In April they would be in Sumatra, and find the S.W. Monsoon too near to admit of their crossing the Bay of Bengal. They remain in port till September (five months), and then proceed, touching (perhaps) at Ceylon, at Kayal, and at several ports of Western India. In one of these, e.g. Kayal or Tana, they pass the S.W. Monsoon of 1293, and then proceed to the Gulf. They reach Hormuz in the winter, and the camp of the Persian Prince Gházán, the son of Arghún, in March, twenty-six months from their departure.
I have been unable to trace Hammer’s authority (not Wassáf I find), which perhaps gives the precise date of the Lady’s arrival in Persia (see infra, p. 38). From his narrative, however (Gesch. der Ilchane, ii. 20), March 1294 is perhaps too late a date. But the five months’ stoppage in Sumatra must have been in the S.W. Monsoon; and if the arrival in Persia is put earlier, Polo’s numbers can scarcely be held to. Or, the eighteen months mentioned at vol. i. p. 35, must include the five months’ stoppage. We may then suppose that they reached Hormuz about November 1293, and Gházán’s camp a month or two later.
The travellers may have stopped some time at Constantinople on their way, or even may have visited the northern shores of the Black Sea; otherwise, indeed, how did Marco acquire his knowledge of that Sea (ii. 486–488) and of events in Kipchak (ii. 496 seqq.)? If 1296 was the date of return, moreover, the six-and-twenty years assigned in the preamble as the period of Marco’s absence (p. 2) would be nearer accuracy. For he left Venice in the spring or summer of 1271.
“From ear to ear the story has past till it reached mine, that when the three Kinsmen arrived at their home they were dressed in the most shabby and sordid manner, insomuch that the wife of one of them gave away to a beggar that came to the door one of those garments of his, all torn, patched, and dirty as it was. The next day he asked his wife for that mantle of his, in order to put away the jewels that were sewn up in it; but she told him she had given it away to a poor man, whom she did not know. Now, the stratagem he employed to recover it was this. He went to the Bridge of Rialto, and stood there turning a wheel, to no apparent purpose, but as if he were a madman, and to all those who crowded round to see what prank was this, and asked him why he did it, he answered: ‘He’ll come if God pleases.’ So after two or three days he recognised his old coat on the back of one of those who came to stare at his mad proceedings, and got it back again. Then, indeed, he was judged to be quite the reverse of a madman! And from those jewels he built in the contrada of S. Giovanni Grisostomo a very fine palace for those days; and the family got among the vulgar the name of the Ca’ Million, because the report was that they had jewels to the value of a million of ducats; and the palace has kept that name to the present day—viz., 1566.” (Genealogies, MS. copy in Museo Civico; quoted also by Baldelli Boni, Vita, p. xxxi.)
The testator describes himself as formerly of Constantinople, but now dwelling in the confine of S. Severo.
His brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, if at Venice, are to be his sole trustees and executors, but in case of their continued absence he nominates Jordano Trevisano, and his sister-in-law Fiordelisa of the confine of S. Severo.
The proper tithe to be paid. All his clothes and furniture to be sold, and from the proceeds his funeral to be defrayed, and the balance to purchase masses for his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
Particulars of money due to him from his partnership with Donato Grasso, now of Justinople (Capo d’Istria), 1200 lire in all. (Fifty-two lire due by said partnership to Angelo di Tumba of S. Severo.)
The above money bequeathed to his son Nicolo, living at Soldachia, or failing him, to his beloved brothers Nicolo and Maffeo. Failing them, to the sons of his said brothers (sic) Marco and Maffeo. Failing them, to be spent for the good of his soul at the discretion of his trustees.
To his son Nicolo he bequeaths a silver-wrought girdle of vermilion silk, two silver spoons, a silver cup without cover (or saucer? sine cembalo), his desk, two pairs of sheets, a velvet quilt, a counterpane, a feather-bed—all on the same conditions as above, and to remain with the trustees till his son returns to Venice.
Meanwhile the trustees are to invest the money at his son’s risk and benefit, but only here in Venice (investiant seu investire, faciant).
From the proceeds to come in from his partnership with his brothers Nicolo and Maffeo, he bequeaths 200 lire to his daughter Maroca.
From same source 100 lire to his natural son Antony.
Has in his desk (capsella) two hyperperae (Byzantine gold coins), and three golden florins, which he bequeaths to the sister-in-law Fiordelisa.
Gives freedom to all his slaves and handmaidens.
Leaves his house in Soldachia to the Minor Friars of that place, reserving life-occupancy to his son Nicolo and daughter Maroca.
The rest of his goods to his son Nicolo.
IV. Digression concerning the Mansion of the Polo Family at Venice.
23. We have seen that Ramusio places the scene of the story recently alluded to at the mansion in the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, the court of which was known in his time as the Corte del Millioni; and indeed he speaks of Probable period of their establishment at S. Giovanni Grisostomo.the Travellers as at once on their arrival resorting to that mansion as their family residence. Ramusio’s details have so often proved erroneous that I should not be surprised if this also should be a mistake. At least we find (so far as I can learn) no previous intimation that the family were connected with that locality. The grandfather Andrea is styled of San Felice. The will of Maffeo Polo the younger, made in 1300, which we shall give hereafter in abstract, appears to be the first document that connects the family with S. Giovanni Grisostomo. It indeed styles the testator’s father “the late Nicolo Paulo of the confine of St. John Chrysostom,” but that only shows what is not disputed, that the Travellers after their return from the East settled in this locality. And the same will appears to indicate a surviving connexion with S. Felice, for the priests and clerks who drew it up and witness it are all of the church of S. Felice, and it is to the parson of S. Felice and his successor that Maffeo bequeaths an annuity to procure their prayers for the souls of 27his father, his mother, and himself, though after the successor the annuity is to pass on the same condition to the senior priest of S. Giovanni Grisostomo. Marco Polo the Elder is in his will described as of S. Severo, as is also his sister-in-law Fiordelisa, and the document contains no reference to S. Giovanni. On the whole therefore it seems probable that the Palazzo in the latter parish was purchased by the Travellers after their return from the East.[1]


24. The Court which was known in the 16th century as the Corte del Millioni has been generally understood to be that now known as the Corte Sabbionera,Relic of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. and here is still pointed out a relic of Marco Polo’s mansion. [Indeed it is called now (1899) Corte del Milione; see p. 30.—H. C.]
M. Pauthier’s edition is embellished with a good engraving which purports to represent the House of Marco Polo. But he has been misled. His engraving in fact exhibits, at least as the prominent feature, an embellished representation of a small house which exists on the west side of the Sabbionera, and which had at one time perhaps that pointed style of architecture which his engraving shows, though its present decoration is paltry and unreal. But it is on the north side of the Court, and on the foundations now occupied by the Malibran theatre, that Venetian tradition and the investigations of Venetian antiquaries concur in indicating the site of the Casa Polo. At the end of the 16th century a great fire destroyed the Palazzo,[2] and under the description of “an old 28mansion ruined from the foundation” it passed into the hands of one Stefano Vecchia, who sold it in 1678 to Giovanni Carlo Grimani. He built on the site of the ruins a theatre which was in its day one of the largest in Italy, and was called the Theatre of S. Giovanni Grisostomo; afterwards the Teatro Emeronitio. When modernized in our own day the proprietors gave it the name of Malibran, in honour of that famous singer, and this it still bears.[3]
[In 1881, the year of the Venice International Geographical Congress, a Tablet was put up on the Theatre with the following inscription:—
QVI FURONO LE CASEDI
MARCO POLO
CHE VIAGGIÒ LE PIÙ LONTANE REGIONI DELL’ASIA
E LE DESCRISSE
MDCCCLXXXI].
There is still to be seen on the north side of the Court an arched doorway in Italo-Byzantine style, richly sculptured with scrolls, disks, and symbolical animals, and on the wall above the doorway is a cross similarly ornamented.[4] The style and the decorations are those which were usual in Venice in the 13th century. The arch opens into a passage from which a similar doorway at the other end, also retaining some scantier relics of decoration, leads to the entrance of the Malibran Theatre. Over the archway in the Corte Sabbionera the building rises into a kind of tower. This, as well as the sculptured arches and cross, Signor Casoni, who gave a good deal of consideration to the subject, believed to be a relic of the old Polo House. But the tower (which Pauthier’s view does show) is now entirely modernized.[5]

29

Fig. A. From the Dürer Map. A.D. 1500.
Fig. B. From Map by Ludovico Ughi. A.D. 1729 Scale 1 to 2500.
Fig. C. From Recent Map. Scale 1 to 1315.
Other remains of Byzantine sculpture, which are probably 30fragments of the decoration of the same mansion, are found imbedded in the walls of neighbouring houses.[6] It is impossible to determine anything further as to the form or extent of the house of the time of the Polos, but some slight idea of its appearance about the year 1500 may be seen in the extract (fig. a) which we give from the famous pictorial map of Venice attributed erroneously to Albert Dürer. The state of the buildings in the last century is shown in (fig. b) an extract from the fine Map of Ughi; and their present condition in one (fig. c) reduced from the Modern Official Map of the Municipality.
[Coming from the Church of S. G. Grisostomo to enter the calle del Teatro on the left and the passage (Sottoportico) leading to the Corte del Milione, one has in front of him a building with a door of the epoch of the Renaissance; it was the office of the provveditori of silk; on the architrave are engraved the words:
PROVISORES SERICIand below, above the door, is the Tablet which] in the year 1827 the Abate Zenier caused to be put up with this inscription:—
AEDES PROXIMA THALIAE CVLTVI MODO ADDICTAMARCI POLO P. V. ITINERVM FAMA PRAECLARI
JAM HABITATIO FVIT.
24a. I believe that of late years some doubts have been thrown on the tradition of the site indicated as that of the Casa Polo, Recent corroboration as to the traditional site of the Casa Polo.though I am not aware of the grounds of such doubts. But a document recently discovered at Venice by Comm. Barozzi, one of a series relating to the testamentary estate of Marco Polo, goes far to confirm the tradition. This is the copy of a technical definition of two pieces of house property adjoining the property of Marco Polo and his brother Stephen, which were sold to Marco Polo by his wife Donata[7] in June 1321. Though the definition is not decisive, from the rarity of topographical references and absence of points of the compass, the description 31of Donata’s tenements as standing on the Rio (presumably that of S. Giovanni Grisostomo) on one side, opening by certain porticoes and stairs on the other to the Court and common alley leading to the Church of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, and abutting in two places on the Ca’ Polo, the property of her husband and Stefano, will apply perfectly to a building occupying the western portion of the area on which now stands the Theatre, and perhaps forming the western side of a Court of which Casa Polo formed the other three sides.[8]

We know nothing more of Polo till we find him appearing a year or two later in rapid succession as the Captain of a Venetian Galley, as a prisoner of war, and as an author.
[1]Marco Barbaro’s story related at p. 25 speaks of the Ca’ Million as built by the travellers.From a list of parchments existing in the archives of the Casa di Ricovero, or Great Poor House, at Venice, Comm. Berchet obtained the following indication:—
“No. 94. Marco Galetti invests Marco Polo S. of Nicolo with the ownership of his possessions (beni) in S. Giovanni Grisostomo; 10 September, 1319; drawn up by the Notary Nicolo, priest of S. Canciano.”
This document would perhaps have thrown light on the matter, but unfortunately recent search by several parties has failed to trace it. [The document has been discovered since: see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
[2]——“Sua casa che era posta nel confin di S. Giovanni Chrisostomo, che hor fà l’anno s’abbrugiò totalmente, con gran danno di molti.” (Doglioní, Hist. Venetiana, Ven. 1598, pp. 161–162.)“1596. 7 Nov. Senato (Arsenal ... ix c. 159 t).
“Essendo conveniente usar qualche ricognizione a quelli della maestranza dell’Arsenal nostro, che prontamente sono concorsi all’incendio occorso ultimamente a S. Zuane Grizostomo nelli stabeli detti di Ca’ Milion dove per la relazion fatta nell collegio nostro dalli patroni di esso Arsenal hanno nell’estinguere il foco prestato ogni buon servitio....”—(Comm. by Cav. Cecchetti through Comm. Berchet.)
[3]See a paper by G. C. (the Engineer Giovanni Casoni) in Teatro Emeronitio Almanacco per l’Anno 1835.[4]This Cross is engraved by Mr. Ruskin in vol. ii. of the Stones of Venice: see p. 139, and Pl. xi. Fig. 4.[5]Casoni’s only doubt was whether the Corte del Millioni was what is now the Sabbionera, or the interior area of the theatre. The latter seems most probable.One Illustration of this volume, p. 1, shows the archway in the Corte Sabbionera, and also the decorations of the soffit.
[6]See Ruskin, iii. 320.[7]Comm. Barozzi writes: “Among us, contracts between husband and wife are and were very common, and recognized by law. The wife sells to the husband property not included in dowry, or that she may have inherited, just as any third person might.”[8]See Appendix C, No. 16.V. Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages.

24. The Court which was known in the 16th century as the Corte del Millioni has been generally understood to be that now known as the Corte Sabbionera,Relic of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. and here is still pointed out a relic of Marco Polo’s mansion. [Indeed it is called now (1899) Corte del Milione; see p. 30.—H. C.]
M. Pauthier’s edition is embellished with a good engraving which purports to represent the House of Marco Polo. But he has been misled. His engraving in fact exhibits, at least as the prominent feature, an embellished representation of a small house which exists on the west side of the Sabbionera, and which had at one time perhaps that pointed style of architecture which his engraving shows, though its present decoration is paltry and unreal. But it is on the north side of the Court, and on the foundations now occupied by the Malibran theatre, that Venetian tradition and the investigations of Venetian antiquaries concur in indicating the site of the Casa Polo. At the end of the 16th century a great fire destroyed the Palazzo,[2] and under the description of “an old 28mansion ruined from the foundation” it passed into the hands of one Stefano Vecchia, who sold it in 1678 to Giovanni Carlo Grimani. He built on the site of the ruins a theatre which was in its day one of the largest in Italy, and was called the Theatre of S. Giovanni Grisostomo; afterwards the Teatro Emeronitio. When modernized in our own day the proprietors gave it the name of Malibran, in honour of that famous singer, and this it still bears.[3]
[In 1881, the year of the Venice International Geographical Congress, a Tablet was put up on the Theatre with the following inscription:—
DI
MARCO POLO
CHE VIAGGIÒ LE PIÙ LONTANE REGIONI DELL’ASIA
E LE DESCRISSE
PER DECRETO DEL COMUNE
MDCCCLXXXI].
There is still to be seen on the north side of the Court an arched doorway in Italo-Byzantine style, richly sculptured with scrolls, disks, and symbolical animals, and on the wall above the doorway is a cross similarly ornamented.[4] The style and the decorations are those which were usual in Venice in the 13th century. The arch opens into a passage from which a similar doorway at the other end, also retaining some scantier relics of decoration, leads to the entrance of the Malibran Theatre. Over the archway in the Corte Sabbionera the building rises into a kind of tower. This, as well as the sculptured arches and cross, Signor Casoni, who gave a good deal of consideration to the subject, believed to be a relic of the old Polo House. But the tower (which Pauthier’s view does show) is now entirely modernized.[5]

29

Fig. A. From the Dürer Map. A.D. 1500.
Fig. B. From Map by Ludovico Ughi. A.D. 1729 Scale 1 to 2500.
Fig. C. From Recent Map. Scale 1 to 1315.
Other remains of Byzantine sculpture, which are probably 30fragments of the decoration of the same mansion, are found imbedded in the walls of neighbouring houses.[6] It is impossible to determine anything further as to the form or extent of the house of the time of the Polos, but some slight idea of its appearance about the year 1500 may be seen in the extract (fig. a) which we give from the famous pictorial map of Venice attributed erroneously to Albert Dürer. The state of the buildings in the last century is shown in (fig. b) an extract from the fine Map of Ughi; and their present condition in one (fig. c) reduced from the Modern Official Map of the Municipality.
[Coming from the Church of S. G. Grisostomo to enter the calle del Teatro on the left and the passage (Sottoportico) leading to the Corte del Milione, one has in front of him a building with a door of the epoch of the Renaissance; it was the office of the provveditori of silk; on the architrave are engraved the words:
and below, above the door, is the Tablet which] in the year 1827 the Abate Zenier caused to be put up with this inscription:—
MARCI POLO P. V. ITINERVM FAMA PRAECLARI
JAM HABITATIO FVIT.
24a. I believe that of late years some doubts have been thrown on the tradition of the site indicated as that of the Casa Polo, Recent corroboration as to the traditional site of the Casa Polo.though I am not aware of the grounds of such doubts. But a document recently discovered at Venice by Comm. Barozzi, one of a series relating to the testamentary estate of Marco Polo, goes far to confirm the tradition. This is the copy of a technical definition of two pieces of house property adjoining the property of Marco Polo and his brother Stephen, which were sold to Marco Polo by his wife Donata[7] in June 1321. Though the definition is not decisive, from the rarity of topographical references and absence of points of the compass, the description 31of Donata’s tenements as standing on the Rio (presumably that of S. Giovanni Grisostomo) on one side, opening by certain porticoes and stairs on the other to the Court and common alley leading to the Church of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, and abutting in two places on the Ca’ Polo, the property of her husband and Stefano, will apply perfectly to a building occupying the western portion of the area on which now stands the Theatre, and perhaps forming the western side of a Court of which Casa Polo formed the other three sides.[8]

We know nothing more of Polo till we find him appearing a year or two later in rapid succession as the Captain of a Venetian Galley, as a prisoner of war, and as an author.
From a list of parchments existing in the archives of the Casa di Ricovero, or Great Poor House, at Venice, Comm. Berchet obtained the following indication:—
“No. 94. Marco Galetti invests Marco Polo S. of Nicolo with the ownership of his possessions (beni) in S. Giovanni Grisostomo; 10 September, 1319; drawn up by the Notary Nicolo, priest of S. Canciano.”
This document would perhaps have thrown light on the matter, but unfortunately recent search by several parties has failed to trace it. [The document has been discovered since: see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
“1596. 7 Nov. Senato (Arsenal ... ix c. 159 t).
“Essendo conveniente usar qualche ricognizione a quelli della maestranza dell’Arsenal nostro, che prontamente sono concorsi all’incendio occorso ultimamente a S. Zuane Grizostomo nelli stabeli detti di Ca’ Milion dove per la relazion fatta nell collegio nostro dalli patroni di esso Arsenal hanno nell’estinguere il foco prestato ogni buon servitio....”—(Comm. by Cav. Cecchetti through Comm. Berchet.)
One Illustration of this volume, p. 1, shows the archway in the Corte Sabbionera, and also the decorations of the soffit.
V. Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages.
24. The Court which was known in the 16th century as the Corte del Millioni has been generally understood to be that now known as the Corte Sabbionera,Relic of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. and here is still pointed out a relic of Marco Polo’s mansion. [Indeed it is called now (1899) Corte del Milione; see p. 30.—H. C.]
M. Pauthier’s edition is embellished with a good engraving which purports to represent the House of Marco Polo. But he has been misled. His engraving in fact exhibits, at least as the prominent feature, an embellished representation of a small house which exists on the west side of the Sabbionera, and which had at one time perhaps that pointed style of architecture which his engraving shows, though its present decoration is paltry and unreal. But it is on the north side of the Court, and on the foundations now occupied by the Malibran theatre, that Venetian tradition and the investigations of Venetian antiquaries concur in indicating the site of the Casa Polo. At the end of the 16th century a great fire destroyed the Palazzo,[2] and under the description of “an old 28mansion ruined from the foundation” it passed into the hands of one Stefano Vecchia, who sold it in 1678 to Giovanni Carlo Grimani. He built on the site of the ruins a theatre which was in its day one of the largest in Italy, and was called the Theatre of S. Giovanni Grisostomo; afterwards the Teatro Emeronitio. When modernized in our own day the proprietors gave it the name of Malibran, in honour of that famous singer, and this it still bears.[3]
[In 1881, the year of the Venice International Geographical Congress, a Tablet was put up on the Theatre with the following inscription:—
DI
MARCO POLO
CHE VIAGGIÒ LE PIÙ LONTANE REGIONI DELL’ASIA
E LE DESCRISSE
PER DECRETO DEL COMUNE
MDCCCLXXXI].
There is still to be seen on the north side of the Court an arched doorway in Italo-Byzantine style, richly sculptured with scrolls, disks, and symbolical animals, and on the wall above the doorway is a cross similarly ornamented.[4] The style and the decorations are those which were usual in Venice in the 13th century. The arch opens into a passage from which a similar doorway at the other end, also retaining some scantier relics of decoration, leads to the entrance of the Malibran Theatre. Over the archway in the Corte Sabbionera the building rises into a kind of tower. This, as well as the sculptured arches and cross, Signor Casoni, who gave a good deal of consideration to the subject, believed to be a relic of the old Polo House. But the tower (which Pauthier’s view does show) is now entirely modernized.[5]

29

Fig. A. From the Dürer Map. A.D. 1500.
Fig. B. From Map by Ludovico Ughi. A.D. 1729 Scale 1 to 2500.
Fig. C. From Recent Map. Scale 1 to 1315.
Other remains of Byzantine sculpture, which are probably 30fragments of the decoration of the same mansion, are found imbedded in the walls of neighbouring houses.[6] It is impossible to determine anything further as to the form or extent of the house of the time of the Polos, but some slight idea of its appearance about the year 1500 may be seen in the extract (fig. a) which we give from the famous pictorial map of Venice attributed erroneously to Albert Dürer. The state of the buildings in the last century is shown in (fig. b) an extract from the fine Map of Ughi; and their present condition in one (fig. c) reduced from the Modern Official Map of the Municipality.
[Coming from the Church of S. G. Grisostomo to enter the calle del Teatro on the left and the passage (Sottoportico) leading to the Corte del Milione, one has in front of him a building with a door of the epoch of the Renaissance; it was the office of the provveditori of silk; on the architrave are engraved the words:
and below, above the door, is the Tablet which] in the year 1827 the Abate Zenier caused to be put up with this inscription:—
MARCI POLO P. V. ITINERVM FAMA PRAECLARI
JAM HABITATIO FVIT.
24a. I believe that of late years some doubts have been thrown on the tradition of the site indicated as that of the Casa Polo, Recent corroboration as to the traditional site of the Casa Polo.though I am not aware of the grounds of such doubts. But a document recently discovered at Venice by Comm. Barozzi, one of a series relating to the testamentary estate of Marco Polo, goes far to confirm the tradition. This is the copy of a technical definition of two pieces of house property adjoining the property of Marco Polo and his brother Stephen, which were sold to Marco Polo by his wife Donata[7] in June 1321. Though the definition is not decisive, from the rarity of topographical references and absence of points of the compass, the description 31of Donata’s tenements as standing on the Rio (presumably that of S. Giovanni Grisostomo) on one side, opening by certain porticoes and stairs on the other to the Court and common alley leading to the Church of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, and abutting in two places on the Ca’ Polo, the property of her husband and Stefano, will apply perfectly to a building occupying the western portion of the area on which now stands the Theatre, and perhaps forming the western side of a Court of which Casa Polo formed the other three sides.[8]

We know nothing more of Polo till we find him appearing a year or two later in rapid succession as the Captain of a Venetian Galley, as a prisoner of war, and as an author.
From a list of parchments existing in the archives of the Casa di Ricovero, or Great Poor House, at Venice, Comm. Berchet obtained the following indication:—
“No. 94. Marco Galetti invests Marco Polo S. of Nicolo with the ownership of his possessions (beni) in S. Giovanni Grisostomo; 10 September, 1319; drawn up by the Notary Nicolo, priest of S. Canciano.”
This document would perhaps have thrown light on the matter, but unfortunately recent search by several parties has failed to trace it. [The document has been discovered since: see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
“1596. 7 Nov. Senato (Arsenal ... ix c. 159 t).
“Essendo conveniente usar qualche ricognizione a quelli della maestranza dell’Arsenal nostro, che prontamente sono concorsi all’incendio occorso ultimamente a S. Zuane Grizostomo nelli stabeli detti di Ca’ Milion dove per la relazion fatta nell collegio nostro dalli patroni di esso Arsenal hanno nell’estinguere il foco prestato ogni buon servitio....”—(Comm. by Cav. Cecchetti through Comm. Berchet.)
One Illustration of this volume, p. 1, shows the archway in the Corte Sabbionera, and also the decorations of the soffit.
V. Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages.

24. The Court which was known in the 16th century as the Corte del Millioni has been generally understood to be that now known as the Corte Sabbionera,Relic of the Casa Polo in the Corte Sabbionera. and here is still pointed out a relic of Marco Polo’s mansion. [Indeed it is called now (1899) Corte del Milione; see p. 30.—H. C.]
M. Pauthier’s edition is embellished with a good engraving which purports to represent the House of Marco Polo. But he has been misled. His engraving in fact exhibits, at least as the prominent feature, an embellished representation of a small house which exists on the west side of the Sabbionera, and which had at one time perhaps that pointed style of architecture which his engraving shows, though its present decoration is paltry and unreal. But it is on the north side of the Court, and on the foundations now occupied by the Malibran theatre, that Venetian tradition and the investigations of Venetian antiquaries concur in indicating the site of the Casa Polo. At the end of the 16th century a great fire destroyed the Palazzo,[2] and under the description of “an old 28mansion ruined from the foundation” it passed into the hands of one Stefano Vecchia, who sold it in 1678 to Giovanni Carlo Grimani. He built on the site of the ruins a theatre which was in its day one of the largest in Italy, and was called the Theatre of S. Giovanni Grisostomo; afterwards the Teatro Emeronitio. When modernized in our own day the proprietors gave it the name of Malibran, in honour of that famous singer, and this it still bears.[3]
[In 1881, the year of the Venice International Geographical Congress, a Tablet was put up on the Theatre with the following inscription:—
DI
MARCO POLO
CHE VIAGGIÒ LE PIÙ LONTANE REGIONI DELL’ASIA
E LE DESCRISSE
PER DECRETO DEL COMUNE
MDCCCLXXXI].
There is still to be seen on the north side of the Court an arched doorway in Italo-Byzantine style, richly sculptured with scrolls, disks, and symbolical animals, and on the wall above the doorway is a cross similarly ornamented.[4] The style and the decorations are those which were usual in Venice in the 13th century. The arch opens into a passage from which a similar doorway at the other end, also retaining some scantier relics of decoration, leads to the entrance of the Malibran Theatre. Over the archway in the Corte Sabbionera the building rises into a kind of tower. This, as well as the sculptured arches and cross, Signor Casoni, who gave a good deal of consideration to the subject, believed to be a relic of the old Polo House. But the tower (which Pauthier’s view does show) is now entirely modernized.[5]

29

Fig. A. From the Dürer Map. A.D. 1500.
Fig. B. From Map by Ludovico Ughi. A.D. 1729 Scale 1 to 2500.
Fig. C. From Recent Map. Scale 1 to 1315.
Other remains of Byzantine sculpture, which are probably 30fragments of the decoration of the same mansion, are found imbedded in the walls of neighbouring houses.[6] It is impossible to determine anything further as to the form or extent of the house of the time of the Polos, but some slight idea of its appearance about the year 1500 may be seen in the extract (fig. a) which we give from the famous pictorial map of Venice attributed erroneously to Albert Dürer. The state of the buildings in the last century is shown in (fig. b) an extract from the fine Map of Ughi; and their present condition in one (fig. c) reduced from the Modern Official Map of the Municipality.
[Coming from the Church of S. G. Grisostomo to enter the calle del Teatro on the left and the passage (Sottoportico) leading to the Corte del Milione, one has in front of him a building with a door of the epoch of the Renaissance; it was the office of the provveditori of silk; on the architrave are engraved the words:
and below, above the door, is the Tablet which] in the year 1827 the Abate Zenier caused to be put up with this inscription:—
MARCI POLO P. V. ITINERVM FAMA PRAECLARI
JAM HABITATIO FVIT.
24a. I believe that of late years some doubts have been thrown on the tradition of the site indicated as that of the Casa Polo, Recent corroboration as to the traditional site of the Casa Polo.though I am not aware of the grounds of such doubts. But a document recently discovered at Venice by Comm. Barozzi, one of a series relating to the testamentary estate of Marco Polo, goes far to confirm the tradition. This is the copy of a technical definition of two pieces of house property adjoining the property of Marco Polo and his brother Stephen, which were sold to Marco Polo by his wife Donata[7] in June 1321. Though the definition is not decisive, from the rarity of topographical references and absence of points of the compass, the description 31of Donata’s tenements as standing on the Rio (presumably that of S. Giovanni Grisostomo) on one side, opening by certain porticoes and stairs on the other to the Court and common alley leading to the Church of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, and abutting in two places on the Ca’ Polo, the property of her husband and Stefano, will apply perfectly to a building occupying the western portion of the area on which now stands the Theatre, and perhaps forming the western side of a Court of which Casa Polo formed the other three sides.[8]

We know nothing more of Polo till we find him appearing a year or two later in rapid succession as the Captain of a Venetian Galley, as a prisoner of war, and as an author.
From a list of parchments existing in the archives of the Casa di Ricovero, or Great Poor House, at Venice, Comm. Berchet obtained the following indication:—
“No. 94. Marco Galetti invests Marco Polo S. of Nicolo with the ownership of his possessions (beni) in S. Giovanni Grisostomo; 10 September, 1319; drawn up by the Notary Nicolo, priest of S. Canciano.”
This document would perhaps have thrown light on the matter, but unfortunately recent search by several parties has failed to trace it. [The document has been discovered since: see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
“1596. 7 Nov. Senato (Arsenal ... ix c. 159 t).
“Essendo conveniente usar qualche ricognizione a quelli della maestranza dell’Arsenal nostro, che prontamente sono concorsi all’incendio occorso ultimamente a S. Zuane Grizostomo nelli stabeli detti di Ca’ Milion dove per la relazion fatta nell collegio nostro dalli patroni di esso Arsenal hanno nell’estinguere il foco prestato ogni buon servitio....”—(Comm. by Cav. Cecchetti through Comm. Berchet.)
One Illustration of this volume, p. 1, shows the archway in the Corte Sabbionera, and also the decorations of the soffit.
V. Digression concerning the War-Galleys of the Mediterranean States in the Middle Ages.
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 1293. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
25. And before entering on this new phase of the Traveller’s biography it may not be Arrangement of the Rowers in Mediæval Galleys: a separate oar to every man.without interest that we say something regarding the equipment of those galleys which are so prominent in the mediæval history of the Mediterranean.[1]
Eschewing that “Serbonian Bog, where armies whole have sunk” of Books and Commentators, the theory of the classification of the Biremes and Triremes of the Ancients, we can at least assert on secure grounds that in mediæval armament, up to the middle of the 16th century or thereabouts, the characteristic distinction of galleys of different calibres, so far as such differences existed, was based on the number of rowers that sat on one bench pulling each his separate oar, but through one portella or rowlock-port.[2] And to the classes 32of galleys so distinguished the Italians, of the later Middle Age at least, did certainly apply, rightly or wrongly, the classical terms of Bireme, Trireme, and Quinquereme, in the sense of galleys having two men and two oars to a bench, three men and three oars to a bench, and five men and five oars to a bench.[3]
That this was the mediæval arrangement is very certain from the details afforded by Marino Sanudo the Elder, confirmed by later writers and by works of art. Previous to 1290, Sanudo tells us, almost all the galleys that went to the Levant had but two oars and men to a bench; but as it had been found that three oars and men to a bench could be employed with great advantage, after that date nearly all galleys adopted this arrangement, which was called ai Terzaruoli.[4]
Moreover experiments made by the Venetians in 1316 had shown that four rowers to a bench could be employed still more advantageously. And where the galleys could be used on inland waters, and could be made more bulky, Sanudo would even recommend five to a bench, or have gangs of rowers on two decks with either three or four men to the bench on each deck.
26. This system of grouping the oars, and putting only one man to an oar, continued down to the 16th century, during the Change of System in the 16th century.first half of which came in the more modern system of using great oars, equally spaced, and requiring from four to seven men each to ply them, in the manner which endured till late in the last century, when galleys became altogether obsolete. Captain Pantero Pantera, the author of a work on Naval Tactics (1616), says he had heard, from veterans 33who had commanded galleys equipped in the antiquated fashion, that three men to a bench, with separate oars, answered better than three men to one great oar, but four men to one great oar (he says) were certainly more efficient than four men with separate oars. The new-fashioned great oars, he tells us, were styled Remi di Scaloccio, the old grouped oars Remi a Zenzile,—terms the etymology of which I cannot explain.[5]
It may be doubted whether the four-banked and five-banked galleys, of which Marino Sanudo speaks, really then came into practical use. A great five-banked galley on this system, built in 1529 in the Venice Arsenal by Vettor Fausto, was the subject of so much talk and excitement, that it must evidently have been something quite new and unheard of.[6] So late as 1567 indeed the King of Spain built at Barcelona a galley of thirty-six benches to the side, and seven men to the bench, with a separate oar to each in the old fashion. But it proved a failure.[7]
Down to the introduction of the great oars the usual system appears to have been three oars to a bench for the larger galleys, and two oars for lighter ones. The fuste or lighter galleys of the Venetians, even to about the middle of the 16th century, had their oars in pairs from the stern to the mast, and single oars only from the mast forward.[8]
27. Returning then to the three-banked and two-banked galleys of the latter part of the 13th century, the number of benches onSome details of the 13th century Galleys. each side seems to have run from twenty-five to twenty-eight, at least as I interpret Sanudo’s calculations. The 100-oared vessels often mentioned (e.g. by Muntaner, p. 419) were probably two-banked vessels with twenty-five benches to a side.

The galleys were very narrow, only 15½ feet in beam.[9] 34But to give room for the play of the oars and the passage of the fighting-men, &c., this width was largely augmented by an opera-morta, or outrigger deck, projecting much beyond the ship’s sides and supported by timber brackets.[10] I do not find it stated how great this projection was in the mediæval galleys, but in those of the 17th century it was on each side as much as ²⁄₉ths of the true beam. And if it was as great in the 13th-century galleys the total width between the false gunnels would be about 22¼ feet.
In the centre line of the deck ran, the whole length of the vessel, a raised gangway called the corsia, for passage clear of the oars.
The benches were arranged as in this diagram. The part of the bench next the gunnel was at right angles to it, but the other two-thirds of the bench were thrown forward obliquely. a, b, c, indicate the position of the three rowers. The shortest oar a was called Terlicchio, the middle one b Posticcio, the long oar c Piamero.[11]
I do not find any information as to how the oars worked on the gunnels. The Siena fresco (see p. 35) appears to show them attached by loops and pins, which is the usual practice in boats of the Mediterranean now. In the cut from D. Tintoretto (p. 37) the groups of oars protrude through regular ports in the bulwarks, but this probably represents the use of a later day. In any case the oars of each bench must have worked in very close proximity. Sanudo states the length of the galleys of his time (1300–1320) as 117 feet. This was doubtless length of keel, for that is specified (“da ruoda a ruoda”) in other Venetian measurements, but the whole oar space could scarcely have been so much, and with twenty-eight benches to a side there could not have been more than 4 feet gunnel-space to each bench. And as one of the objects of the grouping of the oars was to allow room between the benches for the action of cross-bowmen, &c., it is plain that the rowlock space for the three oars must have been very much compressed.[12]
35

36
The rowers were divided into three classes, with graduated pay. The highest class, who pulled the poop or stroke oars, were called Portolati; those at the bow, called Prodieri, formed the second class.[13]
Some elucidation of the arrangements that we have tried to describe will be found in our cuts. That at p. 35 is from a drawing, by the aid of a very imperfect photograph, of part of one of the frescoes of Spinello Aretini in the Municipal Palace at Siena, representing a victory of the Venetians over the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa’s fleet, commanded by his son Otho, in 1176; but no doubt the galleys, &c., are of the artist’s own age, the 37middle of the 14th century.[14] In this we see plainly the projecting opera-morta, and the rowers sitting two to a bench, each with his oar, for these are two-banked. We can also discern the Latin rudder on the quarter. (See this volume, p. 118.) In a picture in the Uffizj, at Florence, of about the same date, by Pietro Laurato (it is in the corridor near the entrance), may be seen a small figure of a galley with the oars also very distinctly coupled.[15] Casoni has engraved, after Cristoforo Canale, a pictorial plan of a Venetian trireme of the 16th century, which shows the arrangement of the oars in triplets very plainly.
The following cut has been sketched from an engraving of a picture by Domenico Tintoretto in the Doge’s palace, representing, I believe, the same action (real or imaginary) as Spinello’s fresco, but with the costume and construction of a later date. It shows, however, very plainly, the projecting opera-morta and the arrangement of the oars in fours, issuing through row-ports in high bulwarks.

28. Midships in the mediæval galley a castle was erected, of 38the width of the ship, and some 20 feet in length; Fighting Arrangements.its platform being elevated sufficiently to allow of free passage under it and over the benches. At the bow was the battery, consisting of mangonels (see vol. ii. p. 161 seqq.) and great cross-bows with winding gear,[16] whilst there were shot-ports[17] for smaller cross-bows along the gunnels in the intervals between the benches. Some of the larger galleys had openings to admit horses at the stern, which were closed and caulked for the voyage, being under water when the vessel was at sea.[18]
It seems to have been a very usual piece of tactics, in attacking as well as in awaiting attack, to connect a large number of galleys by hawsers, and sometimes also to link the oars together, so as to render it difficult for the enemy to break the line or run aboard. We find this practised by the Genoese on the defensive at the battle of Ayas (infra, p. 43), and it is constantly resorted to by the Catalans in the battles described by Ramon de Muntaner.[19]
Sanudo says the toil of rowing in the galleys was excessive, almost unendurable. Yet it seems to have been performed by freely-enlisted men, and therefore it was probably less severe than that of the great-oared galleys of more recent times, 39which it was found impracticable to work by free enlistment, or otherwise than by slaves under the most cruel driving.[20] I am not well enough read to say that war-galleys were never rowed by slaves in the Middle Ages, but the only doubtful allusion to such a class that I have met with is in one passage of Muntaner, where he says, describing the Neapolitan and Catalan fleets drawing together for action, that the gangs of the galleys had to toil like “forçats” (p. 313). Indeed, as regards Venice at least, convict rowers are stated to have been first introduced in 1549, previous to which the gangs were of galeotti assoldati.[21]
29. We have already mentioned that Crew of a Galley and Staff of a Fleet.Sanudo requires for his three-banked galley a ship’s company of 250 men. They are distributed as follows:—
| Comito or Master |
1
|
| Quartermasters |
8
|
| Carpenters |
2
|
| Caulkers |
2
|
| In charge of stores and arms |
4
|
| Orderlies |
2
|
| Cook |
1
|
| Arblasteers |
50
|
| Rowers |
180
|
|
——
|
|
|
250[22]
|
This does not include the Sopracomito, or Gentleman-Commander, who was expected to be valens homo et probus, a soldier and a gentleman, fit to be consulted on occasion by the captain-general. In the Venetian fleet he was generally a noble.[23]
The aggregate pay of such a crew, not including the sopracomito, amounted monthly to 60 lire de’ grossi, or 600 florins, equivalent to 280l. at modern gold value; and the cost for a year to nearly 3160l., exclusive of the victualling of the vessel and the pay of the gentleman-commander. The build or purchase of a galley complete is estimated by the same author at 15,000 florins, or 7012l.
We see that war cost a good deal in money even then.
Besides the ship’s own complement Sanudo gives an estimate for the general staff of a fleet of 60 galleys. This consists of a captain-general, two (vice) admirals, and the following:—
40
|
6
|
Probi homines, or gentlemen of character, forming a council to the Captain-General; |
|
4
|
Commissaries of Stores; |
|
2
|
Commissaries over the Arms; |
|
3
|
Physicians; |
|
3
|
Surgeons; |
|
5
|
Master Engineers and Carpenters; |
|
15
|
Master Smiths; |
|
12
|
Master Fletchers; |
|
5
|
Cuirass men and Helmet-makers; |
|
15
|
Oar-makers and Shaft-makers; |
|
10
|
Stone cutters for stone shot; |
|
10
|
Master Arblast-makers; |
|
20
|
Musicians; |
|
20
|
Orderlies, &c. |
30. The musicians formed an important part of the equipment. Sanudo says that in going into action every vessel should make the greatest possible display of colours; Music; and other particulars.gonfalons and broad banners should float from stem to stern, and gay pennons all along the bulwarks; whilst it was impossible to have too much of noisy music, of pipes, trumpets, kettle-drums, and what not, to put heart into the crew and strike fear into the enemy.[24]
So Joinville, in a glorious passage, describes the galley of his kinsman, the Count of Jaffa, at the landing of St. Lewis in Egypt:—
“That galley made the most gallant figure of them all, for it was painted all over, above water and below, with scutcheons of the count’s arms, the field of which was or with a cross patée gules.[25] He had a good 300 rowers in his galley, and every man of them had a target blazoned with his arms in beaten gold. And, as they came on, the galley looked to be some flying creature, with such spirit did the rowers spin it along;—or rather, with the rustle of its flags, and the roar of its nacaires and drums and Saracen horns, you might have taken it for a rushing bolt of heaven.”[26]
The galleys, which were very low in the water,[27] could not keep the sea in rough weather, and in winter they never willingly kept the sea at night, however fair the weather might 41be. Yet Sanudo mentions that he had been with armed galleys to Sluys in Flanders.
I will mention two more particulars before concluding this digression. When captured galleys were towed into port it was stern foremost, and with their colours dragging on the surface of the sea.[28] And the custom of saluting at sunset (probably by music) was in vogue on board the galleys of the 13th century.[29]
We shall now sketch the circumstances that led to the appearance of our Traveller in the command of a war-galley.
In Sanudo we have a glimpse worth noting of the word soldiers advancing towards the modern sense; he expresses a strong preference for soldati (viz. paid soldiers) over crusaders (viz. volunteers), p. 74.
In after days the artillery occupied the same position, at the bow of the galley.
Great beams, hung like battering rams, are mentioned by Sanudo, as well as iron crow’s-feet with fire attached, to shoot among the rigging, and jars of quick-lime and soft soap to fling in the eyes of the enemy. The lime is said to have been used by Doria against the Venetians at Curzola (infra, p. 48), and seems to have been a usual provision. Francesco Barberini specifies among the stores for his galley: “Calcina, con lancioni, Pece, pietre, e ronconi” (p. 259). And Christine de Pisan, in her Faiz du Sage Roy Charles (V. of France), explains also the use of the soap: “Item, on doit avoir pluseurs vaisseaulx legiers à rompre, comme poz plains de chauls ou pouldre, et gecter dedens; et, par ce, seront comme avuglez, au brisier des poz. Item, on doit avoir autres poz de mol savon et gecter es nefzs des adversaires, et quant les vaisseaulx brisent, le savon est glissant, si ne se peuent en piez soustenir et chiéent en l’eaue” (pt. ii. ch. 38).
The Turkish admiral Sidi ’Ali, about to engage a Portuguese squadron in the Straits of Hormuz, in 1553, describes the Franks as “dressing their vessels with flags and coming on.” (J. As. ix. 70.)
VI. The Jealousies and Naval Wars of Venice and Genoa. Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic; Battle of Curzola; and Imprisonment of Marco Polo by the Genoese.
31. Jealousies, too characteristic of the Italian communities, were, in the case of the three great trading republics of Venice, Genoa, and Pisa, Growing jealousies and outbreaks between the Republics.aggravated by commercial rivalries, whilst, between the two first of those states, and also between the two last, the bitterness of such feelings had been augmenting during the whole course of the 13th century.[1]
The brilliant part played by Venice in the conquest of Constantinople (1204), and the preponderance she thus acquired on the Greek shores, stimulated her arrogance and the resentment of her rivals. The three states no longer stood on a level as bidders for the shifting favour of the Emperor of the East. By treaty, not only was Venice established as the most important ally of the empire and as mistress of a large fraction of its territory, but all members of nations at war with her were prohibited from entering its limits. Though the Genoese colonies continued to exist, they stood at a great 42disadvantage, where their rivals were so predominant and enjoyed exemption from duties, to which the Genoese remained subject. Hence jealousies and resentments reached a climax in the Levantine settlements, and this colonial exacerbation reacted on the mother States.
A dispute which broke out at Acre in 1255 came to a head in a war which lasted for years, and was felt all over Syria. It began in a quarrel about a very old church called St. Sabba’s, which stood on the common boundary of the Venetian and Genoese estates in Acre,[2] and this flame was blown by other unlucky occurrences. Acre suffered grievously.[3] Venice at this time generally kept the upper hand, beating Genoa by land and sea, and driving her from Acre altogether.✛ Four ancient porphyry figures from St. Sabba’s were sent in triumph to Venice, and with their strange devices still stand at the exterior corner of St. Mark’s, towards the Ducal Palace.[4]
But no number of defeats could extinguish the spirit of Genoa, and the tables were turned when in her wrath she allied herself with Michael Palaeologus to upset the feeble and tottering Latin Dynasty, and with it the preponderance of Venice on the Bosphorus. The new emperor handed over to his allies the castle of their foes, which they tore down with jubilations, and now it was their turn to send its stones as trophies to Genoa. Mutual hate waxed fiercer than ever; no merchant fleet of either state could go to sea without convoy, and wherever their ships met they fought.[5] It was something like the state of things between Spain and England in the days of Drake.

The energy and capacity of the Genoese seemed to rise with 43their success, and both in seamanship and in splendour they began almost to surpass their old rivals. The fall of Acre (1291), and the total expulsion of the Franks from Syria, in great measure barred the southern routes of Indian trade, whilst the predominance of Genoa in the Euxine more or less obstructed the free access of her rival to the northern routes by Trebizond and Tana.
32. Truces were made and renewed, but the old fire still smouldered. In the spring of 1294 it broke into flame, in consequence of the seizure in the Grecian seas of three Battle in Bay of Ayas in 1294.Genoese vessels by a Venetian fleet. This led to an action with a Genoese convoy which sought redress. The fight took place off Ayas in the Gulf of Scanderoon,[6] and though the Genoese were inferior in strength by one-third they gained a signal victory, capturing all but three of the Venetian galleys, with rich cargoes, including that of Marco Basilio (or Basegio), the commodore.
This victory over their haughty foe was in its completeness evidently a surprise to the Genoese, as well as a source of immense exultation, which is vigorously expressed in a ballad of the day, written in a stirring salt-water rhythm.[7] It represents the Venetians, as they enter the bay, in arrogant mirth reviling the Genoese with very unsavoury epithets as having deserted their ships to skulk on shore. They are described as saying:—
So they advance carelessly—
44
After relating the battle and the thoroughness of the victory, ending in the conflagration of five-and-twenty captured galleys, the poet concludes by an admonition to the enemy to moderate his pride and curb his arrogant tongue, harping on the obnoxious epithet porci leproxi, which seems to have galled the Genoese.[9] He concludes:—
The community of Genoa decreed that the victory should be commemorated by the annual presentation of a golden pall to the monastery of St. German’s, the saint on whose feast (28th May) it had been won.[11]
The startling news was received at Venice with wrath and grief, for the flower of their navy had perished, and all energies were bent at once to raise an overwhelming force.[12] The Pope (Boniface VIII.) interfered as arbiter, calling for plenipotentiaries from both sides. But spirits were too much inflamed, and this mediation came to nought.
45
Further outrages on both sides occurred in 1296. The Genoese residences at Pera were fired, their great alum works on the coast of Anatolia were devastated, and Caffa was stormed and sacked; whilst on the other hand a number of the Venetians at Constantinople were massacred by the Genoese, and Marco Bembo, their Bailo, was flung from a house-top. Amid such events the fire of enmity between the cities waxed hotter and hotter.
33. In 1298 the Genoese made elaborate preparations for a great blow at the enemy, and fitted out a powerful fleet which they placed Lamba Doria’s Expedition to the Adriatic.under the command of Lamba Doria, a younger brother of Uberto of that illustrious house, under whom he had served fourteen years before in the great rout of the Pisans at Meloria.
The rendezvous of the fleet was in the Gulf of Spezia, as we learn from the same pithy Genoese poet who celebrated Ayas. This time the Genoese were bent on bearding St. Mark’s Lion in his own den; and after touching at Messina they steered straight for the Adriatic:—
On their entering the gulf a great storm dispersed the fleet. The admiral with twenty of his galleys got into port at Antivari on the Albanian coast, and next day was rejoined by fifty-eight more, with which he scoured the Dalmatian shore, plundering all Venetian property. Some sixteen of his galleys were still missing when he reached the island of Curzola, or Scurzola as the more popular name seems to have been, the Black Corcyra of the Ancients—the chief town of which, a rich and flourishing 46place, the Genoese took and burned.[14] Thus they were engaged when word came that the Venetian fleet was in sight.
Venice, on first hearing of the Genoese armament, sent Andrea Dandolo with a large force to join and supersede Maffeo Quirini, who was already cruising with a squadron in the Ionian sea; and, on receiving further information of the strength of the hostile expedition, the Signory hastily equipped thirty-two more galleys in Chioggia and the ports of Dalmatia, and despatched them to join Dandolo, making the whole number under his command up to something like ninety-five. Recent drafts had apparently told heavily upon the Venetian sources of enlistment, and it is stated that many of the complements were made up of rustics swept in haste from the Euganean hills. To this the Genoese poet seems to allude, alleging that the Venetians, in spite of their haughty language, had to go begging for men and money up and down Lombardy. “Did we do like that, think you?” he adds:—
Of one of the Venetian galleys, probably in the fleet which sailed under Dandolo’s immediate command, went Marco Polo as Sopracomito or Gentleman-Commander.[16]
47
34. It was on the afternoon of Saturday the 6th September that the Genoese The Fleets come in sight of each other at Curzola.saw the Venetian fleet approaching, but, as sunset was not far off, both sides tacitly agreed to defer the engagement.[17]
The Genoese would appear to have occupied a position near the eastern end of the Island of Curzola, with the Peninsula of Sabbioncello behind them, and Meleda on their left, whilst the Venetians advanced along the south side of Curzola. (See map on p. 50).
According to Venetian accounts the Genoese were staggered at the sight of the Venetian armaments, and sent more than once to seek terms, offering finally to surrender galleys and munitions of war, if the crews were allowed to depart. This is an improbable story, and that of the Genoese ballad seems more like truth. Doria, it says, held a council of his captains in the evening at which they all voted for attack, whilst the Venetians, with that overweening sense of superiority which at this time is reflected in their own annals as distinctly as in those of their enemies, kept scout-vessels out to watch that the Genoese fleet, which they looked on as already their own, did not steal away in the darkness. A vain imagination, says the poet:—
48
35. The battle began early on Sunday and lasted till the afternoon. The Venetians had the wind in their favour, but the morning sun in their eyes. The Venetians defeated, and Marco Polo a prisoner.They made the attack, and with great impetuosity, capturing ten Genoese galleys; but they pressed on too wildly, and some of their vessels ran aground. One of their galleys too, being taken, was cleared of her crew and turned against the Venetians. These incidents caused confusion among the assailants; the Genoese, who had begun to give way, took fresh heart, formed a close column, and advanced boldly through the Venetian line, already in disorder. The sun had begun to decline when there appeared on the Venetian flank the fifteen or sixteen missing galleys of Doria’s fleet, and fell upon it with fresh force. This decided the action. The Genoese gained a complete victory, capturing all but a few of the Venetian galleys, and including the flagship with Dandolo. The Genoese themselves lost heavily, especially in the early part of the action, and Lamba Doria’s eldest son Octavian is said to have fallen on board his father’s vessel.[19] The number of prisoners taken was over 7000, and among these was Marco Polo.[20]
49

(Joinville, vide ante, p. 40.)
The prisoners, even of the highest rank, appear to have been chained. Dandolo, in despair at his defeat, and at the prospect of being carried captive into Genoa, refused food, and ended by dashing his head against a bench.[21] A Genoese account asserts 50that a noble funeral was given him after the arrival of the fleet at Genoa, which took place on the evening of the 16th October.[22] It was received with great rejoicing, and the City voted the annual presentation of a pallium of gold brocade to the altar of the Virgin in the Church of St. Matthew, on every 8th of September, the Madonna’s day, on the eve of which the Battle had been won. To the admiral himself a Palace was decreed. It still stands, opposite the Church of St. Matthew, though it has passed from the possession of the Family. On the striped marble façades, both of the Church and of the Palace, inscriptions of that age, in excellent preservation, still commemorate Lamba’s achievement.[23] Malik al Mansúr, the Mameluke Sultan of Egypt, as an enemy of Venice, sent a complimentary letter to Doria accompanied by costly presents.[24]


51
The latter died at Savona 17th October, 1323, a few months before the most illustrious of his prisoners, and his bones were laid in a sarcophagus which may still be seen forming the sill of one of the windows of S. Matteo (on the right as you enter). Over this sarcophagus stood the Bust of Lamba till 1797, when the mob of Genoa, in idiotic imitation of the French proceedings of that age, threw it down. All of Lamba’s six sons had fought with him at Meloria. In 1291 one of them, Tedisio, went forth into the Atlantic in company with Ugolino Vivaldi on a voyage of discovery, and never returned. Through Cæsar, the youngest, this branch of the Family still survives, bearing the distinctive surname of Lamba-Doria.[25]
As to the treatment of the prisoners, accounts differ; a thing usual in such cases. The Genoese Poet asserts that the hearts of his countrymen were touched, and that the captives were treated with compassionate courtesy. Navagiero the Venetian, on the other hand, declares that most of them died of hunger.[26]
52
36. Howsoever they may have been treated, here was Marco Polo one of those many thousand prisoners in Genoa; Marco Polo in prison dictates his book to Rusticiano of Pisa. Release of Venetian prisoners.and here, before long, he appears to have made acquaintance with a man of literary propensities, whose destiny had brought him into the like plight, by name Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa. It was this person perhaps who persuaded the Traveller to defer no longer the reduction to writing of his notable experiences; but in any case it was he who wrote down those experiences at Marco’s dictation; it is he therefore to whom we owe the preservation of this record, and possibly even that of the Traveller’s very memory. This makes the Genoese imprisonment so important an episode in Polo’s biography.
To Rusticiano we shall presently recur. But let us first bring to a conclusion what may be gathered as to the duration of Polo’s imprisonment.
It does not appear whether Pope Boniface made any new effort for accommodation between the Republics; but other Italian princes did interpose, and Matteo Visconti, Captain-General of Milan, styling himself Vicar-General of the Holy Roman Empire in Lombardy, was accepted as Mediator, along with the community of Milan. Ambassadors from both States presented themselves at that city, and on the 25th May, 1299, they signed the terms of a Peace.
These terms were perfectly honourable to Venice, being absolutely equal and reciprocal; from which one is apt to conclude that the damage to the City of the Sea was rather to her pride than to her power; the success of Genoa, in fact, having been followed up by no systematic attack upon Venetian commerce.[27] Among the terms was the mutual release of prisoners on a day to be fixed by Visconti after the completion of all formalities. This day is not recorded, but as the Treaty was ratified by the Doge of Venice on the 1st July, and the latest extant document connected with the formalities appears to be dated 18th July, we may believe that before the end of August 53Marco Polo was restored to the family mansion in S. Giovanni Grisostomo.
37. Something further requires to be said before quitting this event in our Traveller’s life. For we confess that a critical reader may have some Grounds on which the story of Marco Polo’s capture at Curzola rests.justification in asking what evidence there is that Marco Polo ever fought at Curzola, and ever was carried a prisoner to Genoa from that unfortunate action?
A learned Frenchman, whom we shall have to quote freely in the immediately ensuing pages, does not venture to be more precise in reference to the meeting of Polo and Rusticiano than to say of the latter: “In 1298, being in durance in the Prison of Genoa, he there became acquainted with Marco Polo, whom the Genoese had deprived of his liberty from motives equally unknown.”[28]
To those who have no relish for biographies that round the meagre skeleton of authentic facts with a plump padding of what might have been, this sentence of Paulin Paris is quite refreshing in its stern limitation to positive knowledge. And certainly no contemporary authority has yet been found for the capture of our Traveller at Curzola. Still I think that the fact is beyond reasonable doubt.
Ramusio’s biographical notices certainly contain many errors of detail; and some, such as the many years’ interval which he sets between the Battle of Curzola and Marco’s return, are errors which a very little trouble would have enabled him to eschew. But still it does seem reasonable to believe that the main fact of Marco’s command of a galley at Curzola, and capture there, was derived from a genuine tradition, if not from documents.
Let us then turn to the words which close Rusticiano’s preamble (see post, p. 2):—“Lequel (Messire Marc) puis demorant en le charthre de Jene, fist retraire toutes cestes chouses a Messire Rustacians de Pise que en celle meissme charthre estoit, au tens qu’il avoit 1298 anz que Jezu eut vesqui.” These words are at least thoroughly consistent with Marco’s capture at Curzola, as regards both the position in which they present him, and the year in which he is thus presented.
There is however another piece of evidence, though it is curiously indirect.
54
The Dominican Friar Jacopo of Acqui was a contemporary of Polo’s, and was the author of a somewhat obscure Chronicle called Imago Mundi.[29] Now this Chronicle does contain mention of Marco’s capture in action by the Genoese, but attributes it to a different action from Curzola, and one fought at a time when Polo could not have been present. The passage runs as follows in a manuscript of the Ambrosian Library, according to an extract given by Baldelli Boni:—
“In the year of Christ MCCLXXXXVI, in the time of Pope Boniface VI., of whom we have spoken above, a battle was fought in Arminia, at the place called Layaz, between xv. galleys of Genoese merchants and xxv. of Venetian merchants; and after a great fight the galleys of the Venetians were beaten, and (the crews) all slain or taken; and among them was taken Messer Marco the Venetian, who was in company with those merchants, and who was called Milono, which is as much as to say ‘a thousand thousand pounds,’ for so goes the phrase in Venice. So this Messer Marco Milono the Venetian, with the other Venetian prisoners, is carried off to the prison of Genoa, and there kept for a long time. This Messer Marco was a long time with his father and uncle in Tartary, and he there saw many things, and made much wealth, and also learned many things, for he was a man of ability. And so, being in prison at Genoa, he made a Book concerning the great wonders of the World, i.e., concerning such of them as he had seen. And what he told in the Book was not as much as he had really seen, because of the tongues of detractors, who, being ready to impose their own lies on others, are over hasty to set down as lies what they in their perversity disbelieve, or do not understand. And because there are many great and strange things in that Book, which are reckoned past all credence, he was asked by his friends on his death-bed to correct the Book by removing everything that went beyond the facts. To which his reply was that he had not told one-half of what he had really seen!”[30]
This statement regarding the capture of Marco at the Battle of Ayas is one which cannot be true, for we know that he did not reach Venice till 1295, travelling from Persia by way of Trebizond and the Bosphorus, whilst the Battle of Ayas of which we have purposely given some detail, was fought in May, 1294. 55The date MCCLXXXXVI assigned to it in the preceding extract has given rise to some unprofitable discussion. Could that date be accepted, no doubt it would enable us also to accept this, the sole statement from the Traveller’s own age of the circumstances which brought him into a Genoese prison; it would enable us to place that imprisonment within a few months of his return from the East, and to extend its duration to three years, points which would thus accord better with the general tenor of Ramusio’s tradition than the capture of Curzola. But the matter is not open to such a solution. The date of the Battle of Ayas is not more doubtful than that of the Battle of the Nile. It is clearly stated by several independent chroniclers, and is carefully established in the Ballad that we have quoted above.[31] We shall see repeatedly in the course of this Book how uncertain are the transcriptions of dates in Roman numerals, and in the present case the LXXXXVI is as certainly a mistake for LXXXXIV as is Boniface VI. in the same quotation a mistake for Boniface VIII.
But though we cannot accept the statement that Polo was taken prisoner at Ayas, in the spring of 1294, we may accept the passage as evidence from a contemporary source that he was taken prisoner in some sea-fight with the Genoese, and thus admit it in corroboration of the Ramusian Tradition of his capture in a sea-fight at Curzola in 1298, which is perfectly consistent with all other facts in our possession.
This Alor! Alor! (“Up, Boys, and at ’em”), or something similar, appears to have been the usual war-cry of both parties. So a trumpet-like poem of the Troubadour warrior Bertram de Born, whom Dante found in such evil plight below (xxviii. 118 seqq.), in which he sings with extraordinary spirit the joys of war:—
In a galley fight at Tyre in 1258, according to a Latin narrative, the Genoese shout “Ad arma, ad arma! ad ipsos, ad ipsos!” The cry of the Venetians before engaging the Greeks is represented by Martino da Canale, in his old French, as “or à yaus! or à yaus!” that of the Genoese on another occasion as Aur! Aur! and this last is the shout of the Catalans also in Ramon de Muntaner. (Villemain, Litt. du Moyen Age, i. 99; Archiv. Stor. Ital. viii. 364, 506; Pertz, Script. xviii. 239; Muntaner, 269, 287.) Recently in a Sicilian newspaper, narrating an act of gallant and successful reprisal (only too rare) by country folk on a body of the brigands who are such a scourge to parts of the island, I read that the honest men in charging the villains raised a shout of “Ad iddi! Ad iddi!”
And in the next verse note the pure Scotch use of the word bra:—
Money on such occasions was frequently raised by what was called an Estimo or Facion, which was a force loan levied on the citizens in proportion to their estimated wealth; and for which they were entitled to interest from the State.
Now the 7th September, 1298, fell on a Sunday.
The inscription on S. Matteo regarding the battle is as follows:—“Ad Honorem Dei et Beate Virginis Marie Anno MCCLXXXXVIII Die Dominico VII Septembris iste Angelus captus fuit in Gulfo Venetiarum in Civitate Scursole et ibidem fuit prelium Galearum LXXVI Januensium cum Galeis LXXXXVI Veneciarum. Capte fuerunt LXXXIIII per Nobilem Virum Dominum Lambam Aurie Capitaneum et Armiratum tunc Comunis et Populi Janue cum omnibus existentibus in eisdem, de quibus conduxit Janue homines vivos carceratos VII cccc et Galeas XVIII, reliquas LXVI fecit cumburi in dicto Gulfo Veneciarum. Qui obiit Sagone I. MCCCXXIII.” It is not clear to what the Angelus refers.
The Armenian Prince Hayton or Héthum has put it under 12
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]
A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”
“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]
During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]
75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.
49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.
77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”
“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”

“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”

“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”

“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
93. (See Langlois, Mém. sur les Relations de Gênes avec la Petite-Arménie.)
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”

“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.
VII. Rusticiano or Rustichello of Pisa, Marco Polo’s Fellow-Prisoner at Genoa, the Scribe who wrote down the Travels.
38. We have now to say something of that Rusticiano to whom all who value Polo’s book are so much indebted.
The relations between Genoa and Pisa had long been so 56hostile that it was only too natural in 1298 to find a Pisan in the gaol of Genoa.Rusticiano, perhaps a prisoner from Meloria. An unhappy multitude of such prisoners had been carried thither fourteen years before, and the survivors still lingered there in vastly dwindled numbers. In the summer of 1284 was fought the battle from which Pisa had to date the commencement of her long decay. In July of that year the Pisans, at a time when the Genoese had no fleet in their own immediate waters, had advanced to the very port of Genoa and shot their defiance into the proud city in the form of silver-headed arrows, and stones belted with scarlet.[1] They had to pay dearly for this insult. The Genoese, recalling their cruisers, speedily mustered a fleet of eighty-eight galleys, which were placed under the command of another of that illustrious House of Doria, the Scipios of Genoa as they have been called, Uberto, the elder brother of Lamba. Lamba himself with his six sons, and another brother, was in the fleet, whilst the whole number of Dorias who fought in the ensuing action amounted to 250, most of them on board one great galley bearing the name of the family patron, St. Matthew.[2]
The Pisans, more than one-fourth inferior in strength, came out boldly, and the battle was fought off the Porto Pisano, in fact close in front of Leghorn, where a lighthouse on a remarkable arched basement still marks the islet of Meloria, whence the battle got its name. The day was the 6th of August, the feast of St. Sixtus, a day memorable in the Pisan Fasti for several great victories. But on this occasion the defeat of Pisa was overwhelming. Forty of their galleys were taken or sunk, and upwards of 9000 prisoners carried to Genoa. In fact so vast a sweep was made of the flower of Pisan manhood that it was a common saying then: “Che vuol veder Pisa, vada a 57Genova!” Many noble ladies of Pisa went in large companies on foot to Genoa to seek their husbands or kinsmen: “And when they made enquiry of the Keepers of the Prisons, the reply would be, ‘Yesterday there died thirty of them, to-day there have died forty; all of whom we have cast into the sea; and so it is daily.’”[3]

A body of prisoners so numerous and important naturally exerted themselves in the cause of peace, and through their efforts, after many months of negotiation, a formal peace was signed (15th April, 1288). But through the influence, as was alleged, of Count Ugolino (Dante’s) who was then in power at Pisa, the peace became abortive; war almost immediately recommenced, and the prisoners had no release.[4] And, when the 6000 or 7000 Venetians were thrown into the prisons of Genoa in October 1298, they would find there the scanty surviving remnant of the Pisan Prisoners of Meloria, and would gather from them dismal forebodings of the fate before them.
It is a fair conjecture that to that remnant Rusticiano of Pisa may have belonged.
We have seen Ramusio’s representation of the kindness shown to Marco during his imprisonment by a certain Genoese gentleman who also assisted him to reduce his travels to writing. We may be certain that this Genoese gentleman is only a distorted image of Rusticiano, the Pisan prisoner in the gaol of 58Genoa, whose name and part in the history of his hero’s book Ramusio so strangely ignores. Yet patriotic Genoese writers in our own times have striven to determine the identity of this their imaginary countryman![5]
39. Who, then, was Rusticiano, or, as the name actually is read in the oldest type of MS., “Messire Rustacians de Pise”?
Rusticiano, a person known from other sources.Our knowledge of him is but scanty. Still something is known of him besides the few words concluding his preamble to our Traveller’s Book, which you may read at pp. 1–2 of the body of this volume.
In Sir Walter Scott’s “Essay on Romance,” when he speaks of the new mould in which the subjects of the old metrical stories were cast by the school of prose romancers which arose in the 13th century, we find the following words:—
“Whatever fragments or shadows of true history may yet remain hidden under the mass of accumulated fable which had been heaped upon them during successive ages, must undoubtedly be sought in the metrical romances.... But those prose authors who wrote under the imaginary names of Rusticien de Pise, Robert de Borron, and the like, usually seized upon the subject of some old minstrel; and recomposing the whole narrative after their own fashion, with additional character and adventure, totally obliterated in that operation any shades which remained of the original and probably authentic tradition,” &c.[6]
Evidently, therefore, Sir Walter regarded Rustician of Pisa as a person belonging to the same ghostly company as his own Cleishbothams and Dryasdusts. But in this we see that he was wrong.
In the great Paris Library and elsewhere there are manuscript volumes containing the stories of the Round Table abridged and somewhat clumsily combined from the various Prose Romances of that cycle, such as Sir Tristan, Lancelot, Palamedes, Giron le Courtois, &c., which had been composed, it would seem, by various Anglo-French gentlemen at the court of Henry III., styled, or styling themselves, Gasses le Blunt, Luces du Gast, 59Robert de Borron, and Hélis de Borron. And these abridgments or recasts are professedly the work of Le Maistre Rusticien de Pise. Several of them were printed at Paris in the end of the 15th and beginning of the 16th centuries as the works of Rusticien de Pise; and as the preambles and the like, especially in the form presented in those printed editions, appear to be due sometimes to the original composers (as Robert and Hélis de Borron) and sometimes to Rusticien de Pise the recaster, there would seem to have been a good deal of confusion made in regard to their respective personalities.
From a preamble to one of those compilations which undoubtedly belongs to Rustician, and which we shall quote at length by and bye, we learn that Master Rustician “translated” (or perhaps transferred?) his compilation from a book belonging to King Edward of England, at the time when that prince went beyond seas to recover the Holy Sepulchre. Now Prince Edward started for the Holy Land in 1270, spent the winter of that year in Sicily, and arrived in Palestine in May 1271. He quitted it again in August, 1272, and passed again by Sicily, where in January, 1273, he heard of his father’s death and his own consequent accession. Paulin Paris supposes that Rustician was attached to the Sicilian Court of Charles of Anjou, and that Edward “may have deposited with that king the Romances of the Round Table, of which all the world was talking, but the manuscripts of which were still very rare, especially those of the work of Helye de Borron[7] ... whether by order, or only with permission of the King of Sicily, our Rustician made haste to read, abridge, and re-arrange the whole, and when Edward returned to Sicily he recovered possession of the book from which the indefatigable Pisan had extracted the contents.”
But this I believe is, in so far as it passes the facts stated in Rustician’s own preamble, pure hypothesis, for nothing is cited that connects Rustician with the King of Sicily. And if there be not some such confusion of personality as we have alluded to, in another of the preambles, which is quoted by Dunlop as an utterance of Rustician’s, that personage would seem to claim to have been a comrade in arms of the two de Borrons. We 60might, therefore, conjecture that Rustician himself had accompanied Prince Edward to Syria.[8]
40. Rustician’s literary work appears from the extracts and remarks of Paulin Paris to be that of an industrious simple man,Character of Rustician’s Romance compilations. without method or much judgment. “The haste with which he worked is too perceptible; the adventures are told without connection; you find long stories of Tristan followed by adventures of his father Meliadus.” For the latter derangement of historical sequence we find a quaint and ingenuous apology offered in Rustician’s epilogue to Giron le Courtois:—
“Cy fine le Maistre Rusticien de Pise son conte en louant et regraciant le Père le Filz et le Saint Esperit, et ung mesme Dieu, Filz de la Benoiste Vierge Marie, de ce qu’il m’a doné grace, sens, force, et mémoire, temps et lieu, de me mener à fin de si haulte et si noble matière come ceste-cy dont j’ay traicté les faiz et proesses recitez et recordez à mon livre. Et se aucun me demandoit pour quoy j’ay parlé de Tristan avant que de son père le Roy Meliadus, je respons que ma matière n’estoist pas congneue. Car je ne puis pas scavoir tout, ne mettre toutes mes paroles par ordre. Et ainsi fine mon conte. Amen.”[9]
In a passage of these compilations the Emperor Charlemagne is asked whether in his judgment King Meliadus or his son Tristan were the better man? The Emperor’s answer is: “I should say that the King Meliadus was the better man, and I will tell you why I say so. As far as I can see, everything that Tristan did was done for Love, and his great feats would never have been done but under the constraint of Love, which was his 61spur and goad. Now that never can be said of King Meliadus! For what deeds he did, he did them not by dint of Love, but by dint of his strong right arm. Purely out of his own goodness he did good, and not by constraint of Love.” “It will be seen,” remarks on this Paulin Paris, “that we are here a long way removed from the ordinary principles of Round Table Romances. And one thing besides will be manifest, viz., that Rusticien de Pise was no Frenchman!”[10]
The same discretion is shown even more prominently in a passage of one of his compilations, which contains the romances of Arthur, Gyron, and Meliadus (No. 6975—see last note but one):—
“No doubt,” Rustician says, “other books tell the story of the Queen Ginevra and Lancelot differently from this; and there were certain passages between them of which the Master, in his concern for the honour of both those personages, will say not a word.” Alas, says the French Bibliographer, that the copy of Lancelot, which fell into the hands of poor Francesca of Rimini, was not one of those expurgated by our worthy friend Rustician![11]
41. A question may still occur to an attentive reader as to the identity of this Romance-compiler Rusticien de Pise with the Messire Rustacians de Pise, Identity of the Romance Compiler with Polo’s fellow-prisoner.of a solitary MS. of Polo’s work (though the oldest and most authentic), a name which appears in other copies as Rusta Pisan, Rasta Pysan, Rustichelus Civis Pisanus, Rustico, Restazio da Pisa, Stazio da Pisa, and who is stated in the preamble to have acted as the Traveller’s scribe at Genoa.
M. Pauthier indeed[12] asserts that the French of the MS. Romances of Rusticien de Pise is of the same barbarous character as that of the early French MS. of Polo’s Book to which we have just alluded, and which we shall show to be the nearest presentation of the work as originally dictated by the Traveller. The language of the latter MS. is so peculiar that this would be almost perfect evidence of the identity of the writers, if it were really the fact. A cursory inspection which I have made of two of those MSS. in Paris, and the extracts which I have given 62and am about to give, do not, however, by any means support M. Pauthier’s view. Nor would that view be consistent with the judgment of so competent an authority as Paulin Paris, implied in his calling Rustician a nom recommandable in old French literature, and his speaking of him as “versed in the secrets of the French Romance Tongue.”[13] In fact the difference of language in the two cases would really be a difficulty in the way of identification, if there were room for doubt. This, however, Paulin Paris seems to have excluded finally, by calling attention to the peculiar formula of preamble which is common to the Book of Marco Polo and to one of the Romance compilations of Rusticien de Pise.
The former will be found in English at pp. 1, 2, of our Translation; but we give a part of the original below[14] for comparison with the preamble to the Romances of Meliadus, Tristan, and Lancelot, as taken from MS. 6961 (Fr. 340) of the Paris Library:—
“Seigneurs Empereurs et Princes, Ducs et Contes et Barons et Chevaliers et Vavasseurs et Bourgeois, et tous les preudommes de cestui monde qui avez talent de vous deliter en rommans, si prenez cestui (livre) et le faites lire de chief en chief, si orrez toutes les grans aventure qui advindrent entre les Chevaliers errans du temps au Roy Uter Pendragon, jusques à le temps au Roy Artus son fils, et des compaignons de la Table Ronde. Et sachiez tout vraiment que cist livres fust translatez du livre Monseigneur Edouart le Roy d’Engleterre en cellui temps qu’il passa oultre la mer au service nostre Seigneur Damedieu pour conquester le Sant Sepulcre, et Maistre Rusticiens de Pise, lequel est ymaginez yci dessus,[15] compila ce rommant, car il en translata toutes les merveilleuses nouvelles et aventures qu’il trouva en celle livre et traita tout certainement de toutes les aventures du monde, et si sachiez qu’il traitera plus de Monseigneur Lancelot du Lac, et Monsr Tristan le fils au Roy Meliadus de Leonnoie que d’autres, porcequ’ilz furent sans faille les meilleurs chevaliers qui à ce temps furent en terre; et li Maistres en dira de ces deux pluseurs choses et pluseurs nouvelles que l’en treuvera escript en tous les autres livres; et porce que le Maistres les trouva escript au Livre d’Engleterre.”

“Certainly,” Paulin Paris observes, “there is a singular 63analogy between these two prefaces. And it must be remarked that the formula is not an ordinary one with translators, compilers, or authors of the 13th and 14th centuries. Perhaps you would not find a single other example of it.”[16]
This seems to place beyond question the identity of the Romance-compiler of Prince Edward’s suite in 1270, and the Prisoner of Genoa in 1298.
42. In Dunlop’s History of Fiction a passage is quoted from the preamble of Meliadus, as set forth in the Paris printed edition of 1528, Further particulars concerning Rustician.which gives us to understand that Rusticien de Pise had received as a reward for some of his compositions from King Henry III. the prodigal gift of two chateaux. I gather, however, from passages in the work of Paulin Paris that this must certainly be one of those confusions of persons to which I have referred before, and that the recipient of the chateaux was in reality Helye de Borron, the author of some of the originals which Rustician manipulated.[17] This supposed incident in Rustician’s scanty history must therefore be given up.
We call this worthy Rustician or Rusticiano, as the nearest probable representation in Italian form of the Rusticien of the Round-Table MSS. and the Rustacians of the old text of Polo. But it is highly probable that his real name was Rustichello, as is suggested by the form Rustichelus in the early Latin version published by the Société de Géographie. The change of one liquid for another never goes for much in Italy,[18] and Rustichello might easily Gallicize himself as Rusticien. In a very long list of Pisan officials during the Middle Ages I find several bearing the name of Rustichello or Rustichelli, but no Rusticiano or Rustigiano.[19]
Respecting him we have only to add that the peace between Genoa and Venice was speedily followed by a treaty between Genoa and Pisa. On the 31st July, 1299, a truce for twenty-five years was signed between those two 64Republics. It was a very different matter from that between Genoa and Venice, and contained much that was humiliating and detrimental to Pisa. But it embraced the release of prisoners; and those of Meloria, reduced it is said to less than one tithe of their original number, had their liberty at last. Among the prisoners then released no doubt Rustician was one. But we hear of him no more.
In documents of the kingdom of Jerusalem there are names still more anomalous, e.g., Gualterius Baffumeth, Joannes Mahomet. (See Cod. Dipl. del Sac. Milit. Ord. Gerosol. I. 2–3, 62.)
“Aussi Luces du Gau (Gas) translata en langue Françoise une partie de l’Hystoire de Monseigneur Tristan, et moins assez qu’il ne deust. Moult commença bien son livre et si ny mist tout les faicts de Tristan, ains la greigneur partie. Après s’en entremist Messire Gasse le Blond, qui estoit parent au Roy Henry, et divisa l’Hystoire de Lancelot du Lac, et d’autre chose ne parla il mye grandement en son livre. Messire Robert de Borron s’en entremist et Helye de Borron, par la prière du dit Robert de Borron, et pource que compaignons feusmes d’armes longuement, je commencay mon livre,” etc. (Liebrecht’s Dunlop, p. 80.) If this passage be authentic it would set beyond doubt the age of the de Borrons and the other writers of Anglo-French Round Table Romances, who are placed by the Hist. Littéraire de la France, and apparently by Fr. Michel, under Henry II. I have no means of pursuing the matter, and have preferred to follow Paulin Paris, who places them under Henry III. I notice, moreover, that the Hist. Litt. (xv. p. 498) puts not only the de Borrons but Rustician himself under Henry II.; and, as the last view is certainly an error, the first is probably so too.
VIII. Notices of Marco Polo’s History, after the Termination of his Imprisonment at Genoa.
43. A few very disconnected notices are all that can be collected of matter properly biographical in relation to the quarter Death of Marco’s Father before 1300. Will of his brother Maffeo.century during which Marco Polo survived the Genoese captivity.
We have seen that he would probably reach Venice in the course of August, 1299. Whether he found his aged father alive is not known; but we know at least that a year later (31st August, 1300) Messer Nicolo was no longer in life.
This we learn from the Will of the younger Maffeo, Marco’s brother, which bears the date just named, and of which we give an abstract below.[1] It seems to imply strong regard for the 65testator’s brother Marco, who is made inheritor of the bulk of the property, failing the possible birth of a son. I have already indicated some conjectural deductions from this document. I may add that the terms of the second clause, as quoted in the note, seem to me to throw considerable doubt on the genealogy which bestows a large family of sons upon this brother Maffeo. If he lived to have such a family it seems improbable that the draft which he thus left in the hands of a notary, to be converted into a Will in the event of his death (a curious example of the validity attaching to all acts of notaries in those days), should never have been superseded, but should actually have been so converted after his death, as the existence of the parchment 66seems to prove. But for this circumstance we might suppose the Marcolino mentioned in the ensuing paragraph to have been a son of the younger Maffeo.
Messer Maffeo, the uncle, was, we see, alive at this time. We do not know the year of his death. But it is alluded to by Friar Pipino in the Preamble to his Translation of the Book, supposed to have been executed about 1315–1320; and we learn from a document in the Venetian archives (see p. 77) that it must have been previous to 1318, and subsequent to February 1309, the date of his last Will. The Will itself is not known to be extant, but from the reference to it in this document we learn that he left 1000 lire of public debt[2] (? imprestitorum) to a certain Marco Polo, called Marcolino. The relationship of this Marco to old Maffeo is not stated, but we may suspect him to have been an illegitimate son. [Marcolino was a son of Nicolo, son of Marco the Elder; see vol. ii., Calendar, No. 6.—H. C.]
44. In 1302 occurs what was at first supposed to be a glimpse of Marco as a citizen, slight and quaint enough; Documentary notices of Polo at this time. The sobriquet of Milione.being a resolution on the Books of the Great Council to exempt the respectable Marco Polo from the penalty incurred by him on account of the omission to have his water-pipe duly inspected. But since our Marco’s claims to the designation of Nobilis Vir have been established, there is a doubt whether the providus vir or prud’-homme here spoken of may not have been rather his namesake Marco Polo of Cannareggio or S. Geremia, of whose existence we learn from another entry of the same year.[3] It is, however, possible 67that Marco the Traveller was called to the Great Council after the date of the document in question.
We have seen that the Traveller, and after him his House and his Book, acquired from his contemporaries the surname, or nickname rather, of Il Milione. Different writers have given different explanations of the origin of this name; some, beginning with his contemporary Fra Jacopo d’Acqui, (supra, p. 54), ascribing it to the family’s having brought home a fortune of a million of lire, in fact to their being millionaires. This is the explanation followed by Sansovino, Marco Barbaro, Coronelli, and others.[4] More far-fetched is that of Fontanini, who supposes the name to have been given to the Book as containing a great number of stories, like the Cento Novelle or the Thousand and One Nights! But there can be no doubt that Ramusio’s is the true, as it is the natural, explanation; and that the name was bestowed on Marco by the young wits of his native city, because of his frequent use of a word which appears to have been then unusual, in his attempts to convey an idea of the vast wealth and magnificence of the Kaan’s Treasury and Court.[5] Ramusio has told us (supra, p. 6) that he had seen Marco styled by this sobriquet in the Books of the Signory; and it is pleasant to be able to confirm this by the next document which we cite. This is an extract from the Books of the Great Council under 10th April, 1305, condoning the offence of a certain Bonocio of Mestre in smuggling wine, for whose penalty one of the sureties had been the Nobilis Vir Marchus Paulo Milioni.[6]
It is alleged that long after our Traveller’s death there was always, in the Venetian Masques, one individual who assumed the character of Marco Milioni, and told Munchausenlike stories 68to divert the vulgar. Such, if this be true, was the honour of our prophet among the populace of his own country.[7]
45. A little later we hear of Marco once more, as presenting a copy of his Book to a noble Frenchman in the service of Charles of Valois.
This Prince, brother of Philip the Fair, in 1301 had married Catharine, daughter and heiress of Philip de Courtenay, titular Emperor ofPolo’s relations with Thibault de Cepoy. Constantinople, and on the strength of this marriage had at a later date set up his own claim to the Empire of the East. To this he was prompted by Pope Clement V., who in the beginning of 1306 wrote to Venice, stimulating that Government to take part in the enterprise. In the same year, Charles and his wife sent as their envoys to Venice, in connection with this matter, a noble knight called Thibault de Cepoy, along with an ecclesiastic of Chartres called Pierre le Riche, and these two succeeded in executing a treaty of alliance with Venice, of which the original, dated 14th December, 1306, exists at Paris. Thibault de Cepoy eventually went on to Greece with a squadron of Venetian Galleys, but accomplished nothing of moment, and returned to his master in 1310.[8]

During the stay of Thibault at Venice he seems to have made acquaintance with Marco Polo, and to have received from him a copy of his Book. This is recorded in a curious note which appears on two existing MSS. of Polo’s Book, viz., that 69of the Paris Library (10,270 or Fr. 5649), and that of Bern, which is substantially identical in its text with the former, and is, as I believe, a copy of it.[9] The note runs as follows:—
“Here you have the Book of which My Lord Thiebault, Knight and Lord of Cepoy, (whom may God assoil!) requested a copy from Sire Marc Pol, Burgess and Resident of the City of Venice. And the said Sire Marc Pol, being a very honourable Person, of high character and respect in many countries, because of his desire that what he had witnessed should be known throughout the World, and also for the honour and reverence he bore to the most excellent and puissant Prince my Lord Charles, Son of the King of France and Count of Valois, gave and presented to the aforesaid Lord of Cepoy the first copy (that was taken) of his said Book after he had made the same. And very pleasing it was to him that his Book should be carried to the noble country of France and there made known by so worthy a gentleman. And from that copy which the said Messire Thibault, Sire de Cepoy above-named, did carry into France, Messire John, who was his eldest son and is the present Sire de Cepoy,[10] after his Father’s decease did have a copy made, and that very first copy that was made of the Book after its being carried into France he did present to his very dear and dread Lord Monseigneur de Valois. Thereafter he gave copies of it to such of his friends as asked for them.
“And the copy above-mentioned was presented by the said Sire Marc Pol to the said Lord de Cepoy when the latter went to Venice, on the part of Monseigneur de Valois and of Madame the Empress his wife, as Vicar General for them both in all the Territories of the Empire of Constantinople. And this happened in the year of the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ one thousand three hundred and seven, and in the month of August.”
Of the bearings of this memorandum on the literary history of Polo’s Book we shall speak in a following section.
46. When Marco married we have not been able to ascertain, but it was no doubt early in the 14th century, for in 1324, we find that he had twoHis marriage and his daughters. Marco as a merchant. married daughters besides one unmarried. His wife’s Christian name was Donata, but of her family we have as yet found no assurance. I suspect, however, that her name may have been Loredano (vide infra, p. 77).
Under 1311 we find a document which is of considerable interest, 70because it is the only one yet discovered which exhibits Marco under the aspect of a practical trader. It is the judgment of the Court of Requests upon a suit brought by the Noble Marco Polo of the parish of S. Giovanni Grisostomo against one Paulo Girardo of S. Apollinare. It appears that Marco had entrusted to the latter as a commission agent for sale, on an agreement for half profits, a pound and a half of musk, priced at six lire of grossi (about 22l. 10s. in value of silver) the pound. Girardo had sold half-a-pound at that rate, and the remaining pound which he brought back was deficient of a saggio, or, one-sixth of an ounce, but he had accounted for neither the sale nor the deficiency. Hence Marco sues him for three lire of Grossi, the price of the half-pound sold, and for twenty grossi as the value of the saggio. And the Judges cast the defendant in the amount with costs, and the penalty of imprisonment in the common gaol of Venice if the amounts were not paid within a suitable term.[11]
Again in May, 1323, probably within a year of his death, Ser Marco appears (perhaps only by attorney), before the Doge and his judicial examiners, to obtain a decision respecting a question touching the rights to certain stairs and porticoes in contact with his own house property, and that obtained from his wife, in S. Giovanni Grisostomo. To this allusion has been already made (supra, p. 31).

FROM A PHOTOGRAPH SPECIALLY TAKEN IN ST. MARK’S LIBRARY BY SIGNOR BERTANI.
47. We catch sight of our Traveller only once more. It is on the 9th ofMarco Polo’s Last Will and Death. January, 1324; he is labouring with disease, under which he is sinking day by day; and he has sent for Giovanni Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, to make his Last Will and Testament. It runs thus:—
“In the Name of the Eternal God Amen!“In the year from the Incarnation of our Lord Jesus Christ 1323, on the 719th day of the month of January, in the first half of the 7th Indiction,[12] at Rialto.
“It is the counsel of Divine Inspiration as well as the judgment of a provident mind that every man should take thought to make a disposition of his property before death become imminent, lest in the end it should remain without any disposition:
“Wherefore I Marcus Paulo of the parish of St. John Chrysostom, finding myself to grow daily feebler through bodily ailment, but being by the grace of God of a sound mind, and of senses and judgment unimpaired, have sent for John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo and Notary, and have instructed him to draw out in complete form this my Testament:
“Whereby I constitute as my Trustees Donata my beloved wife, and my dear daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta,[13] in order that after my decease they may execute the dispositions and bequests which I am about to make herein.
“First of all: I will and direct that the proper Tithe be paid.[14] And over and above the said tithe I direct that 2000 lire of Venice denari be distributed as follows:[15]
“Viz., 20 soldi of Venice grossi to the Monastery of St. Lawrence where I desire to be buried.
72
“Also 300 lire of Venice denari to my sister-in-law Ysabeta Quirino,[16] that she owes me.
“Also 40 soldi to each of the Monasteries and Hospitals all the way from Grado to Capo d’Argine.[17]
“Also I bequeath to the Convent of SS. Giovanni and Paolo, of the Order of Preachers, that which it owes me, and also 10 lire to Friar Renier, and 5 lire to Friar Benvenuto the Venetian, of the Order of Preachers, in addition to the amount of his debt to me.
“I also bequeath 5 lire to every Congregation in Rialto, and 4 lire to every Guild or Fraternity of which I am a member.[18]
“Also I bequeath 20 soldi of Venetian grossi to the Priest Giovanni Giustiniani the Notary, for his trouble about this my Will, and in order that he may pray the Lord in my behalf.
“Also I release Peter the Tartar, my servant, from all bondage, as completely as I pray God to release mine own soul from all sin and guilt. And I also remit him whatever he may have gained by work at his own house; and over and above I bequeath him 100 lire of Venice denari.[19]
73
“And the residue of the said 2000 lire free of tithe, I direct to be distributed for the good of my soul, according to the discretion of my trustees.
“Out of my remaining property I bequeath to the aforesaid Donata, my Wife and Trustee, 8 lire of Venetian grossi annually during her life, for her own use, over and above her settlement, and the linen and all the household utensils,[20] with 3 beds garnished.
“And all my other property movable and immovable that has not been disposed of [here follow some lines of mere technicality] I specially and expressly bequeath to my aforesaid Daughters Fantina, Bellela, and Moreta, freely and absolutely, to be divided equally among them. And I constitute them my heirs as regards all and sundry my property movable and immovable, and as regards all rights and contingencies tacit and expressed, of whatsoever kind as hereinbefore detailed, that belong to me or may fall to me. Save and except that before division my said daughter Moreta shall receive the same as each of my other daughters hath received for dowry and outfit [here follow many lines of technicalities, ending]
“And if any one shall presume to infringe or violate this Will, may he incur the malediction of God Almighty, and abide bound under the anathema of the 318 Fathers; and farthermore he shall forfeit to my Trustees aforesaid five pounds of gold;[21] and so let this my Testament abide in force. The signature of the above named Messer Marco Paulo who gave instructions for this deed.
“‡ I Peter Grifon, Priest, Witness.“* I Humfrey Barberi, Witness.“† I John Giustiniani, Priest of S. Proculo, and Notary, have completed and authenticated (this testament).”[22]
74
We do not know, as has been said, how long Marco survived the making of this will, but we know, from a scanty series of documents commencing in June of the following year (1325), that he had then been some time dead.[23]
48. He was buried, no doubt, according to his declared wish, in the Church of S. Lorenzo; Place of Sepulture. Professed Portraits of Polo.and indeed Sansovino bears testimony to the fact in a confused notice of our Traveller.[24] But there does not seem to have been any monument to Marco, though the sarcophagus which had been erected to his father Nicolo, by his own filial care, existed till near the end of the 16th century in the porch or corridor leading to the old Church of S. Lorenzo, and bore the inscription: “Sepultura Domini Nicolai Paulo de contrata S. Ioannis Grisostemi.” The church was renewed from its foundations in 1592, and then, probably, the sarcophagus was cast aside and lost, and with it all certainty as to the position of the tomb.[25]

75
There is no portrait of Marco Polo in existence with any claim to authenticity. The quaint figure which we give in the Bibliography, vol. ii. p. 555, extracted from the earliest printed edition of his book, can certainly make no such pretension. The oldest one after this is probably a picture in the collection of Monsignor Badia at Rome, of which I am now able, by the owner’s courtesy, to give a copy. It is set down in the catalogue to Titian, but is probably a work of 1600, or thereabouts, to which the aspect and costume belong. It is inscribed “Marcus Polvs Venetvs Totivs Orbis et Indie Peregrator Primus.” Its history unfortunately cannot be traced, but I believe it came from a collection at Urbino. A marble statue was erected in his honour by a family at Venice in the 17th century, and is still to be seen in the Palazzo Morosini-Gattemburg in the Campo S. Stefano in that city. The medallion portrait on the wall of the Sala dello Scudo in the ducal palace, and which was engraved in Bettom’s “Collection of Portraits of Illustrious Italians,” is a work of imagination painted by Francesco Griselini in 1761.[26] From this, however, was taken the medal by Fabris, which was struck in 1847 in honour of the last meeting of the Italian Congresso Scientifico; and from the medal again is copied, I believe, the elegant woodcut which adorns the introduction to M. Pauthier’s 76edition, though without any information as to its history. A handsome bust, by Augusto Gamba, has lately been placed among the illustrious Venetians in the inner arcade of the Ducal Palace.[27] There is also a mosaic portrait of Polo, opposite the similar portrait of Columbus in the Municipio at Genoa.

49. From the short series of documents recently alluded to,[28] we gather all that we know of the remaining history of Marco Polo’s immediate family. Further History of the Polo Family.We have seen in his will an indication that the two elder daughters, Fantina and Bellela, were married before his death. In 1333 we find the youngest, Moreta, also a married woman, and Bellela deceased. In 1336 we find that their mother Donata had died in the interval. We learn, too, that Fantina’s husband was Marco Bragadino, and Moreta’s, Ranuzzo Dolfino.[29] The name of Bellela’s husband does not appear.
Fantina’s husband is probably the Marco Bragadino, son of Pietro, who in 1346 is mentioned to have been sent as Provveditore-Generale to act against the Patriarch of Acquileia.[30] And in 1379 we find Donna Fantina herself, presumably in widowhood, assessed as a resident of S. Giovanni Grisostomo, on the Estimo or forced loan for the Genoese war, at 1300 lire, whilst Pietro Bragadino of the same parish—her son as I imagine—is assessed at 1500 lire.[31] [See vol. ii., Calendar.]
The documents show a few other incidents which may be briefly noted. In 1326 we have the record of a charge against one Zanino Grioni for insulting Donna Moreta in the Campo of San Vitale; a misdemeanour punished by the Council of Forty with two months’ imprisonment.

77
In March, 1328, Marco Polo, called Marcolino, of St. John Chrysostom (see p. 66), represents before the Domini Advocatores of the Republic that certain imprestita that had belonged to the late Maffeo Polo the Elder, had been alienated and transferred in May 1318, by the late Marco Polo of St. John Chrysostom and since his death by his heirs, without regard to the rights of the said Marcolino, to whom the said Messer Maffeo had bequeathed 1000 lire by his will executed on 6th February, 1308 (i.e. 1309). The Advocatores find that the transfer was to that extent unjust and improper, and they order that to the same extent it should be revoked and annulled. Two months later the Lady Donata makes rather an unpleasant figure before the Council of Forty. It would seem that on the claim of Messer Bertuccio Quirino a mandate of sequestration had been issued by the Court of Requests affecting certain articles in the Ca’ Polo; including two bags of money which had been tied and sealed, but left in custody of the Lady Donata. The sum so sealed was about 80 lire of grossi (300l. in silver value), but when opened only 45 lire and 22 grossi (about 170l.) were found therein, and the Lady was accused of abstracting the balance non bono modo. Probably she acted, as ladies sometimes do, on a strong sense of her own rights, and a weak sense of the claims of law. But the Council pronounced against her, ordering restitution, and a fine of 200 lire over and above “ut ceteris transeat in exemplum.”[32]
It will have been seen that there is nothing in the amounts mentioned in Marco’s will to bear out the large reports as to his wealth, though at the same time there is no positive ground for a deduction to the contrary.[33]
The mention in two of the documents of Agnes Loredano as the sister of the Lady Donata suggests that the latter may have belonged to the Loredano family, but as it does not appear whether Agnes was maid or wife this remains uncertain.[34]
78
Respecting the further history of the family there is nothing certain, nor can we give unhesitating faith to Ramusio’s statement that the last male descendant of the Polos of S. Giovanni Grisostomo was Marco, who died Castellano of Verona in 1417 (according to others, 1418, or 1425),[35] and that the family property then passed to Maria (or Anna, as she is styled in a MS. statement furnished to me from Venice), who was married in 1401 to Benedetto Cornaro, and again in 1414 to Azzo Trevisan. Her descendant in the fourth generation by the latter was Marc Antonio Trevisano,[36] who was chosen Doge in 1553.



